This is the only muscle proximal to the knee innervated by the peroneal division of the sciatic nerve.
Short head of the biceps femoris
In this type of aphasia, there is a lesion near the motor cortex. Fluency is impacted; comprehension & repetiton are intact.
Transcortical motor
The anatomical variant characterized by the PCA originating from the ICA, leading to small P1 segment. For example, the PCA is supplied by the anterior circulation, and an ICA lesion can cause a stroke in PCA territory.
Fetal PCA
This test is the most non-invasive way to diagnose narcolepsy, and also the answer on board exams.
Sleep latency test
This disorder is characterized by onset of myotonia in childhood and runs in families. Myotonia will improve after performing the same motor task multiple times in a row.
Myotonia congenita
This nerve innervates the scalp at the back of the head (in the midline) and originates from C2 fibers.
Greater occipital nerve
In this type of aphasia, repetition is the only thing which is impaired. Fluency, comprehension are intact.
Conduction aphasia, lesion in arcuate fasciculus
The anterior choroidal artery receives its supply from this artery.
The ICA just distal from the origin of the PCOM. Branches supply the lateral geniculate body and posterior half of the posterior limb of the internal capsule.
This is the treatment for REM behavior disorder
Clonazepam
This disease is characterized by a risk for malignant hyperthermia with anesthesia use in addition to proximal weakness beginning at birth.
A sample of a patient's muscle biopsy is shown below:
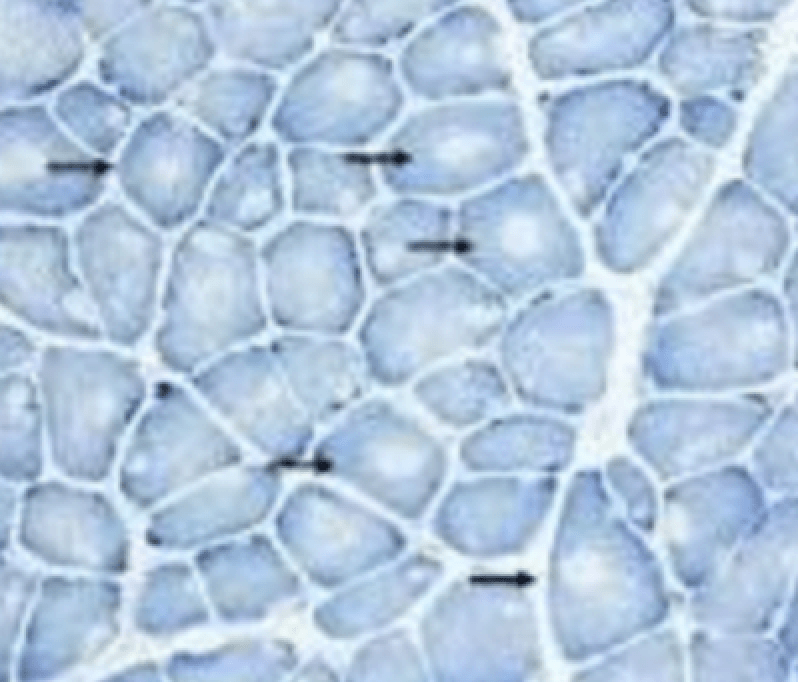
Central core disease
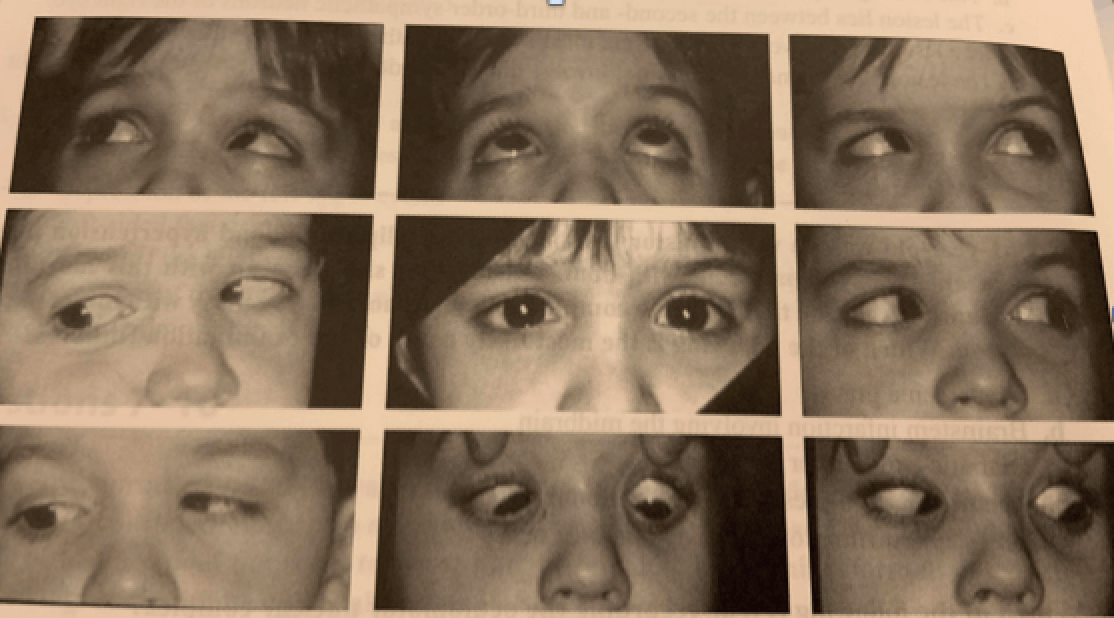
A 78 yo man has had a stroke. He cannot abduct or adduct his left eye at all, the right eye can only abduct with nystagmus. Name the structures involved in his stroke that would cause his symptoms.
Left MLF and left abducens nucleus
In this type of primary progressive aphasia, an individual has impaired single word retrieval in spontaneous speech and naming in addition to profoundly impaired repetition of sentences. Grammar is intact.
Logopenic variant
This artery supplies the anterior limb of the internal capsule, the inferior part head of the caudate, and the anterior part of globus pallidus.
Recurrent artery of heubner
SSEPs record this type of sensory fiber
Dorsal column medial lemniscus
This type of muscular dystrophy is characterized by progressive weakness of the proximal arms with minimal involvement of the legs. There are commonly contractures at the neck, ankles, and elbows. Patients also have significant cardiac problems often requiring pacemaker placement.
Emery-dreifuss
Forearm pronation weakness is the most frequent motor finding in this type of radiculopathy.
C6 radiculopathy
In this type of primary progressive aphasia, an individual may have agrammatism with broken sentences and missing words in emails.
Nonfluent/agrammatic variant
This syndrome is characterized by a triad of inability to perceive the visual field as a whole (simultangnosia), oculomotor apraxia, inability to move the hand in space to an object (optic ataxia).
Balint syndrome. Caused by b/l damage to the posterior parietal cortex
In this sleep disorder which is mostly seen in teenage males, bouts of excessive sleeping are associated with hypersexual behavior, either anorexia or hyperphasia, and depersonalization/cognitive issues.
Kleine-levin syndrome
This disease is characterized by muscle cramping and limb weakness after exercise. Patients can resume activity after a period of rest. During a period of cramping, EMG inserted into the muscle will show electrical silence. Muscle biopsy will show absence of myophosphorylaase.
McArdle's disease
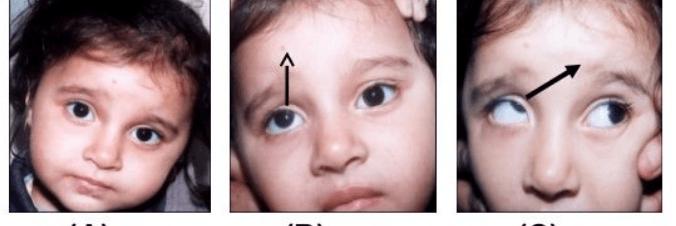
A child presents complaining of diplopia after falling off her bike and hitting her head. This nerve is lesioned.

Left superior oblique
Example of corrective head tilt (although R SO is lesioned in this case)
In this type of aphasia, both fluency and comprehension are impacted, although repetition remains intact.
Mixed transcortical aphasia
This term refers to a patient who cannot stand or sit unsupported for the first few days after a stroke, although is alert and is not weak.
Thalamic astasia
This is the mutation causing the most common hereditary form of dopa-responsive dystonia
Mutation in enzyme GTP cyclohydrolase I on chromosome 14, causing DTY5.
This disorder is characterized by episodes of weakness and inability to move the arms and the legs. EOM, bulbar, respiratory muscles are spared. Gets them with emotional stressors, after exercising, or eating heavy desserts.
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis