Lethal Rhythms
Lethal Rhythms
Lethal Rhythm Scenarios
pacer/defib/cardiovert
Tele Protocol
100
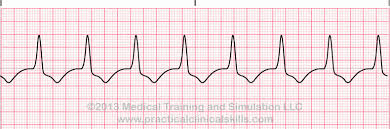
What is Accelerated Idioventricular
100
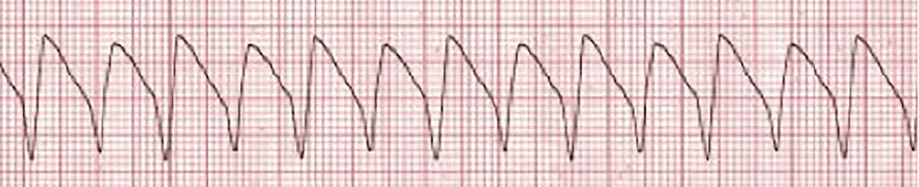
What is Ventricular Tachycardia
100
The nurse is watching the cardiac monitor and notices that the rhythm suddenly changes. There are no P waves, the QRS complexes are wide, and the ventricular rate is regular but more than 140 beats/minute. The nurse determines that the client is experiencing which dysrhythmia?
What is Ventricular Tachycardia
100
A client in sinus bradycardia, with a heart rate of 45 beats/minute, complains of dizziness and has a blood pressure of 82/60 mm Hg. Which action should the nurse anticipate?
What is prepare for transcutaneous pacing.
100
A patient is admitted for chest pain. They undergo a heart catheterization, which shows 80% blockage to the LAD. The doctor states no intervention will be performed. The patient will be managed medically. Does this patient require telemetry monitoring?
What is telemetry IS indicated.
200
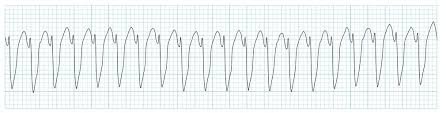
What is Ventricular Tachycardia with Fusion beat
200
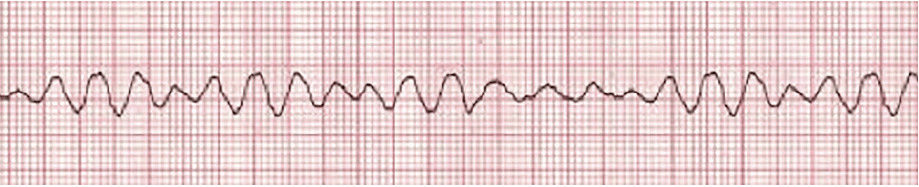
What is Ventricular Fibrillation
200
A client has frequent bursts of ventricular tachycardia on the cardiac monitor. What should the nurse be most concerned about with this dysrhythmia?
What is the ability to develop into ventricular fibrillation.
200
A client in ventricular fibrillation is about to be defibrillated. A nurse knows that to convert this rhythm effectively, the biphasic defibrillator machine should be set at which energy level for the first delivery?
What is 200 Joules.
200
A 90 year old man with a DNR status is admitted with the diagnosis of a UTI. The patient's telemetry monitor shows bigeminy PVCs. The patient is not showing any symptoms of distress. Does this patient require telemetry monitoring?
What is telemetry is NOT required.
300
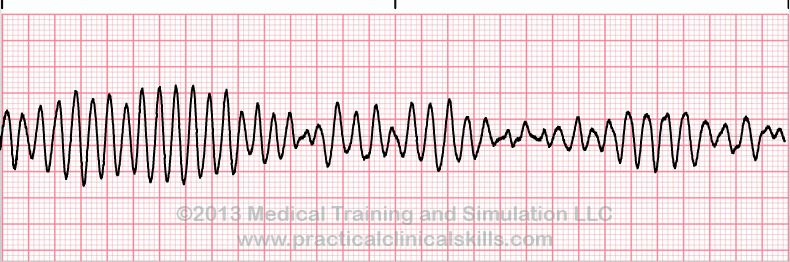
What is Torsades de Pointes
300
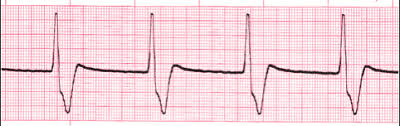
What is Idioventricular Rhythm
300
The nurse notes that a client with sinus rhythm has a premature ventricular contraction that falls on the T wave of the preceding beat. The client's rhythm suddenly changes to one with no P waves and no definable QRS complexes. How should the nurse interpret this rhythm?
What is Ventricular Fibrillation.
300
During synchronized cardioversion, when will the shock be delivered?
What is on the R wave.
300
A patient is admitted for pneumonia who also has a diagnosis of stage 4 lung cancer. Does this patient require telemetry monitoring?
What is telemetry monitoring is NOT required.
400
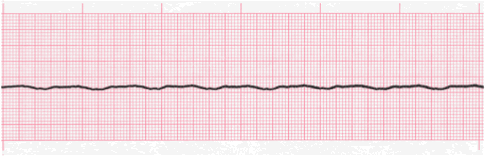
What is Asystole
400
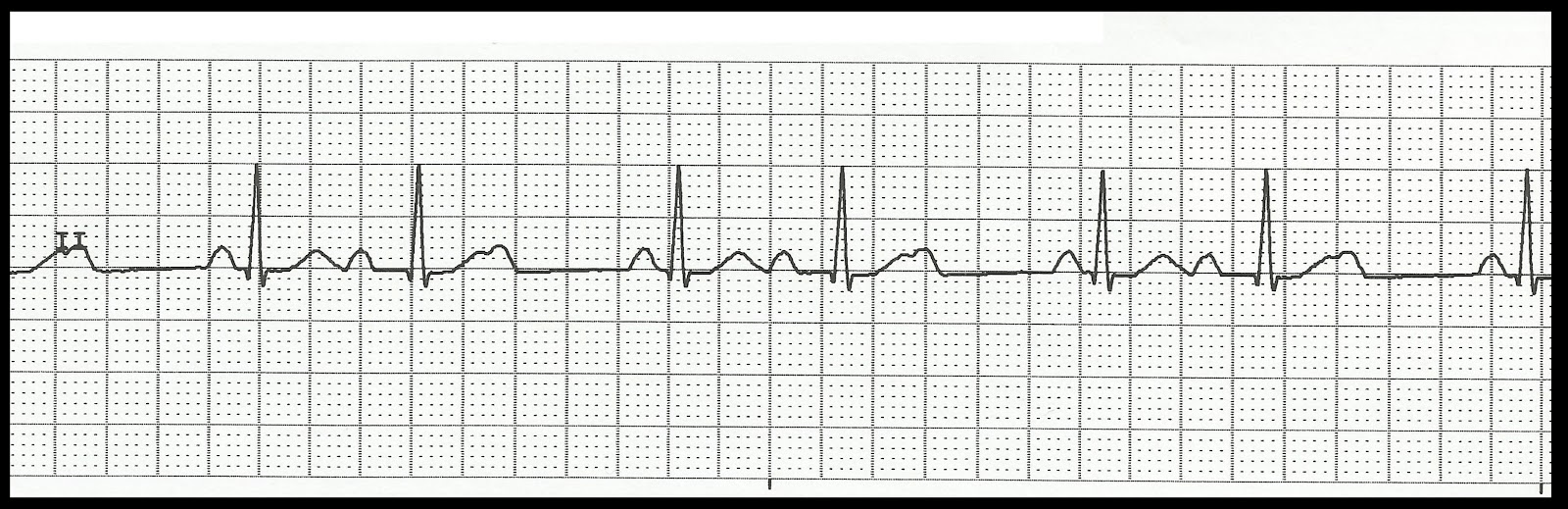
What is Second Degree Type One heart block (Wenckebach)
400
A patient goes into ventricular tachycardia. Upon entering the patient's room, the patient is resting comfortably. How should this situation be treated?
What is with the treatment of antidysrhythmics (Amiodarone, Lidocaine,)
400
A client with a complete heart block has had a permanent demand ventricular pacemaker inserted. The nurse assesses for proper pacemaker function by examining the electrocardiogram (ECG) strip for the presence of pacemaker spikes at what point?
What is before each QRS complex.
400
A patient was admitted last night with the diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation with RVR. The patient responded well to medications overnight and is now rate controlled. Can the telemetry monitor be discontinued?
What is the telemetry monitor can NOT be discontinued.
500
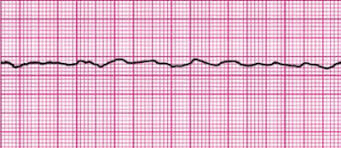
What is Fine Ventricular Fibrillation
500
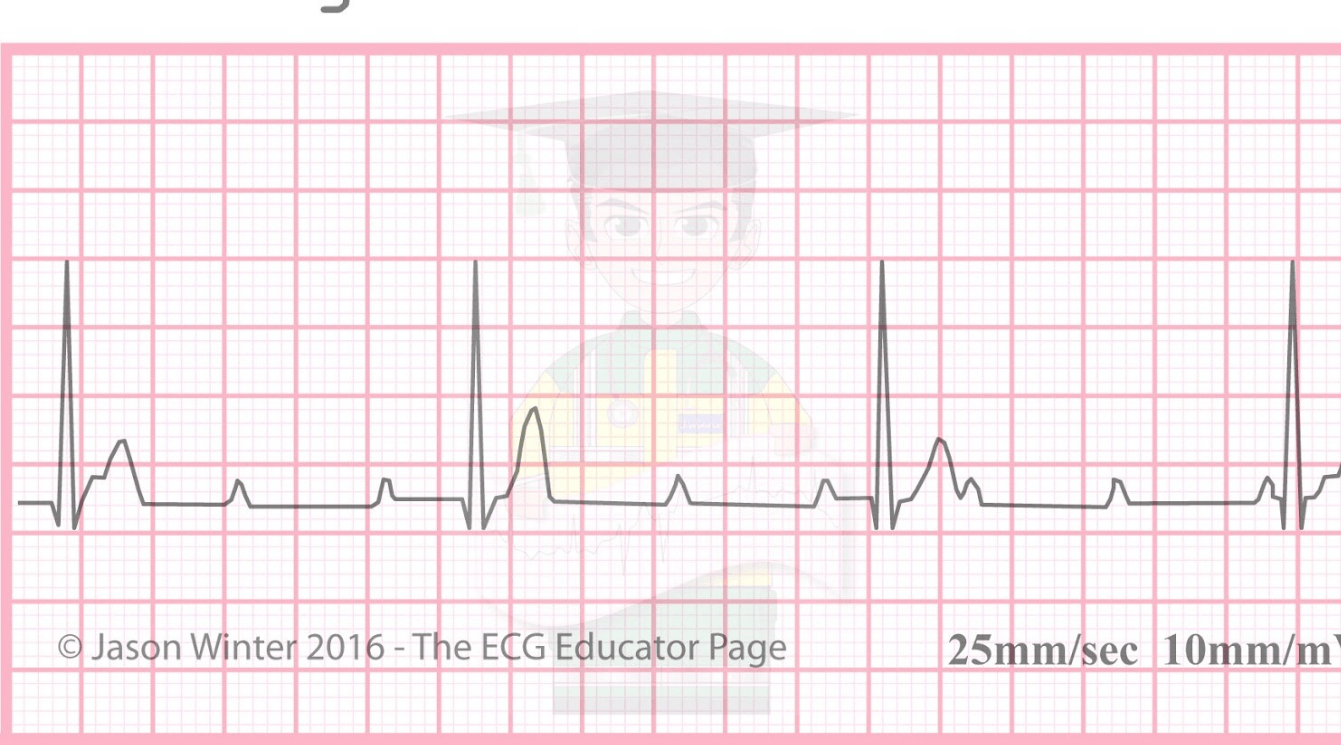
What is Third Degree heart block
500
A client is having frequent premature ventricular contractions. A nurse would place priority on assessment of which of the following items?
What is blood pressure and peripheral perfusion.
500
A patient goes into ventricular fibrillation. The patient is defibrillated, which terminates the ventricular fibrillation. The arrhythmia recurs later in the resuscitation. What is the next step?
What is deliver shocks at the previously successful energy level.
500
The Nurse Driven Telemetry Protocol contains five characteristics indicating telemetry is not required for the patient. What are these characteristics?
What is:
Asymptomatic PVCs, Post Normal Coronary Angiography, Acute medical illness, DNR status, and terminal illness