What test is the best to identify a mineral?
Hardness Test
What kind of rock has smaller pieces "glued" together?
Sedimentary
Physical weathering is also called _______ weathering.
Mechanical
What is the primary cause of erosion?
Moving water (Rivers, streams)
When sand is deposited it creates a ____.
Dune
What layer at the bottom of the soil profile consists of solid, unweathered rock?
Bedrock
When is your midterm exam?
Monday - 1st and 2nd
Tuesday - 3rd and 4th
What mineral identification test is being shown below?
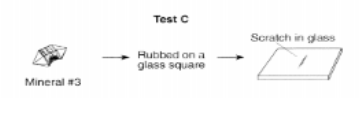
Hardness Test
What kind of rock is formed by "heat and pressure"?
Metamorphic Rock
Agents of Weathering can break rock down. What does "agents" mean?
Causes
A ________ is an enormous mass of moving ice. They form in places where snow stays on the ground year-round.
Glacier
When rivers carry particles and deposit them at the mouth of the river, what landform is created?
Delta
Layers of soil are known as _________.
Horizons
When waves leave sand behind on the beach, this is called _________.
Deposition
The Moh's Hardness Scale is numbered 1 through ___.
10
Name the 3 main "types" of rocks.
1. Sedimentary
2. Metamorphic
3. Igneous
When ice, water, gravity or wind causes sediments to have collisions physical weathering results.
Abrasion
What landform (created by erosion) is shown below?
When wind, water, or ice drops the sediment it is carrying, this process is called ________.
Deposition
The soil horizons combined make up the soil _____.
Profile
When a river is curvy, it is called _______.
Meandering
What is the hardest mineral on the Moh's Hardness scale?
Diamond
What kind of rock is formed through Deposition, Compaction and Cementation?
Sedimentary Rock
Physical Weathering changes what 2 things?
1. Shape
2. Size
Glaciers can carve out river valleys, leaving them the shape of what letter?
"U"
A massive pile of sediment deposited on the edge of a glacier is called a ________.
A. Iceberg
B. Moraine
C. Delta
D. Marsh
B. Moraine
Which horizon is this describing?
The layer located underneath the topsoil.
It is packed more tightly than topsoil.
It does not have a lot of humus, but it does have small rocks in it.
Not very good for growing plants.
Subsoil
The freezing and thawing causes rocks to eventually break apart is called ____ _____. (Also known as ice wedging)
Frost Action

Name one material can scratch Quartz (Hardness 7).
Drill bit (Hardness 8.5)
Which kind of igneous rock would cool quickly and therefore contain small crystals?
Extrusive Igneous Rock
When pollutants like Carbon Dioxide mix with rainwater creating acid rain, which can dissolve limestone and harm the living environment.
Chemical Weathering - Acid
Name 2 types of Rapid Mass Movement.
1. Rockfall
2. Mudslide
3. Landslide
Where would the most deposition take place?
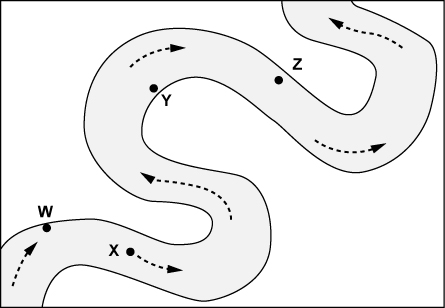
Point Y. The water flow is weaker and not able to carry rocks and sediment, so it deposits.
Which horizon is composed of dark soil, humus and other organic, decomposing matter?
Topsoil
Slow mass movement is more common and less noticeable. More material is moved slowly over time. This is known as _____.
Creep
Why is coal NOT considered a mineral?
It contains organic material. (plants)
What is the natural process of changing a rock into another rock called?
The Rock Cycle
How does chemical weathering change rock?
It changes its composition (what it is made of).
The process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity transports soil and sediment from one location to another is called _______.
Erosion
Name 3 of the 5 Agents of Deposition.
1. Running Water
2. Shoreline Waves
3. Wind
4. Ice
5. Gravity
Which horizon is located underneath the subsoil that consists of larger pieces of weathered rock?
Rock Fragments
What chemical dissolves most minerals and metals in our environment?
Water (H2O)
A rock is made of minerals. A mineral is a pure substance made of elements.
Name the types of rocks seen below:
X - Igneous
Y - Metamorphic
Z - Sedimentary
The process of oxygen combining with minerals to form "rust" is called ________.
Oxidation
Name 3 out of the 5 Agents of Erosion.
1. Running Water
2. Shoreline Waves
3. Wind
4. Ice
5. Gravity
Deposition along the shore when waves lay down various materials (sand, rock fragments, dead coral, and shells) it forms a ______.
Beach
________ is mostly composed (made) of weathered rock and decomposed, organic material.
Soil
Name 2 steps in the rock cycle to turn a sedimnetary rock into magma.
1. The rock needs heat and pressure to become metamorphic.
2. Add enough heat for the rock to melt.
What does N.I.S.C.D. stand for? (you must name them all)
Naturally Occurring
Inorganic
Solid
Crystal Structure
Definite Chemical Composition
What kind of rock is this describing?
The rock was buried deep underground and warmed by the heat from the Earth’s core. The minerals inside it softened. Then, the weight of the overlying rocks above it pressed it into a rock.
Metamorphic Rock
What kind of weathering occurs when plants grow their root system and cause cracks in rock to expand?
Biological Action
Which agent of erosion causes mass movement of land down a slope?
Gravity
Which landform is created when a river meander gets cut off from the main flow, leaving a U-shaped body of water?
A) Delta
B) Oxbow lake
C) Floodplain
D) Moraine
E) Alluvial fan
Oxbow Lake
Which soil profile is the most complete?
A. B. C.

Profile B is the oldest and most complete because it has fully formed horizons.
Which rock sample would weather more quickly and why?
Sample B - it will weather more quickly than sample A because the pieces are smaller, so the surface area of sample B is greater.