What is the function of vitamins?
vitamins help your body use energy from the the food you eat
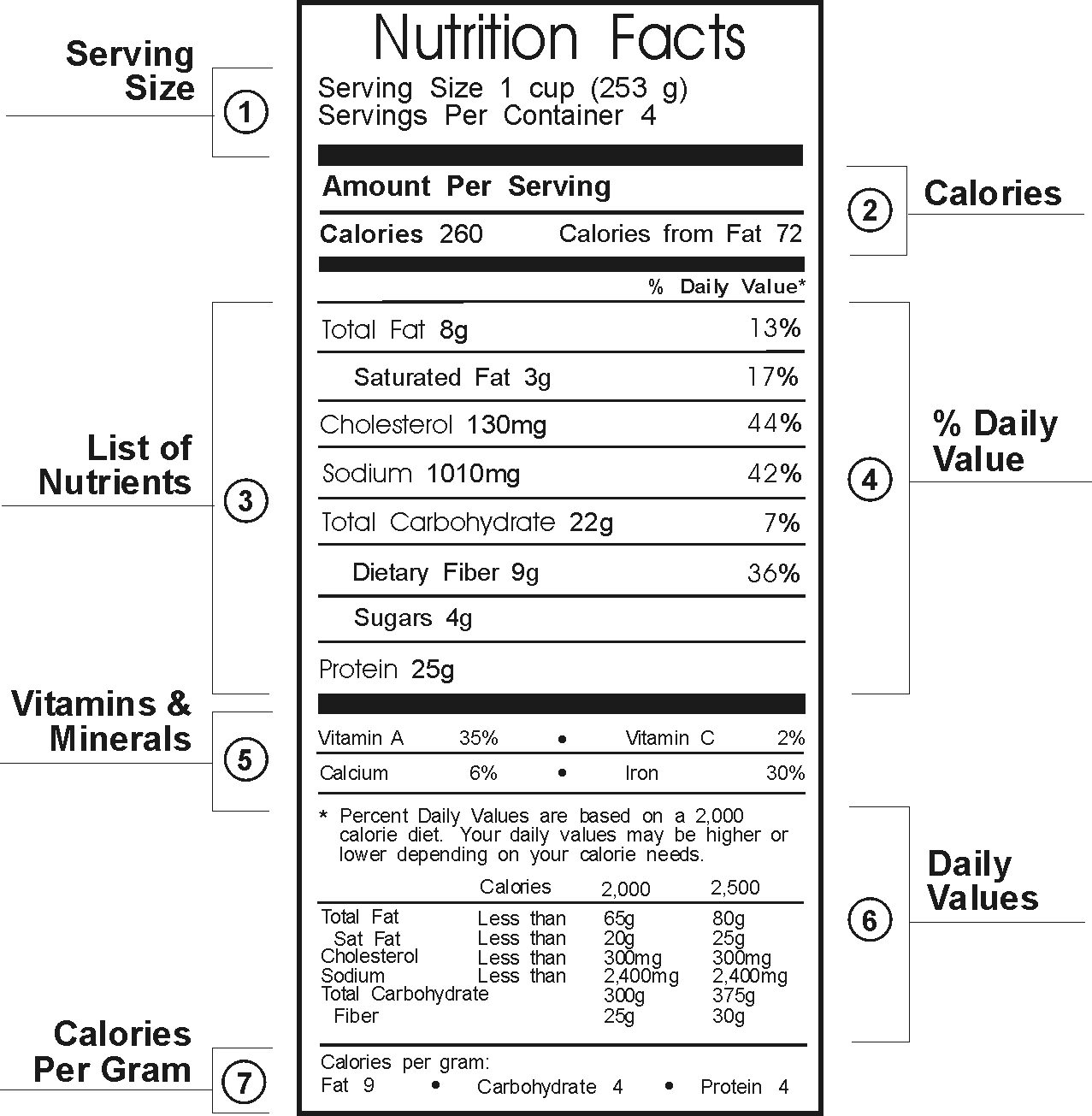
- Cholesterol; fat
- Sodium; mineral
- Dietary fiber, sugars; carbohydrates
- Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Calcium, Iron: vitamins
What can lacking a specific nutrient do to you?
Deficiencies can lead to digestion problems, skin disorders, defective bone growth, and even dementia
Specific: when you don't have enough protein you have muscle cramping, weakness, soreness, can eventually cause muscle wasting or atrophy as direct result of chronic, low dietary protein
What is Chemical and medical digestion?
Mechanical: involves physically breaking the food into smaller pieces, brings in the mouth s food is chemical
Chemical: involves breaking down the food into nutrients that can be used by the cells, begins in the mouth when food mixes with saliva
What is the function of the gallbladder?
it holds bile produced in the liver until it's needed for digesting fatty foods in the duodenum of the small intestine
- stores bile until it's secreted directly into the first section of the small intestine
Chemical digestion based on statements
The enzymes present in saliva also begin to chemically break down food.
What is the function of minerals?
are chemical elements that help regulate your body's processes
Potassium: helps your nerves & muscle function
Calcium: helps your teeth & bones stay strong
What is Ghrelin?
a hormone that is secreted by the stomach to signal hunger in the brain.
- A hormone that is produced and released mainly by the stomach with small amounts also released by the small intestine, pancreas, and brain. Ghrelin has numerous functions, "hunger hormone" because it stimulates appetite, increases food intake and promotes fast storage.
What does the stomach do?
food is being mechanically (churning) and chemically (enzymes to digest complex proteins; come from specific cells, makes an acid compound called gastric juices) digested.
- water soluble vitamins, 4 main parts; fundus, cardia, body, pylons
- the stomach coats the food with a mixture of acid and digestive enzymes to help the food break further down. Layers of mucus protects the stomach lining from being damaged by the acid. The bottom of the stomach is able to contract which helps to speed the process up. When food is broken down sufficiently the stomach releases its contents into the duodenum.
What is the role of the small intestine?
- has 3 sections with slightly different roles:
1st: duodenum; enzymes to deal with sugars, Gastric juices (acid) mixed with pancreatic juice (base)-- neutralizes it
2nd: jejunum; absorption of nutrients, some chemical digestion continues-- Villi (hairlike projection)
3rd: ileum; primarily absorption of nutrients
-food enters the duodenum, the pancreas releases enzymes to help break down fat, protein, and carbohydrates. Gallbladder releases bile; to help further break fats into a form that can be absorbed by the intestines. The small intestine is lined by projections (Villi) which provides large surface area facilitates the absorption of nutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats into the bloodstream. It regulates blood glucose levels; contains a number of receptive cells which detect the presence of macronutrients and secrete hormones which instructs the pancreas on how much insulin and glucagon to release.
Mechanical digestion in statements
you eat a burger using chewing and swallowing methods
What is the function of fats?
the body uses fat as a fuel source, and fat is the major storage form of energy in the body
What is Neuropeptide Y?
It is secreted by the brain to stimulate food intake (mostly carbohydrates)
What does the mouth do?
It is a site of ingestion, beginning of digestion
- teeth begin to break down; shape of teeth determines function, types of food
- enzymes digest complex sugars; comes from salivary glands
- The mouth and esophagus; saliva acts to start to break down carbohydrates thanks to amylase. The esophagus is a tube controlled by the muscles and autonomic nerves, that helps food travel from the mouth to the stomach.
What is the role of the large intestine?
- it is also known as the colon
- final stages of the digestive system; absorbs water and salts before the remains are passed out of th erectum as feces. The colon can help to absorb remaining carbohydrates and some fats
- houses lots of bacteria- can't leave or you can get septic
- appendix may id in this
- cecum controls valve between small intestine and large intestine
- absorbs minerals and vitamins (made by bacteria) - - eliminates waste
how is appetite Cyclical?
Your appetite is hormone controlled.
When increased or decreased, you become hungry or full. The cycle repeats to signal the brain about your hunger. Leptin constantly increases or decreases.
What is the function of carbohydrates?
to provide your body with energy
most of the carbohydrates in the foods we eat are digested and broken down into glucose before entering the bloodstream.
What is Leptin?
it is secreted by adipose tissue to signal appetite reduction
What is the role of the liver?
- Liver detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes drugs. Secretes bile that end sup back in the intestines, makes protein important for blood clotting. The liver produces bile which helps digest lipids, bile is stored in the gallbladder and flows from the gallbladder to the duodenum where it helps digest fats.
What are the steps of digestion?
Organ: movements
Mouth: chewing
Esophagus: peristalsis
Stomach: Upper muscle in stomach relaxes to let food enter, and lower muscle mixes food with digestive juice
Small intestine: Peristalsis
Pancreas
Liver
Large intestine: peristalsis
What is the function of proteins?
to regulate the activity of cells or organs
for example: enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body and hormones like insulin are proteins
What are the stages of digestion?
Ingestion: have to eat first, takes in macromolecules for breakdown
Digestion: breaking down macromolecules, Hydrolysis, catabolic reactions of enzymes, can be mechanical (chewing) or chemical (enzymes)
Absorption: pull in monomers, blood stream or fat stream
Elimination: removal of undigested waste, plant parts are fibers
What is the role of the Pancreas?
- plays a roll in converting the food into fuel for your body's cells, exocrine function that helps in digestionand endocrine function that regulates blood sugar.
- has 3 functions to help the digestive system change food into a form that can be used by the cells;
- it produces enzymes which help break don proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates
- produces the hormones, insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels
- produces sodium bicarbonate; helps to neutralize stomach acids