What is the storage form of glucose in humans?
Glycogen
Any enzyme that moves a functional group from one molecule to another is called a ____
transferase
In glycolysis, what enzyme converts glucose to glucose 6-phosphate?
hexokinase (or glucokinase)
Unfolding of a protein due to exposure to heat or acid solution is called...
denaturation
Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering what?
Activation energy of a reaction
Alpha helices and beta sheets are examples of this level of protein structure.
Secondary
Which vitamin is most needed for clotting factor synthesis?
Vitamin K
The oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA is accompanied by the reduction of ___?
NAD+ to NADH
Any compound with the general formula (CH2O)n
Carbohydrate
What is the name of the place on an enzyme where its substrate binds?
active site
Fatty acids link to glycerol via this type of bond
ester
Which glucose transport protein is insulin dependent
GLUT-4
Aldolase cleaves fructose 1,6 bisphosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and ___?
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Conversion of pyruvate into alcohol or lactate is called...
fermentation
What is the name of the model of enzyme kinetics which plots reaction rate against substrate concentration?
Michaelis-menten
This lipid serves as the precursor to all steroid hormones
cholesterol
Which of these enzymes are synthesized by intestinal mucus membrane?
carboxypeptidase, pepsin, maltase, amylase
maltase
What are the substrates of citrate synthase?
Oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA
What is this functional group?
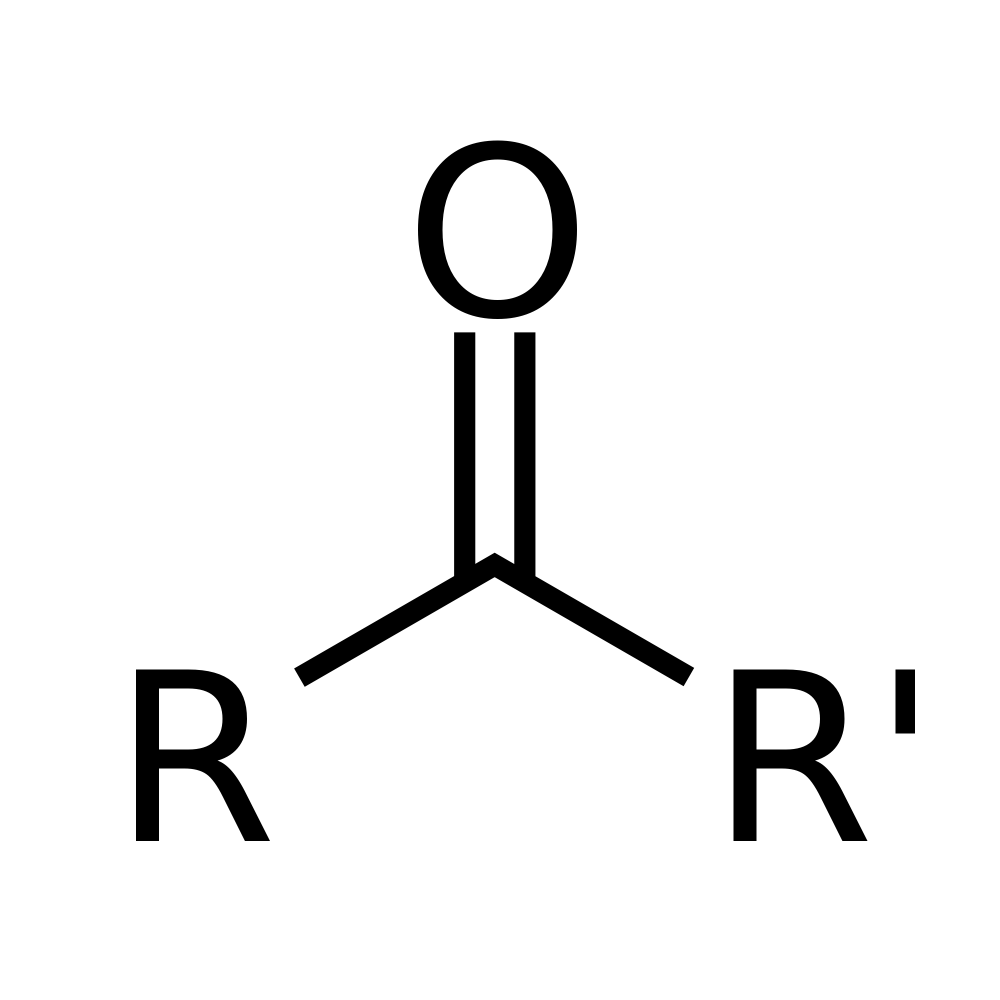
ketone
allosteric regulation
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base
What are three substrates used for gluconeogenesis?
glucogenic amino acids, glycerol, lactate, pyruvate
The catabolism of fatty acids into acetyl Co-A is called
beta oxidation
Identify the difference between ionic and covalent bonds.
Ionic - give and take electrons
Covalent - sharing electrons
Name the enzyme that catalyzes the rate limiting step in cholesterol synthesis and is the target of statin drugs?
HMG-CoA reductase