CRL diagnostic of pregnancy failure with absent cardiac activity.
What is 7mm?
Name of this sign seen in woman with +Hcg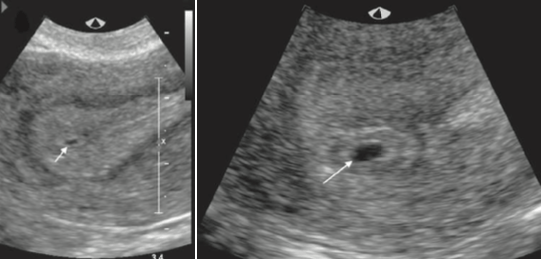
What is intradecidual sign?
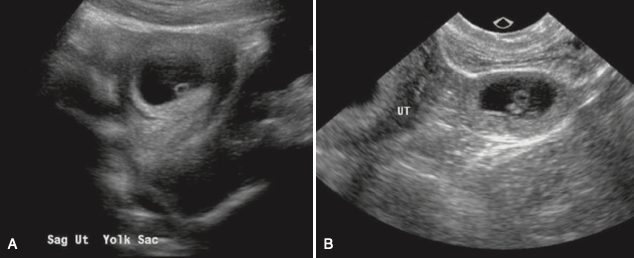
Small cystic-fluid collection with rounded edges and no visible contents, located in the central echogenic portion of the uterus.
Represents gestational sac, can first be seen at 4.5-5 weeks.
Any round or oval fluid collection in a woman with a positive pregnancy test most likely represents an intrauterine gestational sac and should be reported as such; it is much less likely to be a pseudogestational sac or decidual cyst, findings that can be present in a woman with an ectopic pregnancy.
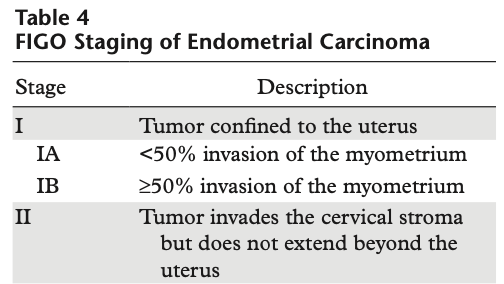
The organization that developed the most widely used staging system for endometrial carcinoma?
What is the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO)?
Cancer staging is fundamentally important in treating patients with cancer and must be reliable, reproducible, and practical.
Unified criteria allows treatment planning, assessment of tumor response, prognosis prediction, information to be exchanged between different treatment centers.
Hamartomatous proliferation of small airways that communicates with the bronchial tree.
What is Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation?
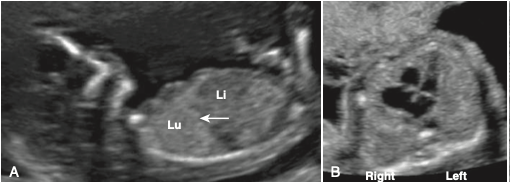
(Above) Normal fetal chest, Lungs homogenous hyper echoic compared to liver. Dome shaped diaphragm, (B) Axial Lungs around heart (4 chamber cystic appearing structure).
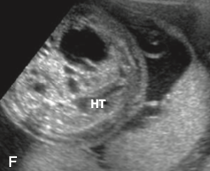
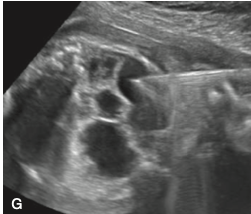
Diagnosis.
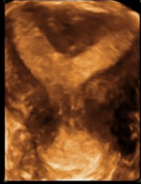
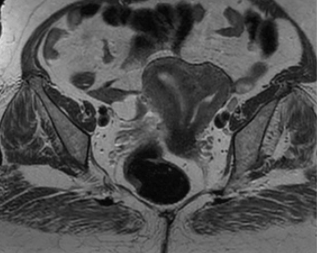
What Is septate uterus?
two uterine cavities, divided by a fibrous or muscular septum.
Septate uterus is the most likely of all uterine anomalies to be implicated in pregnancy loss since the fibrous septal tissue or myometrium is relatively avascular.
MSD size that is diagnostic of pregnancy failure when there is absence of an embryo?
What is > or = 25mm?
 Recommendation for this woman who is 6 weeks by LMP.
Recommendation for this woman who is 6 weeks by LMP.
What is Follow up in 7 -14 days?
Calcified yolk Sac
Not diagnostic of pregnancy failure but poor predictor and should have short term interval follow up.
Finding that is the strongest predictor for disease recurrence in endometrial carcinoma.
What is lymph node metastasis?
Para-aortic has worse prognosis
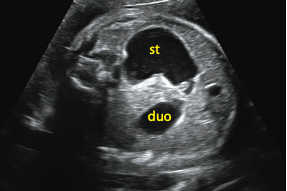
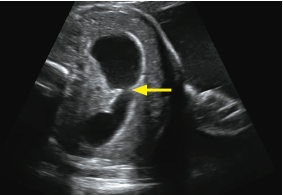
Diagnosis and most common association?
Duodenal atresia, most commonly associated with downs.
Name of the sign seen below.
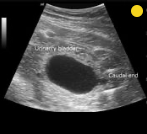
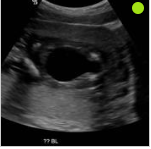
What is the keyhole sign?
Seen in posterior urethral valves.

Normal junctional zone in uterus should measure < this number. Larger is concerning for adenomyosis.
What is <12mm?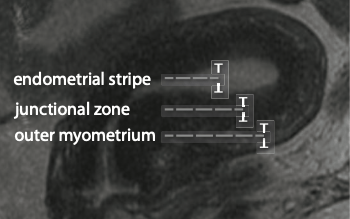
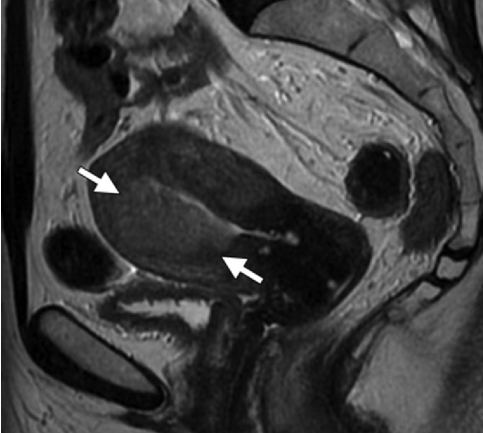
 Diagnosis in this 30 year old female who underwent IVF.
Diagnosis in this 30 year old female who underwent IVF.
What is heterotropic gestation?
Stage of this endometrial carcinoma with no other abdominal or pelvic findings.
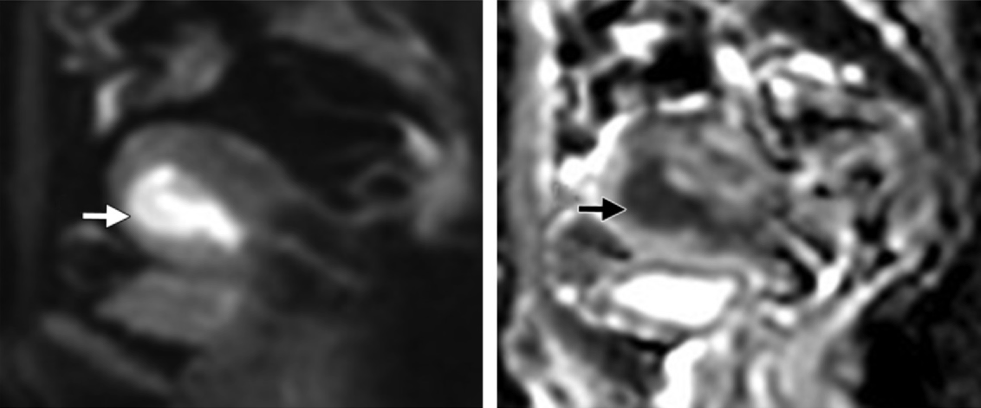
What is stage IB?
T2 image shows intermediate to high intensity lesion endometrial tumor. DWI/ADC shows restricted diffusion extending to >50% of the myometrium.

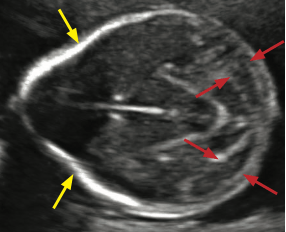
Name of this sign which is specific for Chiari II malformations?
The banana sign (red arrows).
Banana sign describes the characteristic flattened cerebellar hemispheres in
the small posterior fossa.Very specific for Chiari II. If the banana sign is seen, then a myelomeningocele is presumed to be present even if not identified on ultrasound.
Yellow arrows point to lemon sign- scalloping of the frontal bones (not specific).
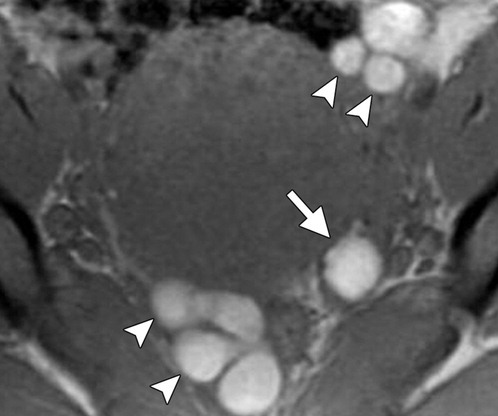
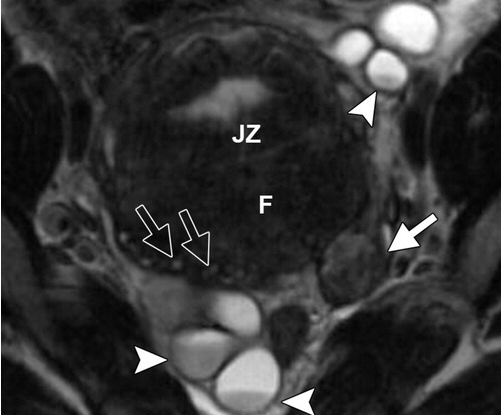 Diagnosis.
Diagnosis.
What is endometriosis?
T1 Hyper
T2 Decreased hyper (shading)
No loss of signal on fat suppression, (teratomas do)
HR which indicates a poor prognosis after GA of 6 weeks.
What is <90?
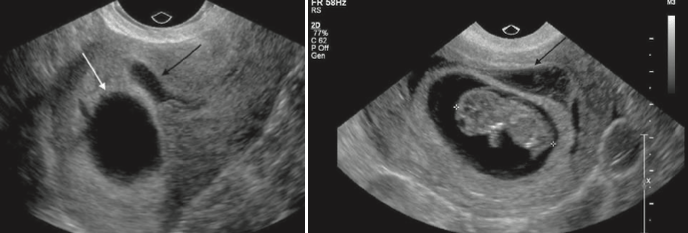
Diagnosis (2 different patients Embryo not in the field of view in A).
What is Subchorionic hemorrhage?
Results from elevation of the placental margin or marginal sinus rupture
May be associated with vaginal bleeding.
Hematoma <50% the size of gestational sac have no difference in pregnancy outcome than patients without. >50% shown to have increased rates of pregnancy loss.
According to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics endometrial carcinoma is stage IVA when it spreads to either of which two sites.
What are the bladder or bowel mucosa?
Para-aortic is worse prognosis (don't need to have pelvic LAD for poor prognosis of para-aortic)


Diagnosis and common association.
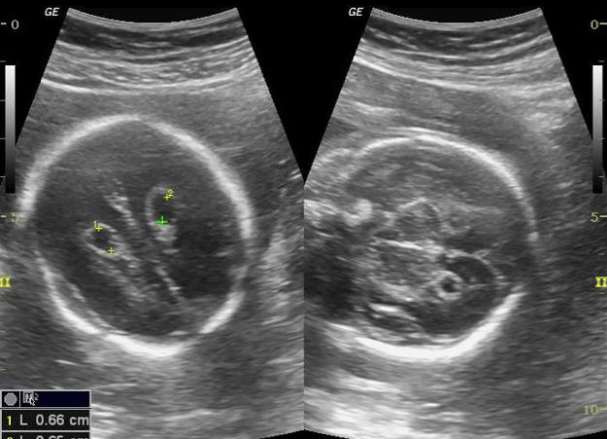
What is Choroid plexus cysts, associated with Trisomy 18?
Cysts within the choroid plexus are common (seen in 1–5% of fetal surveys). The vast majority of choroid plexus cysts are present in normal fetuses and resolve on follow- up scans.
Up to 50% of trisomy 18 fetuses will have choroid plexus cysts.
Choroid plexus cysts can be considered an incidental finding in the absence of any other sonographic abnormality and with a normal maternal serum screen.
Butterfly sign (normal)
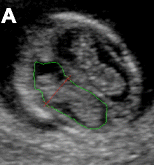
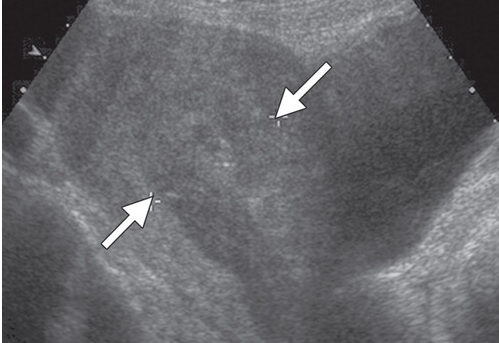
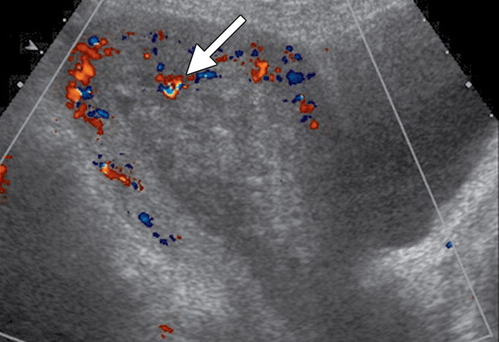
Diagnosis in this 39 yo F with continued PPH.
What is RPOC?
Heterogenous endometrial mass.
+flow
(+flow can help differentiate RPOC from clot but beware of pitfalls such as polyps, /submucosal fibroids which may give appearance of + flow.
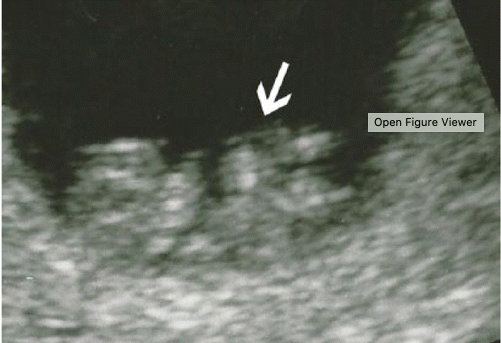 GA at which this can be diagnosed as abnormal.
GA at which this can be diagnosed as abnormal.
What is 13 weeks?
The midgut normally herniates through the ventral abdominal wall in the first trimester. During this herniation, the midgut rotates 270 degrees around the axis of the SMA.
Physiologic midgut herniation is usually complete by 12–13 weeks. Therefore, a pathologic ventral wall defect, such as omphalocele or gastroschisis, is not diagnosed before 13 weeks.
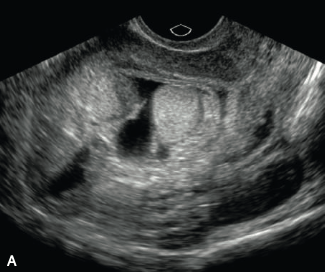
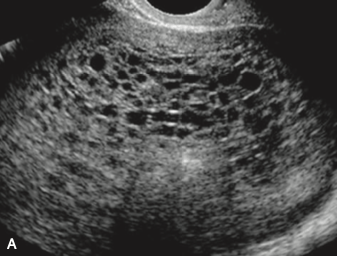 Diagnosis and name of the cystic structures in the US of the uterus in a 27 y/o F with no previous imaging or obstetric care and b-Hcg of 841000.
Diagnosis and name of the cystic structures in the US of the uterus in a 27 y/o F with no previous imaging or obstetric care and b-Hcg of 841000.
What is Molar pregnancy?
What are hydronic vili?
The classic sonographic features of complete molar pregnancy include an ENLARGED UTERUS with a central heterogeneous echogenic mass that expands the endometrial canal. The mass contains multiple cystic spaces of varying size, representing the hydropic villi.
In the first trimester, molar pregnancies have a variable appearance on ultrasound, sometimes appearing as a solid, echogenic mass9 8 week US below)
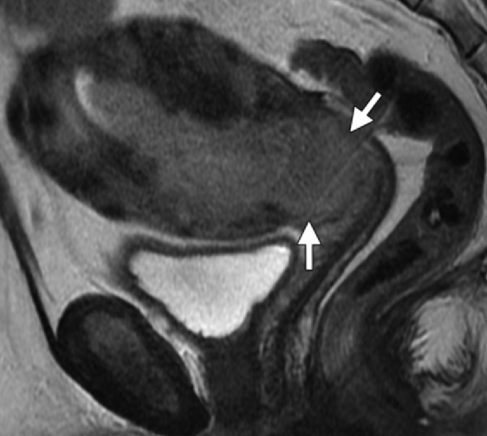
Stage of this endometrial carcinoma with no other imaging findings.
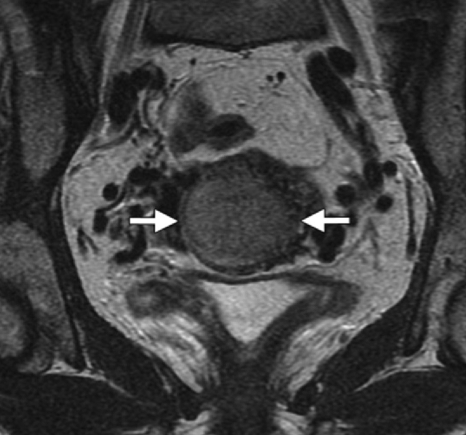
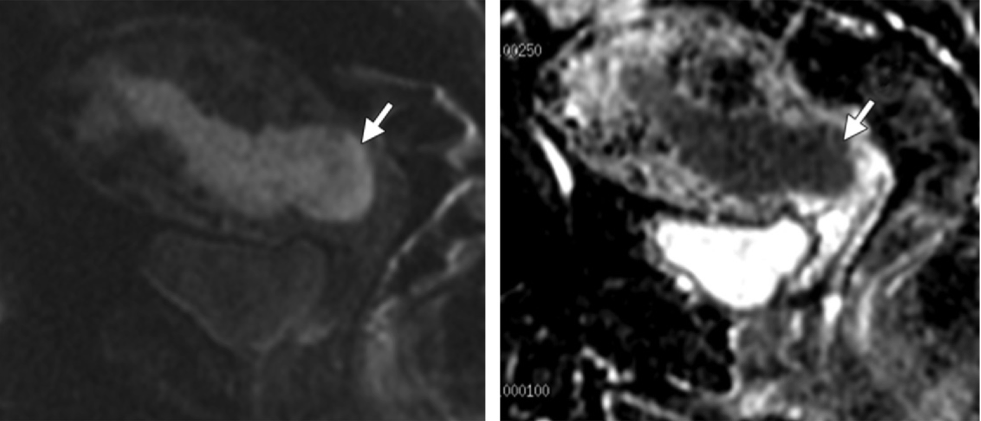
What is stage II?
T2-weighted MR image shows an intermediate- to high-signal-intensity endometrial tumor (arrows) invading the normal, low-signal-intensity cervical stroma.
Axial oblique T2-weighted MR image, obtained perpendicular to the endocervical canal, shows the tumor (arrows) invading the cervical stroma but not the parametrium.
Sagittal diffusion-weighted image and ADC map show restricted diffusion within the endometrial tumor (arrow), with invasion of the cervical stroma and the outer one-half of the myometrium but not the serosa.
Rare disorder consisting of:
Ectopia cordis (extra-thoracic heart)
Omphalocele
Diaphragmatic defect
Pericardial defect or disruption of the sternum
Cardiac Defects (eg VSD, ASD, ToF)
What is Pentalogy of Cantrell?
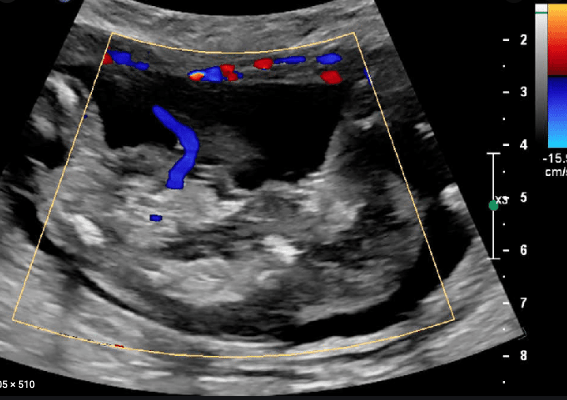
Diagnosis. Multiple gestations (2) US of the umbilical artery of one fetus.
What is Acardiac twin?
Umbilical artery flowing toward fetus (usually away)
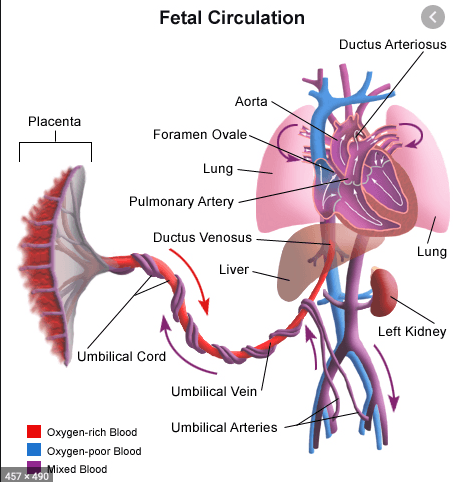
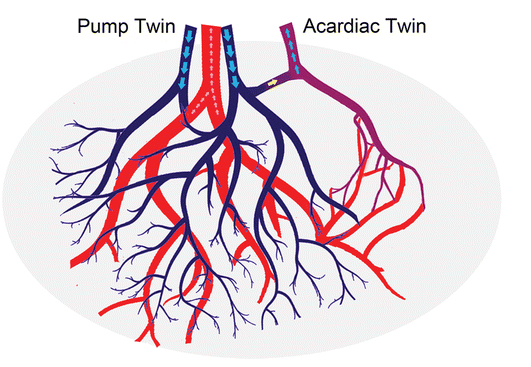
Acardiac twinning, also called twin reversed arterial perfusion (TRAP) sequence, is a severe variant of twin–twin perfusion syndrome. Similar to TTTS, acardiac twinning is a complication of monochorionic twins (either mono- or di-amniotic).
Donor fetus supplies circulation to itself and an acardiac twin, enabled by placental fistulous connections.
Doppler of the umbilical arteries and vein shows reversed flow in the acardiac twin.
Normally, the umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood out of the fetus, pumped by the fetal heart. In the acardiac twin, the umbilical arteries carry nutrient-depleted, poorly oxygenated blood into the fetus, pumped by the donor twin’s heart. Doppler of the acardiac twin’s umbilical arteries show an arterial waveform going into the fetus.
Normally, the umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood into the fetus, from the placenta. In the acardiac twin, the umbilical vein carries deoxygenated blood out of the fetus. Doppler of the acardiac twin’s umbilical vein shows a venous waveform going out of the fetus.
Treatment is coagulation of the acardiac twin’s umbilical cord.