In this condition, the urethra opens at a point on the underside of the penis rather than at the very tip.
Hypospadias
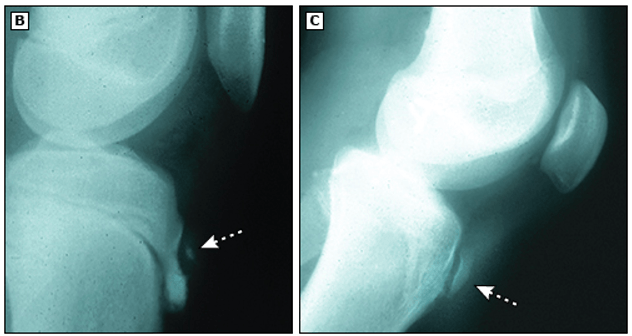
14 yo M, plays soccer. What's the diagnosis?
Osgood-Schlatter typically occurs in the 13 to 14-year-old boy or skeletally equivalent 11 to 12-year-old girl who has recently undergone a rapid growth spurt [17].
The most common presenting complaint is anterior knee pain that increases gradually over time, from a low-grade ache to pain that causes a limp and/or impairs activity [18]. Pain is exacerbated by direct trauma, kneeling, running, jumping, squatting, climbing stairs, or walking uphill, and is relieved by rest. Involvement usually is asymmetric, although both knees are involved in 25 to 50 percent of cases [3,4,9].
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/osgood-schlatter-disease-tibial-tuberosity-avulsion?search=osgood%20schlatter%20children&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~95&usage_type=default&display_rank=1#H4
According to CDC guidelines what is the minimum amount of time that GBS prophylactic antibiotics may be effective?
2 hours is minimum but 4 hours is ideal
According to JNC 8 HTN Guidelines, what are the 4 classes of "initial drugs of choice" for treatment? (Name ALL 4 classes)
Initial Drugs of Choice for Hypertension
• ACE inhibitor (ACEI)
• Angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)
• Thiazide diuretic
• Calcium channel blocker (CCB)
Streptomycin and kanamycin have what common teratogenic effects?
Hearing loss and CN VIII damage
The proportion of people who have a disease and test (+) is the ___________.
Sensitivity
This tumor takes its name from the "grape-like" gross appearance of the tumor. Usually a polypoid mass grows beneath an epithelial surface.

Botryoid variant — The botryoid variant of embryonal RMS (sarcoma botryoides)
Dense subepithelial aggregates of rhabdomyoblasts (the so-called "cambrium" layer) are characteristic (picture 2). As noted above, the botryoid variant typically arises within the wall of the bladder or vagina (picture 3 and picture 4) and is seen almost exclusively in infants.
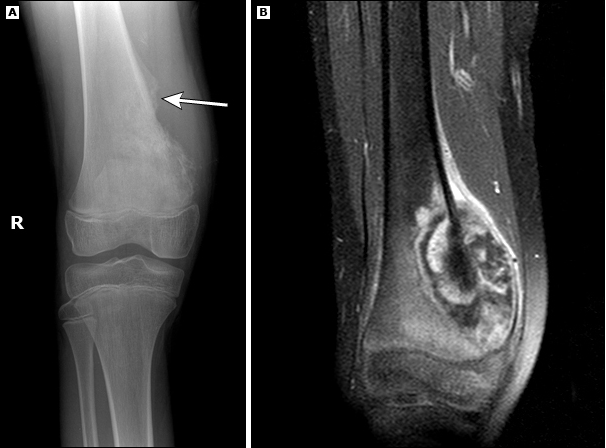
Most likely diagnosis?
Osteosarcoma
(A) Radiograph showing a destructive sclerotic lesion in the medial aspect of the right distal femur with an associated aggressive periosteal reaction, including a Codman triangle (arrow).
(B) Postcontrast T1 fat-saturated coronal MRI of the tumor showing both an intraosseous and extraosseous component.
Pneumonia hospitalization criteria in adults.... (Hint: What's the mnemonic and what do they stand for?)
How many criteria do you need to meet?
CURB-65 pneumonia severity score
- Confusion (based upon a specific mental test or new disorientation to person, place, or time)
- Urea (blood urea nitrogen in the United States) >7 mmol/L (20 mg/dL)
- Respiratory rate ≥30 breaths/minute
- Blood pressure (systolic <90 mmHg or diastolic <60 mmHg)
- Age ≥65 years
1 point is assigned for each criterion that is met. UpToDate authors generally favor hospital admission for patients with a score of 1 or 2, although patients with a score of 1 due to being ≥65 years of age who do not have major comorbidities do not necessarily require admission. For patients with a score of 3 to 5, hospitalization is indicated, and the patient should be assessed for possible intensive care unit admission, especially if the score is 4 or 5.
These are the 3 components of Virchow's triad....
VIRCHOW'S TRIAD
A major theory delineating the pathogenesis of venous thromboembolism (VTE), often called Virchow's triad [3,4], proposes that VTE occurs as a result of:
●Alterations in blood flow (ie, stasis)
●Vascular endothelial injury
●Alterations in the constituents of the blood (ie, inherited or acquired hypercoagulable state)
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-the-causes-of-venous-thrombosis?search=virchow%20triad§ionRank=1&usage_type=default&anchor=H2&source=machineLearning&selectedTitle=1~13&display_rank=1#H2
What division of the nervous system is responsible for the erection portion of the erection-emission-ejaculation triad?
Emission - sympathetic (shoot)
Ejaculation - Chiefly sympathetic
This bias is introduced when screening detects a disease earlier and thus lengthens the time from diagnosis to death, but does not improve survival.
Lead-time bias.
Which of the following is the correct equation to estimate pediatric bladder capacity in mL?
A. AGE + 2 = BLADDER CAPACITY
B. AGE + 5 = BLADDER CAPACITY
C. (AGE + 2)30 = BLADDER CAPACITY
D. (AGE + 5)30 = BLADDER CAPACITY
D. (AGE + 2)30 = BLADDER CAPACITY (in milliliters/cubic centimeters)
AGE + 2 = BLADDER CAPACITY (in ounces

Diagnosis?
Plain radiograph of an infant with duodenal atresia
Duodenal Atresia.Note the double bubble caused by dilation of the stomach and proximal duodenum; distal gas is absent.
Duodenal atresia — The duodenum is derived partly from the embryonic foregut and partly from the midgut. During early gestation (weeks six and seven), portions of the intestinal tract become occluded as the endodermal epithelium proliferates. Patency is restored as recanalization occurs during weeks eight to ten. Duodenal atresia is thought to result from failure of the bowel to recanalize during this period.
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/intestinal-atresia?search=duodenal%20atresia§ionRank=1&usage_type=default&anchor=H5&source=machineLearning&selectedTitle=1~16&display_rank=1#H5
According to the AAFP, what are the top 3 most common cause of bacterial pneumonia in the age group 4 months to 5 years?
This beta-blocker has been shown to cross the blood brain barrier and have beta-adrenergic effects in the brain and therefore should be avoided in the elderly (55-80 yo)?
Atenolol
It could be due to impairment of hepatic metabolism (especially in the aging liver) and complex neurotransmitter-related effects on brain beta-adrenoceptors and serotonin (5-HT) receptors.7 Moreover, beta-blockers have been shown to reduce the production of melatonin via specific inhibition of adrenergic beta1-receptors.
The LIFE study compared losartan with atenolol in patients (age 55 to 80 years) with hypertension and LVH,592 showing reduced stroke rate in the losartan-treated group despite comparable BP reduction in both treatment groups. The first occurrence of death, stroke, or CV mortality was reduced in favor of losartan and there was also a greater effect on LVH regression versus atenolol.
This hematological disease is autosomal dominant, involves disorder of platelet adhesion due to a deficiency of platelet glycoprotein GPIb-IX.
On peripheral blood smear, platelets are abnormally large. Overall platelet count is mildly low.
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
This bias occurs when individuals modify an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed.
Hawthorne effect (bias)
This medication can be used to stop enuresis in children but once the medication is stopped almost 100% of cases will reoccur. This medication can also be very toxic in children.
Tofranil (imipramine)
Monitoring response and follow-up – The response to imipramine should be assessed after one month. If imipramine therapy is successful, the family should taper to the lowest effective dose. Approximately every three months, imipramine should be discontinued for at least two weeks to decrease the risk of tolerance [51]. If there is no improvement after three months, imipramine should be gradually discontinued [2].

10 yo M PMH obesity, presents with painful limp for 1 week, restricted ROM, especially limited internal rotation and abduction of the hip. Found to have the above radiographic finding. What endocrinological disorder should be ruled out in this pt?
Hypothyroidism.
Typical SCFE — Patients with a typical presentation of SCFE (obese child in early adolescence) are unlikely to have an underlying cause of physeal weakness (eg, genetic disease, renal failure or endocrine disorder). Because the findings of hypothyroidism in children may be subtle, some authors recommend screening T4, TSH, and bone age for all patients newly diagnosed with SCFE
Source: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-and-management-of-slipped-capital-femoral-epiphysis-scfe?search=slipped%20capital%20femoral%20epiphysis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~37&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
What are the 2 main contraindications to starting someone on PrEP?
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• HIV-positive
• Estimated creatinine clearance (eCrCl) < 60 ml/min
CAUTION
• Hepatitis B (HBV) infection (can flare when stopping the medications used for PrEP; check HBsAb/Ag prior to initiation of PrEP)
• Concomitant illness (i.e. diabetes mellitus or hypertension) that increases risk for kidney disease; consider more frequent creatinine monitoring
• Acute flu-like illness; defer PrEP and retest in 4 weeks or evaluate for acute HIV infection, including HIV RNA PCR, before initiation
• Pregnancy or breastfeeding; discuss risks/benefits • Osteoporosis
• Adolescents
According to JNC 8 HTN Guidelines these 4 Beta-1 selective beta-blockers are considered possibly safer in patients with COPD, asthma, diabetes, and peripheral vascular disease. (Name 2 of 4)
• metoprolol
• bisoprolol
• betaxolol
• acebutolol
Source: https://thepafp.org/website/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/2014-JNC-8-Hypertension.pdf
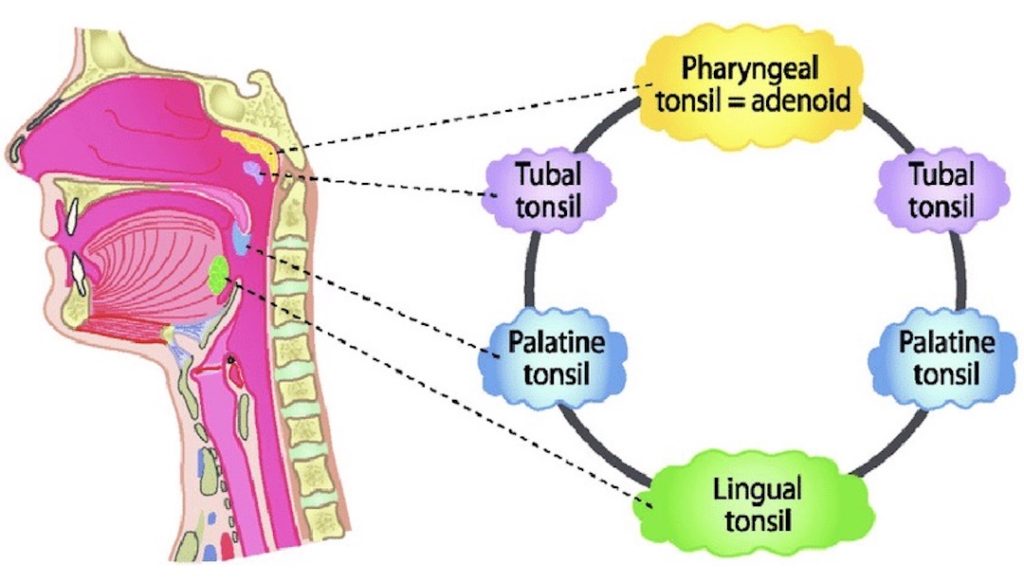
Name 3 of the 4 sets of tonsils found in the pharynx that compose Waldeyer's ring.
Waldeyer's ring
-Pharyngeal
-Palatine
-Lingual
-Tubal
If a trial comparing SuperStatin to placebo stated an OR 0.5 95% CI 0.4-0.6
What would that mean?
A) The odds of death in the SuperStatin arm are 50% less than in the placebo arm with the true population effect between 2% and 6%.
B) The odds of death in the SuperStatin arm are 50% less than in the placebo arm with the true population effect between 60% and 40%.
C) There is no statistical significance since the CI does not cross 1.
D) There is no statistical significance since the CI does not cross 0.
B) The odds of death in the SuperStatin arm are 50% less than in the placebo arm with the true population effect between 60% and 40%.
In regards to posterior urethral valves, how many types have been classified?
(Bonus bragging points if you can name which is most frequent)

Congenital membranes obstructing the posterior urethra are called posterior urethral valves.
Three types have been classified:
- Type 1. Valves representing folds extending inferiorly from the veru to the membranous urethra.
- Type 2. Valves as leaflets radiating from the veru proximally to the bladder neck.
- Type 3. Valves as concentric diaphragms within the prostatic urethra, either above or below the veru.
https://urologyweb.com/topics/pediatric-urology/posterior-urethral-valves/

MRI of a 7yo M with a painless limp and antalgic gait. Diagnosis?
LCP - Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
T1-weighted coronal MR of the pelvis demonstrates lack of signal in the left capital femoral epiphysis compared with the right (arrow). Fragmentation is present. Note that the overlying synovial cartilage is maintained, as is the joint space.
A 30-year-old woman reported that her chronic eczema had worsened over the previous several months. She had used emollient creams and topical and oral steroids in the past. Although the rash improved with steroids, it recurred when the treatment stopped. The patient was otherwise healthy.
Physical examination revealed a pruritic rash with peeling and cracking on the palmar and plantar surfaces of her hands and feet. The underlying skin was erythematous. No other areas of her body were affected. She had no occupational exposures or contact with irritants, chemicals, or livestock.


Based on the patient's history and physical examination findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
The answer is dyshidrotic eczema. This very pruritic condition (also called dyshidrotic dermatitis and pompholyx) is limited to the palms and soles.1,2 It presents as vesicles or larger bullae on the sides of the palms and soles.1 The lesions tend to persist for several weeks and resolve with desquamation. Recurrence is possible. The etiology is probably multifactorial, with some evidence pointing to atopic dermatitis, exposure to contact allergens, systemic exposure to contact allergens (e.g., ingestion of nickel or cobalt), dermatophyte infection, intravenous immune globulin, and hyperhidrosis.3 The diagnosis is based on the history and clinical appearance of the lesions. Patch testing, rapid plasma reagin testing, and potassium hydroxide preparation may be considered for initial workup.
Management of dyshidrotic eczema includes avoiding exposure to known irritants. Mild to moderate cases can be treated with two to four weeks of topical corticosteroids, whereas more severe cases may require an oral steroid taper. Topical immunomodulators, such as tacrolimus (Protopic), and phototherapy are options for refractory cases.1
This autosomal dominant disorder is characterized by abnormalities of the upper limbs and shoulder girdle, associated with a congenital heart lesion. The typical combination is considered to be a triphalangeal thumb with a secundum atrial septal defect (ASD), but there is a great range in the severity of both the heart and skeletal lesions.
Holt-Oram syndrome
12q24.21
AD
INHERITANCE
- Autosomal dominant
CARDIOVASCULAR
Heart
- Atrial septal defect (ostium secundum type)
- Ventricular septal defect
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Vascular
- Patent ductus arteriosus
CHEST
External Features
- Absent pectoralis major muscle
Ribs Sternum Clavicles & Scapulae
- Pectus excavatum or carinatum
SKELETAL
Spine
- Vertebral anomalies
- Thoracic scoliosis
Limbs
- Absent thumb
- Bifid thumb
- Triphalangeal thumb
- Carpal bone anomalies
- Upper extremity phocomelia
- Radial-ulnar anomalies
- Asymmetric involvement
What structures traverse the posterior triangle of the neck?
-Nerves: name 3 of 4
OR
-Arteries: name 2 of 3
OR
-Muscles: name 1 of 1
Nerves:
-brachial plexus
-phrenic nerve
-branches of cervical plexus
-spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
Arteries:
-subclavian artery (3rd part)
-suprascapular artery
-transverse cervical artery
Muscle:
-omohyoid muscle (inferior belly)
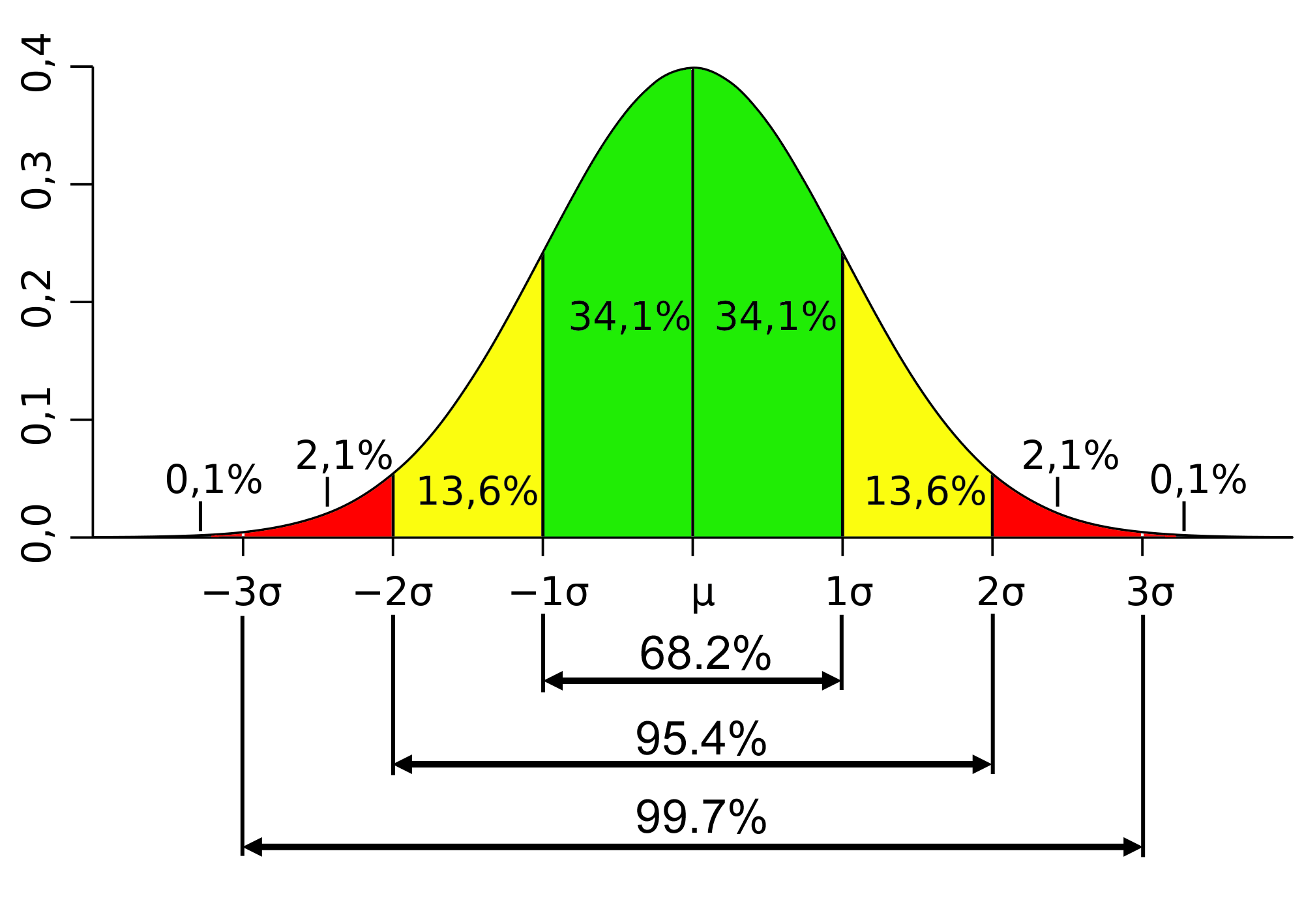
In a normal gaussian curve, what percentage falls within 1 standard deviation, 2 SDs and 3 SDs of the mean? (to the closest whole number is acceptable)
1 SD - 68%
2 SD - 95.4%
3 SD - 99.7%