1. What do we call an organ whose sole function is to secrete hormones?
a- Gland
b- Monoamine
c- Tissue
d- Steroid
A - gland
5.What attaches the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)?
a- Hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract
b- Sella turcica
c- Hypophyseal portal system
d- Supraoptic nucleus
c- Hypophyseal portal system
**BONUS**
11.What is the target organ of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
a) Gonads
b) Kidneys
c) Thyroid gland
d) Adrenal Cortex
10.What hormone is secreted by the supraoptic nucleus?
a- Oxytocin
b- Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
c- Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
d- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
c- Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
26.What does the binding of a hormone to it’s cell surface receptor activate?
a- ATP
b- G-protein
c- cAMP
d- DAG
b- G-protein
**BONUS**
15. What is the overall effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion?
a) Increase in hematocrit levels
b) Increase in blood calcium levels
c) Decrease in hematocrit levels
d) Decrease in blood calcium levels
20.What type of hormone is this?
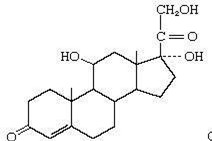
a- Steroid
b- Monoamine
c- Peptide
d- Eicosanoid
a- Steroid
2.Which of the following is false?
a- Hormone concentration in blood is very low compared to other solutes found within blood
b- Target cells have specific receptors for specific hormones
c- Hormones can be excreted in the urine
d- Hormones are only exposed to their target cells
d- Hormones are only exposed to their target cell
6.Hypothalamic neurons secrete hormones via a process known as…
a- Diffusion
b- Neurosecretion
c- Excretion
d- Osmosis
b- Neurosecretion
17.What is the target organ/effect of anti-diuretic hormone secretion?
a- ADH stimulates the pancreas to secrete insulin
b- ADH stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk
c- ADH stimulates the kidney to retain water
d- ADH stimulates the liver to secrete bile
c- ADH stimulates the kidney to retain water
28.After a G-protein is activated what enzyme does it turn on within the cell?
a- Phospholipase C
b- Adenolipase
c- Adenylate Cyclase
d- A or C
d- A or C
21.What type of hormone is this?
a- Steroid
b- Monoamine
c- Peptide
d- Eicosanoid
c- Peptide
4.Which of the following is NOT a cellular change caused by hormones?
a- Metabolism
b- Growth
c- Secretion
d- Gene expression
e- None of the above
e- None of the above
**BONUS**-
29. What does IP3 cause?
a) Ca+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum
b) Decreases the effects of cAMP
c) Glucose uptake in the blood
d) An increase in cellular activity
8.What prefix/suffix is typically associated with steroid hormones?
a- -ol
b- -one
c- Hema-
d- A & B
e- All of the above
d- A & B
3.What happens in response to decreased body temperature?
a- The anterior pituitary decreases its secretion of TSH
b- The pancreas secretes insulin
c- The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormone
d- The hypothalamus secretes growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
c- The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormone
**BONUS**
13.What is the target organ of oxytocin?
a) Uterus
b) Mammary Glands
c) Ovaries
d) A & B
e) All of the above
25.After a hormone binds to an intracellular receptor the H-R complex binds to a specific segment of DNA (target gene). What process does this initiate?
a- Mitosis
b- Transcription
c- Metabolism
d- Increase in cell size
b- Transcription
23.What type of hormone is this?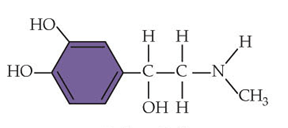 a- Steroid
a- Steroid
b- Peptide
c- Monoamine
d- Eicosanoid
c- Monoamine
9.How are all endocrine responses regulated?
a- Negative feedback
b- Positive feedback
c- Leucopoiesis
d- Hemostasis
a- Negative feedback
27.What are cAMP, DAG, and IP3 all known as?
a- G-proteins
b- Second messengers
c- Proteins
d- Hormones
b- Second Messengers
7.If we removed the thyroid gland how would thyrotropin (TSH) levels be affected?
a- Decreased
b- Increased
c- No change
d- Completely stopped
b- Increased
**BONUS**
12.What is the releasing organ of testosterone?
a) Ovaries
b) Testes
c) Hypothalamus
d) Smooth Muscle
30.What do protein kinases do?
a- Phosphorylation
b- Cause Ca+ release in the endoplasmic reticulum
c- Aid hydrophobic hormones in traveling around the blood
d- Transcription
a- Phosphorylation
22.Which of the following is false regarding eicosanoids?
a- They initiate inflammation
b- They initiate coagulation
c- They may induce fever
d- They are specialized for long distance communication
d- They are specialized for long distance communication
24.What type of molecule is a hormone receptor?
a- Carbohydrate
b- Protein
c- Enzyme
d- Nucleus
b- Protein
14.What gland is responsible for the secretion of epinephrine?
a) Sympathetic Nervous System Gland
b) Pituitary Gland
c) Adrenal Gland
d) Parathyroid Gland
c- Adrenal Gland
18.What is the job of the pancreas and what hormones does it secrete?
a- Regulation of blood glucose levels. Insulin & glucagon
b- Regulation of blood glucose levels. Glucagon & erythropoietin
c- Regulation of plasma calcium levels. Insulin & glucagon
d- Regulation of plasma calcium levels. Insulin & luteinizing hormone
a- Regulation of blood glucose levels. Insulin & glucagon
31.True or false, certain hormones activate the same second messenger pathways in each cell they bind to.
a- True
b- False
b- False
19.Of all four chemical classes of hormones, which bind to intracellular receptors?
a- Steroids and all monoamines
b- Peptides and Monoamines
c- Steroids and thyroid hormones
d- Steroids and all Peptides
c- Steroids and thyroid hormones