Where does most of the energy in ecosystems on earth come from?
The Sun
What is one direct relationship in this food web?
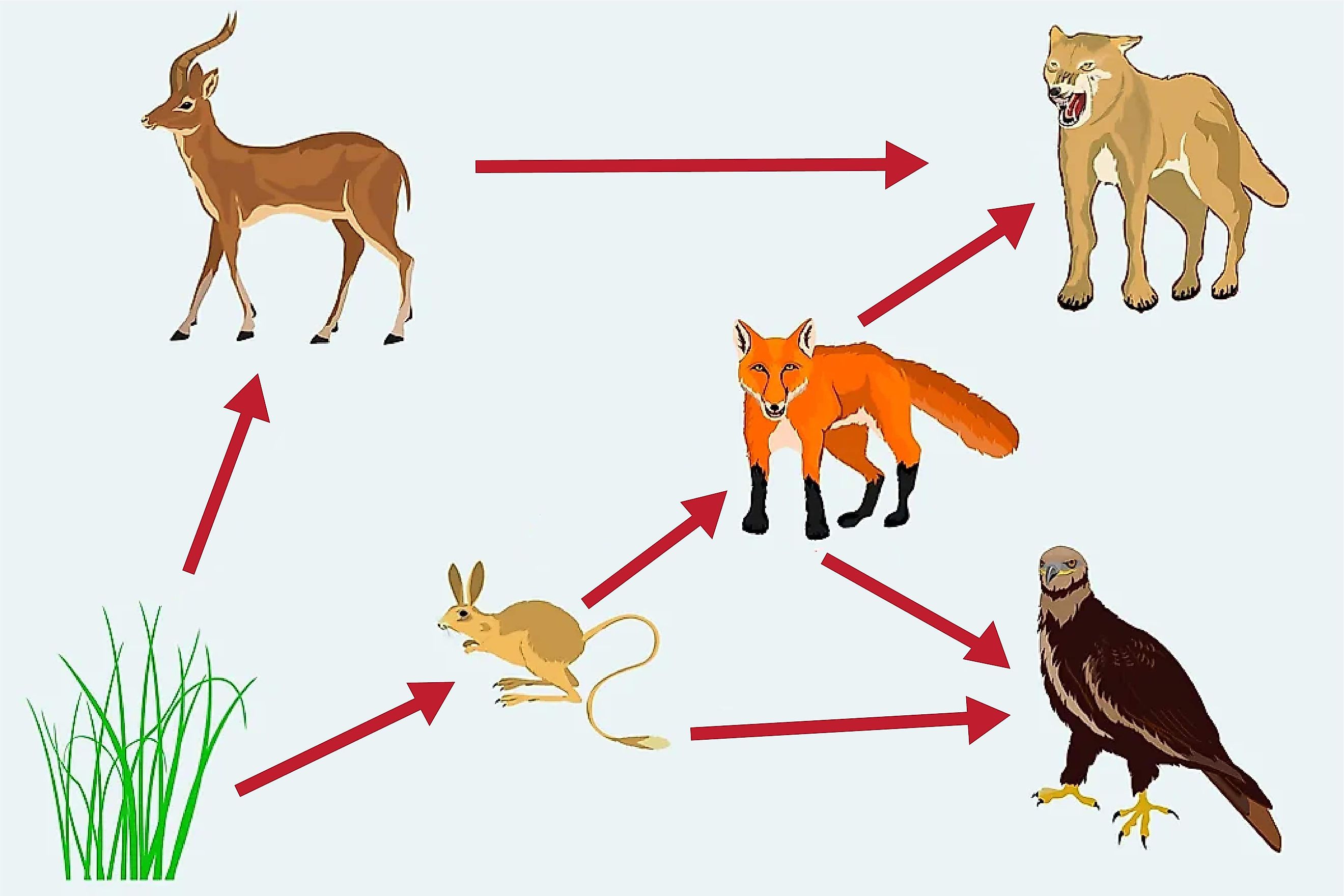
Answers Vary
An ant species defends a plant, and in exchange the plant provides food for them. This is a:
mutualism
Which has more biodiversity - a field (A) with 1000 of the same species, or (B) 50 each of 5 different species?
B
Name 3 biotic factors.
Which group of species converts all of the energy from the Sun to be useful for the ecosystem?
Producers
What is one indirect relationship in this food web?

Answers Vary.
What is a commensalism?
A relationship where one species benefits and the other is not changed.
This is a measurement of how many species are in an area.
What is biodiversity?
Name 3 abiotic factors.
answers vary
How much energy is lost at each step of the energy pyramid?
90%
What does a primary consumer eat?
Producers
Which relationship is the only one where both species are negatively impacted by it?
Competition
True or false: a healthy ecosystem would have a high amount of biodiversity.
True
How much energy moves on to each step of the energy pyramid?
10%
Which group on the energy pyramid has the most biomass?
Producers
Explain how a predator (that eats meat only) can change the population of producers.
A vine grows on a bush, preventing the bush from getting sunlight. The vine gets all the sunlight. This is a:
parasitism
Ecosystems that provide valuable ecosystem services generally have a (low, high) amount of biodiversity
High
Explain how abiotic factors can limit a species' population.
Without access to water, soil, land, etc. the species would be unable to sustain a population
Explain the difference between how matter and energy go through an ecosystem.
Matter is recycled (water cycle, carbon cycle, etc. ) and energy flows ( through the pyramid).
What is an apex predator?
Define the difference between a mutualism and a commensalism.
both species benefit in a mutualism, one benefits / one is neutral in a commensalism
Biodiversity is important to this ecosystem that helps protect Hoboken from floods and provide us clean drinking water.
What is the wetlands ecosystem?
Explain how species can change the abiotic factors of an ecosystem.