What two properties determine what will pass through the plasma membrane?
Size and charge. Small things are more likely to pass through than large. If a molecule is said to be large it is not getting through that membrane. Anything non-polar small or polar small should pass through the membrane. If there is any positive or negative charge on that molecule it won't pass through the membrane by itself.
Give me all the macromolecules and their monomers?
There is protein and it's monomers are amino acids. There is nucleic acids and their monomers are nucleotides. There are lipids and their monomers are glycerol and fatty acids. There are carbohydrates and their monomers are monosaccharides.
What is a covalent bond and what is a hydrogen bond?
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed between two atoms when they share electrons. Covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar. Polar bonds happen when electrons are shared unequally because one has a much higher electronegativity like a bond between oxygen and hydrogen. Non-polar bonds happen when electrons are shared equally because both atoms have similar electronegativity like a bond between carbon and hydrogen. A hydrogen bond is a temporary weak attraction between partial charges. Remember we only see full charges in ionic bonds when electrons are stolen.
Give me some differences and similarities between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? Think size, structures, and complexity?
Eukaryotes are larger than prokaryotes. Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles like mitochondria, ER, golgi, and the nucleus but prokaryotes don’t. Both have a plasma membrane, cytosol, carry out similar biochemical reactions, have ribosomes, and have chromosomes of DNA.
Define an independent variable, dependent variable, controlled variables, control group, and test group, correlation, and causation.
An independent variable is what we are intentionally manipulating. The dependent variable is the factor you expect to change and that you measure or observe. The controlled variables are factors held the same for all groups. The test group is the group we are experimenting on. The control group is identical to the test group but not exposed to the independent variable. Causation is being able to say something happened because of this specific thing. Correlation is being able to say that there is a link but not a cause.
Explain to me the arrangement of the phospholipid bilayer and draw me a phospholipid?
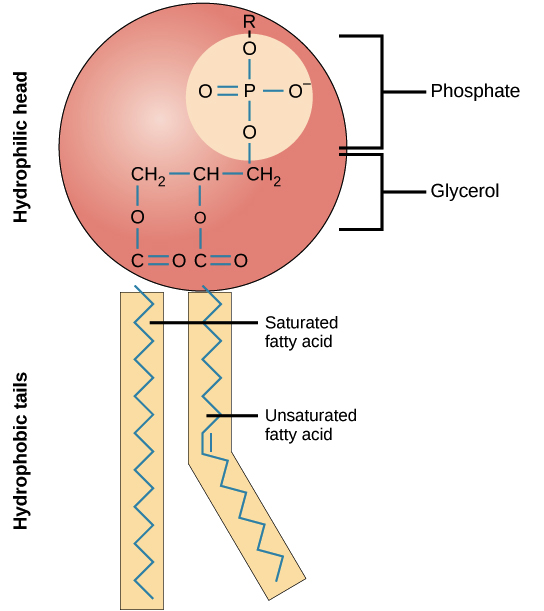
As we can see the phospholipid has a hydrophilic head with a phosphate and glycerol. It also has two hydrophobic tales. One of these tails is a saturated fatty acid and the other is an unsaturated fatty acid. The phospholipid bilayer is arranged with the hydrophobic tails in the center and the hydrophilic heads on the tips.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Remember saturated fatty acids have the maximum amount of hydrogen bonds and only have single bonds and are solid at room temperature. Also unsaturated fatty acids don't have the maximum amount of hydrogen bonds and do have double bonds. These double bonds are rigid and create kinks and that is why unsaturated fats are solid at room temperature.
Explain ionic bonding?
An ionic bond is an electrostatic attraction between two atoms where one atom transfers an electron to another atom. Think about NaCI. Sodium gives up its electron to chlorine and becomes positively charged while chlorine becomes negatively charged. This creates that electrostatic attraction. 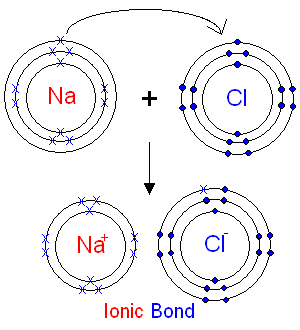
Give me parts of the endomembrane system?
The nuclear envelope, rough ER, smooth ER, Golgi, and vesicles.
Define what an observational study and controlled experiment are and how they are different and give me an example?
In an observational study we don't manipulate anything we just observe and subjects assign themselves to test groups and control groups. Also an observational study usually has a larger sample size, fewer moral dilemmas, and can only tell us about correlation. In a controlled experiment we do manipulate something and scientists assign subjects to test groups and control groups. Also controlled experiments are more reliable and can tell us about the cause of a result.
If you place a cell in a hypertonic solution what happens and why?
A hypertonic solution has a high amount of solutes and low amount of water. Meanwhile the cell has a low amount of solutes and high amount of water. So both the solutes and water go down their gradients. Water comes out and solutes come in. So the cell shrinks.
Differences in DNA vs RNA?
RNA is single stranded and DNA is double stranded. DNA uses A, T, C, and G. RNA uses A, U, C, and G. So RNA doesn't have thymine. DNA is more stable than RNA. RNA uses ribose and DNA uses deoxyribose. Remember in ribose we have an OH at carbon 2 and in deoxyribose we have just an H.

What makes a bond polar vs nonpolar in terms of electrons and how does this relate to hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity. Include electronegativity?
A bond is polar when electrons are shared unequally because one atom has a higher electronegativity than the other. Think about a bond between Hydrogen and Oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative so the electrons will be closer to oxygen than hydrogen. Also remember when something is polar it is also hydrophilic. A bond is non-polar when electrons are shared equally because both atoms have similar electronegativities. Think about a bond between carbon and hydrogen the electrons will be equally shared because they both have low electronegativites. Also remember electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. Also remember on the periodic table electronegativity increases as you go up and to the right.

What are the functions of the different parts of the endomembrane system?
The smooth ER makes lipids and detoxifies drugs. The rough ER has ribosomes that synthesize proteins. The Golgi modifies and packages proteins. Vesicles transport things from the RER to the Golgi. The nuclear membrane is contiguous with the ER and separates the cytoplasm from the nucleus.
What is a hypothesis and what is a theory? Can either prove anything?
A hypothesis is a testable and falsifiable explanation for an observation. A theory is a well substantiated explanation for natural phenomena. Neither can prove anything. Also hypothesis tend to be narrower in scope whereas theories tend to be broader.
Explain passive transport to me and active transport and give me examples.
Passive transport doesn't require ATP or energy. It includes simple diffusion and passive diffusion. In simple diffusion the solutes can move across the membrane on it's own down it's concentration gradient. In faciliaited diffusion the solutes are moving down their concentration gradient but they need help from some kind of protein to get through. They may need a channel protein where it's open completely through the membrane. They may need a carrier protein. The carrier protein is open one side of the membrane or the other at any given time. So it opens on one side then the other.
Explain a dehydration and condensation reaction to me like what they do and what comes in and out? Include monomers and polymers?
In a dehydration/condensation reaction water is taken away to build or to add monomers to a polymer. In a hydrolysis reaction water is added to break a monomer of off a polymer.
Does a polar or nonpolar bond have more potential energy?
A non-polar bond has more potential energy. Remember the seesaw analogy we talked about.
How does the endosymbiotic theory explain the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells? What evidence supports this theory?
Chloroplasts and mitochondria actually evolved from a process called endosymbiosis. The theory of endosymbiosis states that basically an ancient eukaryote engulfed free-living prokaryotes, which were able to perform specific functions like photosynthesis (for chloroplasts) or cellular respiration (for mitochondria). These prokaryotes then became endosymbionts, forming a symbiotic relationship with the host. Again to make it clear these prokaryotes became mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Evidence
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are the same size as prokaryotes
Both have circular DNA without histones with similar sequence to photosynthetic bacterium (cyanobacteria) and obligate intracellular rickettsia bacteria
Both mitochondria and chloroplasts divide by fission like prokaryotes
They have their own protein synthesis machinery (ribosomes) more like bacteria than eukaryotes (sensitivity to streptomycin)
Inner membrane of mitochondria contains unusual phospholipid characteristics of bacterial membranes
What is the null hypothesis and what is the alternate hypothesis?
The null hypothesis assumes there will be no difference and it is the opposite of what we think will happen. The alternate hypothesis assumes there will be a difference and that is what we think will happen.
What is endocytosis and what is exocytosis and what makes these processes so important?
Endocytosis brings thing into the cell and exocytosis brings things out. They are important because they particularly work with big things.
What is primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure? What is denaturation and what causes it?
The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids. The bonds responsible for primary structure are covalent, peptide bonds that link the amino group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next amino acid.
 The secondary structure is beta sheet or alpha helix. The bonds responsible for secondary structure are hydrogen bonds between atoms in the protein's backbone. The tertiary structure is the overall shape of the polypeptide and all types of bonds are responsible for the tertiary structure. Like covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and Van der Waals attraction. Also disulfide bonds are very important in tertiary structure. A disulfide bond is a bond between two cysteine amino acids. Quaternary structure is the binding of two or more polypeptides and again all types of bonds are responsible for quaternary structure and not all proteins have quaternary structure.
The secondary structure is beta sheet or alpha helix. The bonds responsible for secondary structure are hydrogen bonds between atoms in the protein's backbone. The tertiary structure is the overall shape of the polypeptide and all types of bonds are responsible for the tertiary structure. Like covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and Van der Waals attraction. Also disulfide bonds are very important in tertiary structure. A disulfide bond is a bond between two cysteine amino acids. Quaternary structure is the binding of two or more polypeptides and again all types of bonds are responsible for quaternary structure and not all proteins have quaternary structure.
Draw two water molecules and label where there would be hydrogen bonds?

Remember the actual bonds in one water molecule are actually polar covalent bonds. But the bonds formed between different water molecules are hydrogen bonds.
Are chloroplasts and mitochondria found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
The mitochondria and chloroplasts are only found in eukaryotes. Mitochondria is found in all eukaryotes and chloroplasts are only found in plants.
A pharmaceutical company wants to test the effectiveness of a new pill designed to reduce headache pain. They conduct a study using 100 participants. Half of the participants receive the new pill, while the other half receive a placebo that looks the same but contains no active ingredients. All participants rate their headache pain before and one hour after taking the pill.
Identify the following:
Independent variable
Dependent variable
Control group
Test group
1. The independent variable is whether or not you get the pill.
2. The dependent variable is the rate of the headache pain.
3. The control group is the group that got the placebo.
4. The test group is the group that got the pill.