What antigens are present in a type A+ patient?
Contains A antigens and Rh (D) antigen
What is the estimated hematocrit of packed RBC?
70-80%
What is the horizontal incision in the chest called that is used for lung transplants?
Clamshell incision or transverse sternotomy
What year, country, and surgeon was the first human to human heart transplant?
1967 in South Africa with Dr. Christiaan Barnard
Does 2,3 DPG make hemoglobin have more or less affinity for O2?
Less
What decade was the first successful liver transplant?
1960s (1967)
What is normal capillary refill time?
2 second (longer indicates poor perfusion)
What does it mean to be on "total" bypass?
Two bicaval cannulae in, caval snares tightened... there should be no venous return getting into the heart
What is a procedure that will likely require ACP/ RCP?
Aortic arch replacement
(or hemi-arch, total arch, FET, etc)
As temperature goes down,
oxygen consumption _________ and blood viscocity __________.
decreases; increases
Which strategy measures blood at 37C, and which measures blood at the actual hypothermic temperature?
Alpha stat: 37C
pH stat: actual temperature
What is NIRS, and what does it tell us?
Near infared spectroscopy tells us regional oxygen saturation of the brain by comparing the ratio of oxy to deoxy hgb
What is the primary vein used for grafting? What is a backup?
Greater saphenous vein in the leg, alternative is a lesser saphenous vein or a radial artery
Taking blood from a patient pre bypass and replacing it with colloid or crystalloid is called what?
Acute normovolemic hemodilution (ANH)
What is the name of the professional organization that develops standards for blood banks and transfusion services?
AABB (Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies, formerly the American Association of Blood Banks)
What is contained in FFP?
All clotting factors, albumin, and other plasma proteins
Permanent and worsening scarring in the lungs causes what condition, that is the leading reason for lung transplantation?
Pulmonary fibrosis/ idiopathic lung disease
What are HLA antibodies, and what does HLA stand for?
Human Leukocyte Antigen-- the MHC genetic marker on one's own cells that indicates "self". Reducing mismatch with the donor minimizes the risk of rejection
Every gram of hemoglobin can transport how much oxygen?
1.34 mL of O2
What is a MELD score?
"Model for End-Stage Liver Disease" that predicts 3-month mortality for liver transplant candidates
What is the patient temperature site that reflects temperature changes the fastest 1. when cross clamped 2. when not cross clamped?
1. nasopharyngeal
2. central line (PA port)
When we are not using vacuum, what two forces are we relying on in order to get drainage?
Gravity and CVP
Where is cannulation placed for RCP typically?
SVC, with a caval snare around it
What is the maximum temperature range between venous blood to heat exchanger, and arterial blood to patient?
10 C (for adults)
What happens to water neutrality as temperature goes down?
As temperature decreases, the neutral pH
of water increases (becomes more alkaline)
What does a capnography tracing tell us?
What region of the heart does the LAD typically perfuse?
The anterior wall, the anterior septum, and the apex
What is "pump brain"?
It is postoperative "brain fog" or cognitive dysfunction, often due to multiple different factors (cerebral hypoperfusion, GME, neuroinflammation)
Blood products should be used within how many hours of being spiked?
What condition results from the transfusion causing hypovolemia, resulting in pulmonary edema
TACO (Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload)
What are two advantages of using ECMO versus CPB for lung transplants?
No air-blood interface (less inflammation, hemolysis, GME risk)
Less priming volume (less need for blood products/ dilution act)
Less surface area (less anticoagulation needed and less inflammation and activation)
What are three big causes of needing a heart transplant?
Non-ischemic or ischemic cardiomyopathy
Dilated or hypertrophic heart failure
Myocarditis
Connective tissue disorders
(for pediatrics: congenital abnormalities)
What is an anoxic corner according to OPFT?
There is a region of tissue that the capillary is unable to perfuse due an insufficient radius/ radius ratio of tissue:capillary
What is a contraindication for liver transplant?
Active infection or sepsis
Advanced cardiopulmonary disease
Active substance abuse
Uncontrolled malignancy outside the liver
What is an appropriate amount of volume for the typical patient to receive to "bump the valve" or begin to see ejection?
200-350 mL (this ranges with patient size)
Mini bypass circuits, RAP, VAP, MUF all aid us in what way?
Blood conservation
When we only perfuse one carotid, how do we assume both hemispheres of the brain are perfused?
What happens to vascular tone and heart rate when cooling?
As temperature decreases, vasoconstriction occurs and heart rate decreases (becomes bradycardic, with potential for fibrillation or asystole)
pH stat, as it disrupts the cerebral autoregulation with hypercarbia
Red and infared LED wavelengths, deoxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more red, oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more infared wavelegths.... the ratio of what is absorbed is compared
What is the word used to describe when valve leaflets come together and seal shut?
Coaptation
What is GME, and what does it stand for?
Gaseous microemboli, too small to be detected by a bubble detector but often introduced in various manners (venous line air, suckers and vents) and can cause silent infarcts or damaged endothelium
What is an allogeneic blood component that does not have to be kept at a refrigerated/ frozen temperature?
Platelets
(Technically also albumin)
What is the condition that occurs when there is respiratory compromise secondary to an immune response from transfused blood?
TRALI (Transfusion related acute lung injury)
Which time is typically longer: warm ischemic or cold ischemic?
Which time is more dangerous? warm ischemic or cold ischemic?
Cold ischemic is longer (it involves the whole procurement travel)
Warm ischemic is more dangerous (cold offers ischemic protection/ lower metabolic demands when there is no perfusion)
What are two factors that would make an heart NOT eligible to be donated?
Poor heart function/ assessment on TEE
Structural or ischemic disease (CAD, CM, valvular disease)
Active infection or malignancy
Size mismatch
Advanced age
Prolonged CPR
HLA incompatibility
ABO mismatch (not always!)
(this is a non-exhaustive list)
What are the two states of hemoglobin, and which has more affinity for oxygen binding?
Tensed/ Taut
Relaxed ** Has more affinity
What are the three donor types for a liver?
Deceased donor
Living donor
Split liver
What makes the Korotkoff sounds?
Turbulence of blood moving past the occlusion as the systemic pressure overcomes the cuff pressure
What is the maximum that our VAVD should be set to?
-40 to -60 mmHg
**Please indicate negative with this. This answer is only correct if you say "negative", as 40 or 60 could be misunderstood and be VERY DANGEROUS
What is a safe cerebral blood flow, either in % or cc/kg/min?
15-20%
10-20 cc/kg/min
What is Q10, and what is the value for the average adult?
2.3 for normal adult
What is the general range for cerebral autoregulation?
50- 150 mmHg
What is BIS, and what does it tell us?
Bispectral Index, indicates to us the depth of anesthesia
Why might retrograde or follow-up small CPG doses be more common with CAD/ CABG patients?
When is the most dangerous time to re-enter a sternotomy due to fibrosis and revascularization?
~3 months following the initial sternotomy
150 - 270 microns
What are two synthetic colloid solutions as an alternative to albumin?
Dextran, Hespan
What are two disadvantages of using minized support (ECMO) versus full CPB? As in, when might we justify using full bypass?
Ability to use suckers and vents if there is great bleeding or dissension
Ability to drain the heart and physically manipulate it, or if there is persistent fibrillation especially with any cooling
Ability to arrest the heart in case of there is an unforeseen injury or repair
What is the standard temperature management for heart procurements?
New options include normothermic regional perfusion (NRP) or hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP)
Air at sea level is composed of what, from the perspective of Dalton's Law?
593 mmHg Nitrogen
159 mmHg Oxygen
7 mmHg Argon
Trace CO2 and other gases
(Totaling 760 mmhg, or 1 atm)
What are the typical components of a VV bypass circuit for liver transplant?
Bubble trap, pump, heat exchanger
(note NO oxygenator)
When should anesthesia begin to ventilate again? Please be specific
Right before we begin to give volume to the patient to wean (once we are warm and the heart is beating)
What are two dangers with excessive negative suction/ VAVD?
Tissue damage
Gaseous microemboli (GME)
Shear stress and damage
Cavitation of air
Reduction of flow forward when using a non-occlusive pump
What do you expect to happen to cerebral saturations during ACP/RCP? What about leg saturations?
Cerebral saturations should remain steady, near baseline, assuming an intact Circle of Willis.
Leg saturations will gradually fall
What is one advantage, and one disadvantage, of hypothermia on bypass?
Advantage: lower tissue metabolism and oxygen demands, lower flows necessary, more time for the surgeon, decreased blood trauma
Disadvantage: Takes time to cool and rewarm, platelet dysfunction
Why is alpha-stat called alpha-stat?
Refers to “the alpha charge state”-imidazole
histidine residues on proteins that regulate cellular pH
Where is the TEE probe placed?
In the esophagus, with the tip either in the upper esophagus, mis esophagus, or in the stomach
What is the benefit, and downside, to both biologic and mechanical valve replacements?
Biologic do not require anticoagulants, but eventually degrade and need another replacement
Mechanical valves last "forever" but require anticoagulation which is tedious and perhaps dangerous
What does the RCA perfuse/ supply?
The right atrium and right ventricle, as well as the apex
Which blood types are sampled with this smear? 
A+, B+, AB+, O-
An allergic immune response is classified by release of __________ from ________ cells in response to proteins in the blood product.
Histamine from mast cells/ basophils
When using electrocautery around the airway, what is the reason for turning FiO2 to 21%?
Primarily, reduction of risk for starting a surgical fire
(21% throughout the whole procedure would help prevent ROS)
What is GDMT prior to needing an OHT, and what are two examples?
Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy, AKA "medical management"
Ace inhibitors
Beta-blockers
Aldosterone antagonists
Angiotensin receptor blocker
Diuretics
What is the equation for Fick principle?
AKA Oxygen consumption (VO2)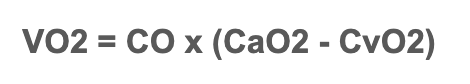
What are the three categories of pathophysiologies that would merit a liver transplant?
Acute liver disease
Chronic liver disease
Neuroplastic liver disease
What makes fibrillation dangerous on bypass?
Distension of the LV when we do not have a vent, especially with aortic insufficiency
What is KAVD, and why is it not commonly used?
Kinetic assisted venous drainage, where a pump is in the venous line helping to "pull" drainage
It is not commonly used as it is dangerous (can cavitate air, overpressurize, or stop) and is often unnecessary
Typically, which pressure monitoring site do we need for ACP to ensure safe flow and perfusion? (Other than arterial line pressure) What about for RCP?
ACP: Right radial pressure
RCP: SVC pressure
What is the generally recommended maximum rewarming rate to allow proper tissue equilibration?
0.5 C - 1 C per minute
What is the theoretical risk with pH stat?
Increased flow makes for increased microemboli risk to the brain
What is the most common TEE view, that shows us the septum, tricuspid, and mitral valve?
Mid-esophageeal 4-chamber view
The surgeon has an extra vein graft, but the remaining RCA has only 50% occlusion. Why would they not graft this?
50% occlusion is enough to cause competing flow, which would inadvertently perfuse "up" or "retrograde" the graft
You are flowing 5.2 LPM with 1300 mL in your reservoir. What is your "response time"?
15 seconds
What are two compositional changes that occur to RBCs the longer they are kept stored (prior to transfusion)?
Decreased 2,3 DPG, ATP, and pH (acidosis), plasma free hemoglobin
Increased K+, lactate
An anaphylactic transfusion reaction is mediated by which antibody class?
IgE
What is the primary determinant of whether of not a lung transplant will be able to performed without support (ECMO/ CPB)?
Congestion secondary to pHTN when clamping out one of the lungs
What is the order of anastomoses for a heart transplant?
First: LA cuff
SVC/ IVC
PA
Last: Aorta
What is the equation for content of oxygen in blood?

What is typical cannulation for VV bypass in a liver transplant?
Drainage from the femoral vein and portal vein
Reinfusion in the IJV or axillary vein
What are the two heart sounds (lub and dub) and what makes them?
S1 is the turbulence of blood with the closing of the AV valves
S2 is the turbulence of blood with the closing of the semilumar valves
When you begin to give volume to the patient (discontinuing VAVD is analogous to partially clamping the venous line... both inhibit drainage)
What is the argument toward lowering hematocrit for ACP/ RCP?
What is the argument toward raising hematocrit for ACP/ RCP?
A lower hematocrit will prevent high viscocity "sludging" and the metabolic demand is not high when cold anyway
A higher hematocrit will provide superior oxygen delivery and high metabolic reserve for the rest of the body when it is ischemic during ACP/ RCP
At full hypothermia (18C) what is the "safe ischemic time" for the brain, approximately?
45 minutes
What is the "philosophy" or "strategy" of pH stat?
Maintain pCO2 at 40mmHg at the patient’s actual
temperature, while looking at a temperature
corrected ABG.... extra CO2 will be added to achieve this pCO2, and resultant luxury perfusion
What would be a good TEE view would be best for IABP insertion or femoral aortic cannulation?
Anything that shows the descending aorta, such as a midesophageal descending aorta short axis
What does it mean to "skeletonize" the LIMA, and why would we do it?
To carefully dissect the LAD from any fat and tissue, which gives clearer exposure and graft visibility, which gives us a little length and flexibility but also helps to maintain sternal perfusion and prevent sternal infection
What is the course of action if you were to accidentally pump air?
Tell the team
Assess the source/ get rid of any remaining air in the circuit
Trendenlenburg (head down)
Begin cooling, increase flows and FiO2
RCP
Neuroprotection by anesthesia