the number of sets of complete chromosomes in a cell
ploidy
G1, S, and G2
Interphase phases
What type of organism uses meiosis to reproduce?
Eukaryotes
What happens when a prokaryote experiences starvation?
The cell would not be able to divide
If it’s already dividing, but experiences sudden starvation, it could stop dividing
When a mixture of the phenotypes is expressed
What is incomplete dominance?
is that type of ploidy with a singe set (n) of chromosomes
haploid
Cell growth and normal cell function
Occurs during the G1 phase
What is the purpose of meiosis in humans?
Germline cell division for the purpose of producing haploid gametes for reproduction
A signal to divide
What is a growth factor?
What is codominance?
When both phenotypes are expressed at the same time
is that type of ploidy with two sets (2n) of chromosomes
diploid
What is the purpose of mitosis in humans?
Somatic cell division for the purpose of producing diploid cells for repair of old cells and growth
What occurs during metaphase I?
Alignment of homologous pairs of chromosomes (independent assortment)
* Different than mitosis where there is a line of single chromosomes
Specific points that can halt the cell cycle
What are checkpoints?
What defines continuous traits?
They vary along a continuum
- Many alleles are involved with these traits
- Most traits are continuous
Ex) height (no distinct categories)
How many sets of chromosomes does a polyploid cell have?
More than two sets
Alignment of chromosomes in the middle
Metaphase of mitosis
What occurs during anaphase II?
Sister chromatids are separated to opposite sides of the cell
What might cause division to be stopped at a checkpoint?
- There is not sufficient nutrients
- There is DNA damage
- There are external signals to not divide
Are different genes that control for the same trait ever on different chromosomes?
Yes! Traits are often controlled by multiple genes and those genes can be on loci of different chromosomes
-This means that independent assortment plays a role in the expression of traits
Are humans haploid or diploid for most of their lives?
Diploid (having two sets of each chromosome)
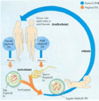
What is the product of mitosis in humans?
Two diploid daughter cells (thats are CLONES of the parent cell)!
Are the daughter cells clones of the parent cells?
No, there is variation due to crossing over and independent assortment
They are also haploid whereas the parent cells are diploid
What is the signal pathway?
- A growth factor will produce a cyclin protein
*there are different cyclins for each checkpoint!
- The cyclins interact with CDK (cyclin dependent kinase) and activates it
- The CDK will interact with another protein and adds a phosphate group to it, thus regulating the cell cycle (activating of inhibiting it)
Why are X-linked recessive alleles more commonly expressed in men?
If men inherit the recessive allele that’s the only ONE they have, so they will express it
Women have TWO alleles and its less common that they will inherit alleles that are both recessive