Fats, steroids, and waxes are all examples of
Lipid
What is the energy molecule created by the mitochondria
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Which biomolecule is the primary source of energy in the human diet
Carbohydrate
Which process takes places in the ribosomes
Protein synthesis
What is the process of osmosis?
The process of osmosis involves the diffusion of water across a membrane

What is the primary function of nucleic acid
To store genetic information
What is the primary function of the Golgi Apparatus
Sorting, packaging, and transport
Does the process of diffusion (passive transport) move solutes/particles from a high to low concentration or a low to high concentration?
High to Low
Which biomolecule is fundamental to the function of biological membranes, such as cell membranes
Lipid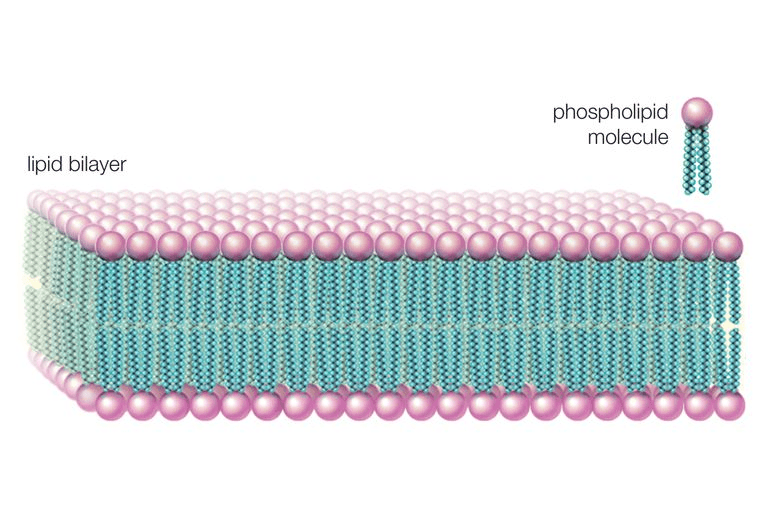
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
Control what enters and leaves the cell (separates the inside from the outside)
Does the process of active transport (NEEDS ENERGY) move solutes/particles from a high to low concentration or a low to high concentration?
Low to high (against the concentration gradient)
Three of the four biomolecules are found within the cell membrane; _____________ are not
Nucleic Acid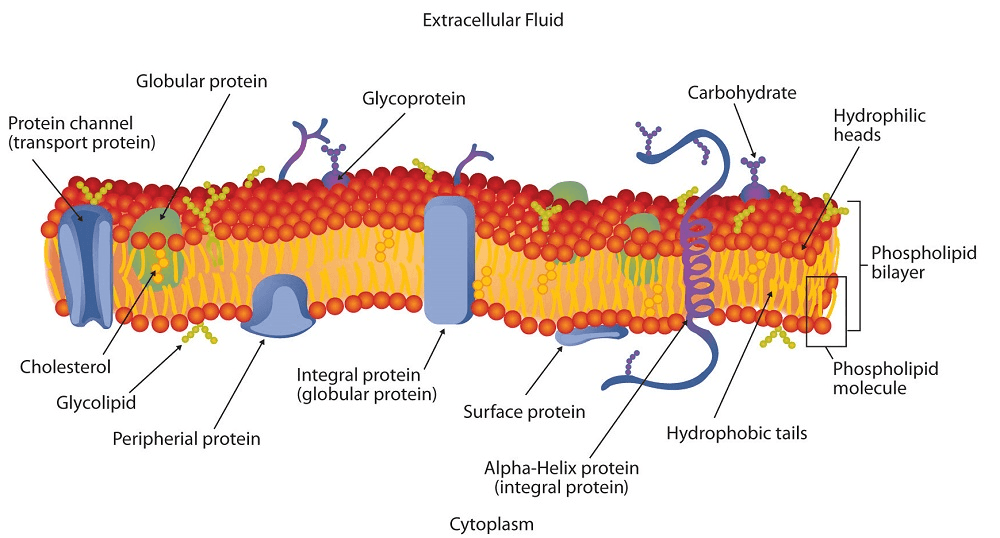
What is the main difference between Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus
What is the difference between a hypertonic and hypotonic solution?
Hypotonic solution: a solution in which the solute (dissolved particles) concentration outside the cell is lower than the solute concentration inside the cell
Hypertonic solution: solute (dissolved particles) concentration is higher outside the cell than it is inside the cell