Which biomolecules store energy and provide structural support in plants?
A. lipids B. Carbohydrates
C. Proteins D. Nucleic acids
b. carbohydrates
What attaches to the enzyme and is specific to that enzyme?
a. a cell b. a nucleus c. a substrate
c. A substrate
Which of these is active transport?
a. osmosis b. facilitated diffusion
c. protein pump d. diffusion
c. protein pump
What happened to our egg that was put into the ISOTONIC solution?
It stayed mostly the same.
Which biomolecules function as a protective layer against water loss in the cells of plants, bird feathers, and some animal skins?
a. carbohydrates b. nucleic acids
c. proteins d. lipids
d. lipids
What type of cell would have mitochondria?
prokaryotic , eukaryotic, or both ?
Eukaryotic. The mitochondria is a membrane bound organelle.
What does this picture show?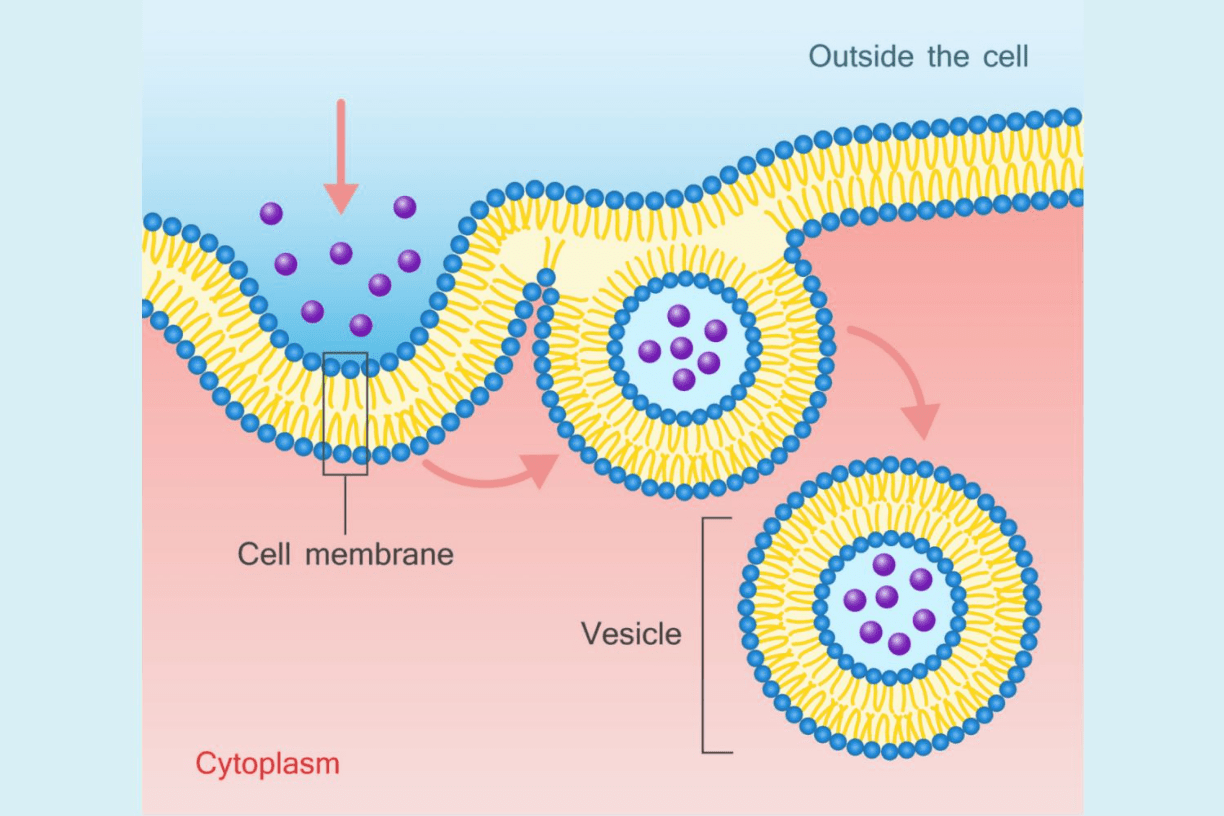
Endocytosis
What happened to the egg that was put into the hypotonic solution?
The egg swelled up a lot.
DNA and RNA are responsible for what crucial cell functions?
a. energy storage and structural support
b. storage and expression of genetic information
c. cellular respiration
b. storage and expression of genetic information
What is the function of the mitochondria ?
How do you know this image shows active transport?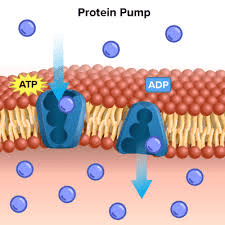
Protein pump and ATP - energy is being used.
A student is looking at structures of different cells under a microscope. Which cell is most likely a prokaryote?
Cell w- has a cell membrane, cell wall, DNA, and a nucleus.
Cell x -has a cell membrane, cell wall, DNA, and no nucleus
Cell x
Which biomolecules function as enzymes in cellular functions?
a. lipids b. carbohydrates c. proteins
c. proteins
What type of cell does not have a nucleus?
What happened to the egg that was put in a hypertonic solution?
It shrunk. Water left the cell to enter the solution.
What is the cell membrane made of that part is hydrophilic and the other side is hydrophobic?
Phospholipid bilayer.
Enzymes can work well at any temperature and pH (acid or base).
True or false?
False, temperature and pH are very important to the function of an enzyme.
Where is the DNA in the prokaryotic cell?
a. in the nucleus b. in the cytoplasm
c. in the nucleolus d. in the ribosomes
b. in the cytoplasm
What types of molecules pass through the cell membrane by diffusion?
a. large molecules b. ions
c. non-polar d. glucose
non- polar , small
Why are transport proteins needed? 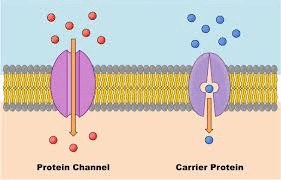
To transport ions, molecules that go against the concentration gradient, or large molecules.