The "educated guess" of the scientific method.
What is a hypothesis?
A change in an organism’s surroundings that causes it to react.
What is a stimulus?
What is a polymer?
What is a eukaryotic cell?
The hydrophilic portion of the lipid bilayer.
What is the phosphate head?
The variable that you manipulate and change.
What is an independent variable?
The basic unit of life.
What is a cell?
Amino acids are the monomers for this macromolecule.
What are proteins?
The organelle that stores genetic material.
What is the nucleus?
The hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer.
What are fatty acid tails?
These factors remain the same throughout the experiment to ensure accuracy and reliability.
What are constant variables/factors?
The reason you do not remain as a baby for your entire life.
What is growth and development?
DNA is an example of this macromolecule.
What is a nucleic acid?
The POWERHOUSE of the cell.
What is the mitochondria?
This membrane protein spans across the entire membrane and acts as a channel.
What is a transmembrane protein?
The variable that you measure and record.
What is the dependent variable?
Metabolism is an example of this characteristic of life.
What is obtain and use energy?
The energy required to overcome a chemical reaction.
What is activation energy?
This organelle modifies, packages, and ships proteins.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The type of solution that would do this to your cells.
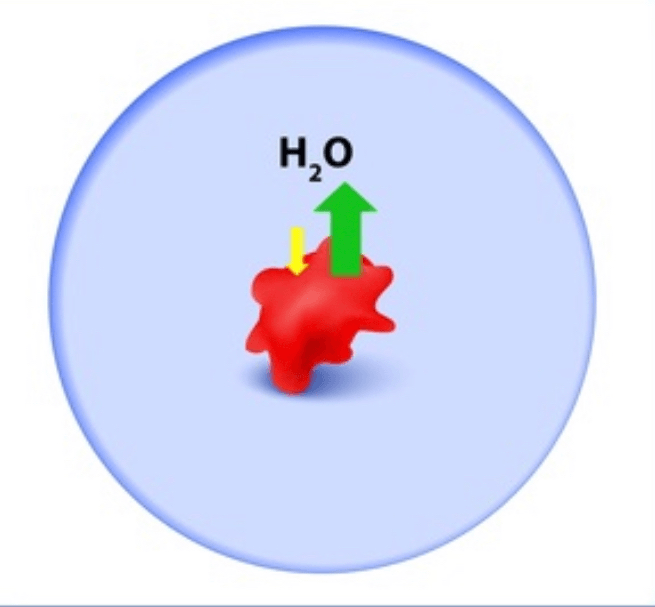
What is a hypertonic solution?
The untreated experimental setup meant to represent normal unchanged conditions.
What is the control group?
Your children, your children’s children, and your children’s children’s children.
What is reproduction?
The monomer for a carbohydrate.
What is a monosaccharide?
This organelle breaks down and digests material.
What is a lysosome?
The diffusion of water.
What is osmosis?