What are the two types of cells?
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
What is the nucleus's purpose?
it is the control center and it tells all the organelles what to do
Find the Surface Area and Volume of this cube
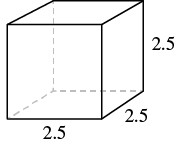
SA = 37.5
V = 15.625
When a virus is attacking a cell, what is it's goal?
It's goal is to take control of the nucleus
What is the power-house of the cell?
Mitochondria
What is the Smoothe ER's purpose
Makes lipids, breaks down carbs, and destroys drugs and poisons
What lays on the rough ER and what is its purpose?
Ribosomes and they package proteins to be taken elsewhere
identify what each line points to
Why do the free-floating ribosomes want to be mobile?
So they can communicate throughout the cell and check on the other parts of the cell
What is the equation to find the Surface Area and Volume of a Cube
SA= l x w x 6 : V= l x w x d
What is the neucleolos?
It is where the ribosomes are made (ribosome nursery)
What is a lysosome and what does it do?
It's an organelle that absorbs anything that is threatening to the cell, breaks it down and attempt to reuse it. If anything is sketchy, then the lysosome will leave the cell and self destruct.
Why do you want the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) so close to the nucleus?
so it is easy to deliver the ribosomes
When the surface area (radius) of a cell is increased, what happens to the efficiency of the cell and why?
the efficiency decreases because there is so much stuff inside the cell which makes it hard to move around within the cell and do what it needs to do
How many chromosomes does a human have?
46, get 23 from each parent
What type of cell is bacteria, and how do you know?
Prokaryote, because prokaryotes don't have a nuclei, and bacteria don't have nuclei
What do the hydrolytic enzymes breakdown and what does it turn into?
Breaks down threats to the cell and it breaks it down into monomers
Where are the pores on a nuclear envelope, and cell membrane, and what is their purpose?
To control what enters and exits the cell/nucleus
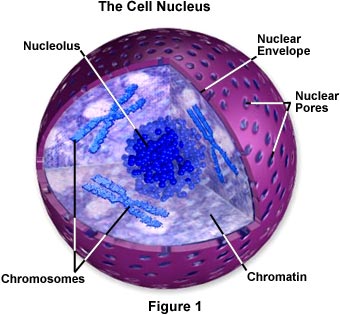
Why is the DNA in the nucleus but ribosomes are more protected by being in the neucleolos?
Because the ribosomes are the workers to make the DNA, so if the DNA is attacked the ribosomes can always make more but that means the ribosomes need more protection.
What do cis and trans mean/do?
Cis- receives the vesicles
Trans- ships the vesicles
What is the hierarchy of life?
Cell--> tissue--> organ--> organ system--> organism--> population
What is the purpose of the vesicle?
It protects the proteins while they are being transported from place to place. (like a box)
Identify the central vacuole and explain its function
it stores materials such as food, water, minerals, pigments, and poison
Why is it this shape?
To maximize surface area without compromising efficiency
What are ribosomes composed of and what are the two different types?
They are composed of rRNA and protein. The two types are free-floating ribosomes and bound ribosomes