Definition: A way to describe large groups of test scores; helpful because they classify large sets of scores into meaningful arrangements that visually summarize and illustrate the relationship between the scores.
Distributions
Give an example.
The symbol that stands for the sum.
∑
What is the meaning of the symbol below?
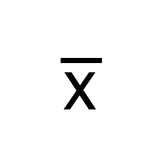
Definition: This involves analyzing the relationship between a test and other independent criteria of effectiveness. For example, this would be important in evaluating the SAT to see if it really predicts students’ academic success in college.
Criterion-related validity
Criterion-referenced validity refers to its predictive validity, or the ability to predict future performances, OR its concurrent validity. What does concurrent validity refer to?
Definition: Sets of scores developed from the scores of a carefully selected sample of students who take a test in a precise manner.
Test Norms
Some testing experts indicate that it takes at least 100 subjects for each grade or age level on the test to create test norms. Name at least three characteristics that would need to be taken into consideration when selecting a group of students to create test norms.
lWhen scores cluster at either the high or low end of the distribution, rather than the middle, the distribution is said to be what?
Skewed
When would you want the distribution of scores in your class to be skewed?
Everyone must turn to a neighbor and share a boring fact about themselves.
Free Points!
This term refers to how well a test covers the domain or learning area measured by the test.
Content Validity
If you were evaluating a reading test for content validity, what might you look for?
Definition: Structuring test materials, administration procedures, scoring methods and procedures for interpreting results to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Standardization
Which kinds of assessments would require standardization and why?
Definition: The design or pattern of a normal distribution
Bell-curve
Name one problem with using a bell-curve model to interpret test data.
Definition: This refers to the accuracy and consistency of scores from tests and from other assessments that measure student achievement, performance and behavior.
Reliability
What does a reliability coefficient of 1.00 tell you about a test?This kind of test assessment takes a long, drawn out process which entails synthesizing scientific research data about the relationship between test performance and the theoretical attributes that are being tested.
Construct Validity
Discuss face validity OR cash validity. Define
The three remaining items refer to bias. Which one refers to bias that occurs when decision makers use tests results in an unfair manner?
External bias
Tell what item bias OR internal bias might look like.
What are the most common forms of measures of central tendency?
Mean, median and mode
When are these measures not considered accurate with regard to determining the average performance of students on a test?What are some ways to estimate reliability?
Test-Retest, Alternate Form, Split-Half
Describe the way that one of these forms shows reliability.
This relatively new question about validity concerns whether a test, such as a state achievement test, fulfills its goal to improve classroom instruction, upgrade educational standards or clarify expected achievement levels for students.
Consequences of Testing
What kinds of consequences of state achievement tests may lead assessors to conclude that they are not valid? Name two.
Everyone in the room must stand up and stretch!
Free points
Definition: The measure of the average distance of individual scores from the mean of the distribution.
Standard Deviation
In order to determine how well a student has performed on an assessment in comparison to other test-takers, you must know the standard deviation and the ________.Definition: An estimate of the correlation of the observations of two independent observers.
Interrater Reliability
Give an example of how you tested interrater reliability when you were working on the Perspectives Project.
Which kind of assessment is closely tied to instruction and interprets performance on the basis of relatively small units of information?
Criterion-referenced Assessment
How is this different from Norm-referenced Assessment?
When a student’s test score is given as a band of scores, or confidence band, rather than as a single score, it is because the reporters are taking into consideration the __________________.
Standard error of measurement
Give one example of when looking at a range of scores rather than a single score could make a significant difference for a student.