The force that pulls two objects together

What is gravity?
A species ___________ is its ability to survive, find a mate, produce offspring — and ultimately leave its genes in the next generation

What is fitness?
Another name for an earthquake wave.

This is the process in which a eukaryotic cell divides. It creates two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
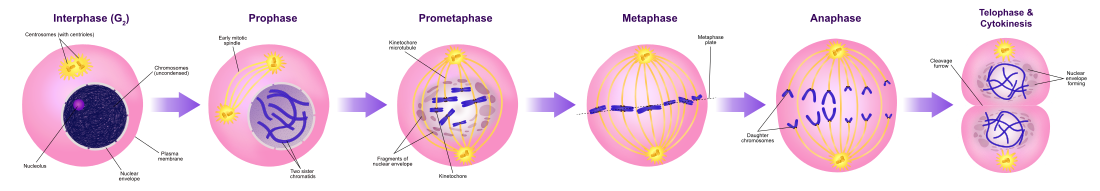
What is mitosis?
The step that usually comes first.

What is asking a question?
This type of electric force results from a buildup of charge.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ElectricHair-RichVintage-5bb2871b46e0fb0026f449a6.jpg)
What is static electricity? (or electrostatic force)
An organism's trait that changes to become better suited for its environment is called an __________. Darwin's bird beaks that he studied are an example.

What is an adaptation?
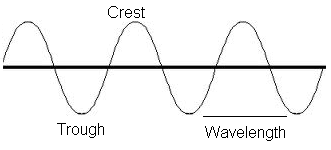 Is this a transverse wave or longitudinal wave?
Is this a transverse wave or longitudinal wave?
What is a transverse wave?
Bacteria replicates through this process.

What is binary fission?
This step involves making an educated guess or prediction about an experiment.

What is a hypothesis?
In a magnet, opposite ______________ attract each other.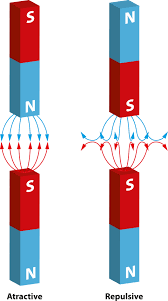
What are poles?
This is the mechanism that Darwin proposed for evolution. He believed that organisms with traits that favor survival and reproduction will tend to leave more offspring.
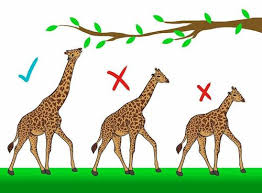
What is natural selection?
This is the distance from one wave crest to another.
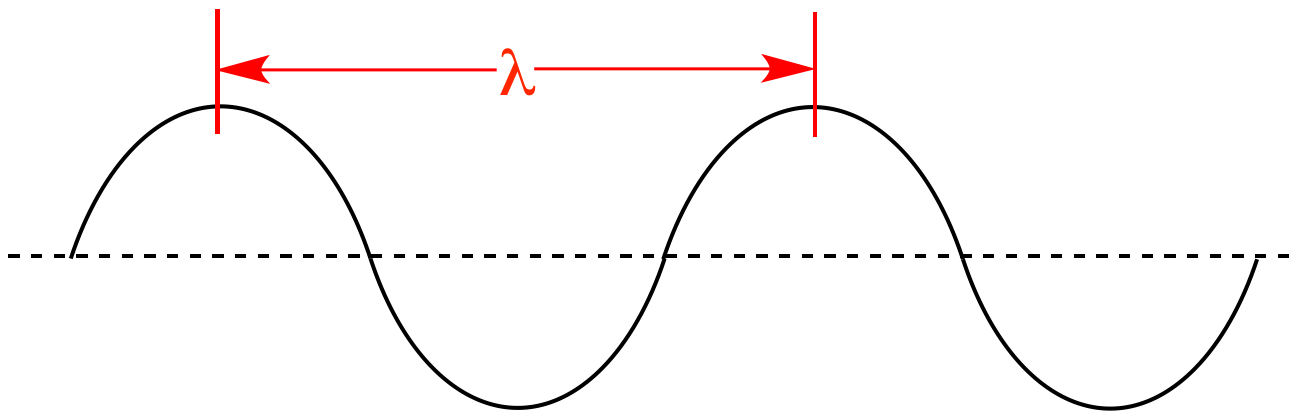
What is wavelength?
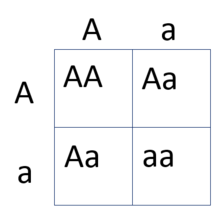
We use these to predict outcomes of genetic crosses.
What are Punnett Squares
This is the step where you test your hypothesis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/medical-student-doing-experiment-in-laboratory-457992393-588fca043df78caebc418fc3.jpg)
What is an experiment?
The force of gravity is affected by these two measurements:________ and _________
(These are m and r in the picture)

What are mass and distance?
This is the study of evolutionary trees.
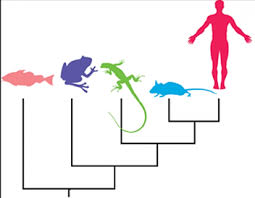
What is phylogenetics?
A sound's pitch is related to what part of a wave?

What is frequency?
In pea plants, T is the gene for tallness and t is the gene for shortness. Tall is dominant over short. If you cross two heterozygous tall plants, what is the likelihood of getting an offspring plant that is short?
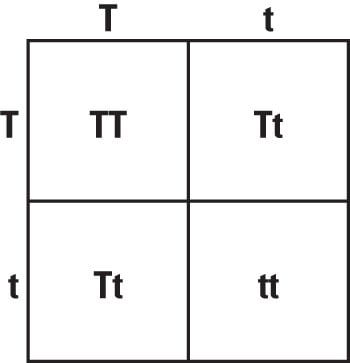
What is 25% or 1/4?
The step where you make a claim if your hypothesis is true after examining data and evidence

What is making a conclusion
These are a result of when a moving object is trapped in the gravity of a much larger object.
What are orbits?
Name of the island where Darwin recorded most of his observations.

What is the Galapagos Islands?
Light exhibits both the properties of a waves AND __________.

What are particles?
These kind of cells are produced during meiosis.

What are gametes (haploid cells)?
The step where you create tables, charts and graphs showing your evidence you've collected
What is analyzing results?