What is a Monosaccharide? What are some examples of Monosaccharides
- A monosaccharide is the monomer of a carbohydrate.
- Is the simplest form of a carbohydrate
- Examples are: Glucose, Fructose, Ribose, Galactose, Deoxyribose, Glyceraldehyde
- Lipids are non-polar compounds that are made mostly of Carbons, Hydrogens and less amounts of Oxygens.
- They are fats
- A Polypeptide consist of more than 50 amino acids.
What is the purpose of the element Phosphate in the function of ATP?
- In ATP, it stores potential energy in phosphate bonds which releases energy when converted to ADP.
What are monomers?
- Monomers are the individual subunits
A Ribose is an example of?
- A Monosaccharide
A Ester Linkage
What bond/link is shown below?
https://www.azom.com/images/Article_Images/ImageForArticle_11177(2).jpg
A peptide bond
Differentiate between DNA and RNA. What do they form?
- DNA is double stranded and anti-parallel- oriented in opposite directions.
-RNA is short and single stranded
- DNA and RNA consist of chains of nucleotides- Polynucleotide chains
What is a Dehydration Synthesis?
A Dehydration Synthesis is the creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers and water is released.
What link is shown below?
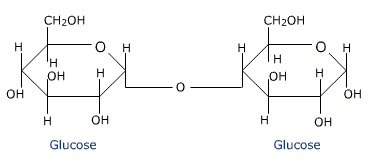
A Glyosidic Linkage
What does a glycerol molecule consist of?
- 3 carbon molecules
-Each carbon has a hydroxyl group attached to it (-OH)
Label both structures of a and b and where exactly they are found.
a) α helix
(b) β pleated sheet,
They are found in the secondary structure of a protein with the coiling and folding of the short section of a polypeptide.
What is a Nucleotide and what does it consist of?
- Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids.
- They consist of a 5 -Carbon sugar, A nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group
What is a Fatty acid composed of?
- A fatty acid consists of unbranched chain of carbons and a carboxyl (-COOH) group at one end.
What are the major functions of Polysaccharides?
- Energy Storage
- Structural Support
- Cell to Cell Communication
Distinguish between Saturated and Unsaturated fats. Which is more healthy?
- Saturated Fats are solids at room temperature. No double bonds occur between carbons. (Butter, Lard)
- Unsaturated Fats are liquids at room temperature. They form many double bonds between carbons. ( Olive oil, plants fat)
- Unsaturated fat is more healthy
What is the structure of a Tertiary protein? What other major key ideas are occurring as well?
- The overall 3-D Shape of the protein is due to the interactions between the R groups (side chains).
- It has hydrophobic interactions- Cytoplasm is water based so non polar amino acid cluster away from water.
- H bonds, Ionic bonds, and Disulfide bonds
- Purine bases are two-ringed organic structures and they include Guanine and Adenine.
- Pyrimidine bases are single organic structures and they include Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil. Thymine is only in DNA and Uracil is only in RNA.
A(Adenine) pairs with T(Thymine) and G (Guanine pairs with C(Cytosine). -A-T-G-C
What are the names and functions of the two Nucleic Acid Polymers?
2. RNA- Translates DNA into functional proteins and stores genetic information for some viruses.( tRNA, mRNA, rRNA)
_____________________________ is designated when the OH group bonded to the 1-Carbon is down.

x-glycosidic linkage
What are the 4 major functions in Lipids? Briefly explain each function and provide an example
1. Triglycerides- Are stored by cells as a long term energy source. Insulation and cushioning of internal organs. ( Fatty acid and Glycerol)
2. Phospholipids- Form of cell membrane. Consist of a polar and non polar head. (Lipid bilayer)
3. Steroids- Hormonal signaling of cell response to the environment and growth. (Testosterone)
4. Waxes- Used as a flexible waterproofing coating on various plants and animals to conserve water and acts a barrier. (Wax coating on fruits, leaves, and stems).
What does an amino acid consist of? What do the functional groups embedded in them provide?
-An Amino acid consist of : A central carbon group attached group attached to : An amino group (-NH2), A Carboxyl group (-COOH), Hydrogen group, and A R group (side group).
- The differences in the side group gives the amino acids their individual properties such as: Polar or non-polar, positive or negative, acts as acids or bases.
What is a Phosphodiester linkage?
- A Phosphodiester linkage is a Phosphate group on the 5-'Carbon of one sugar to the 3'- carbon of another sugar.
- This forms the backbone
What are Hydrogen bonds and what are some macromolecules that involve in hydrogen bonding?
- Hydrogen bonds form between the negative (oxygen) region of one water molecule and the positive (hydrogen) region of another nearby water molecule.
- Proteins have Hydrogen bonds in the secondary and tertiary structure. In the secondary structure, Hydrogen bonds are between adjacent amino acid backbones (N,O).
-In Nucleic Acids, Guanine forms 3 Hydrogen bonds with Cytosine and Adenine forms 2 Hydrogen bonds with Thymine