This muscle is responsible for opening the jaw during mastication.
A defective development of the 3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouches leads to this syndrome.
What is Digeorge Syndrome?
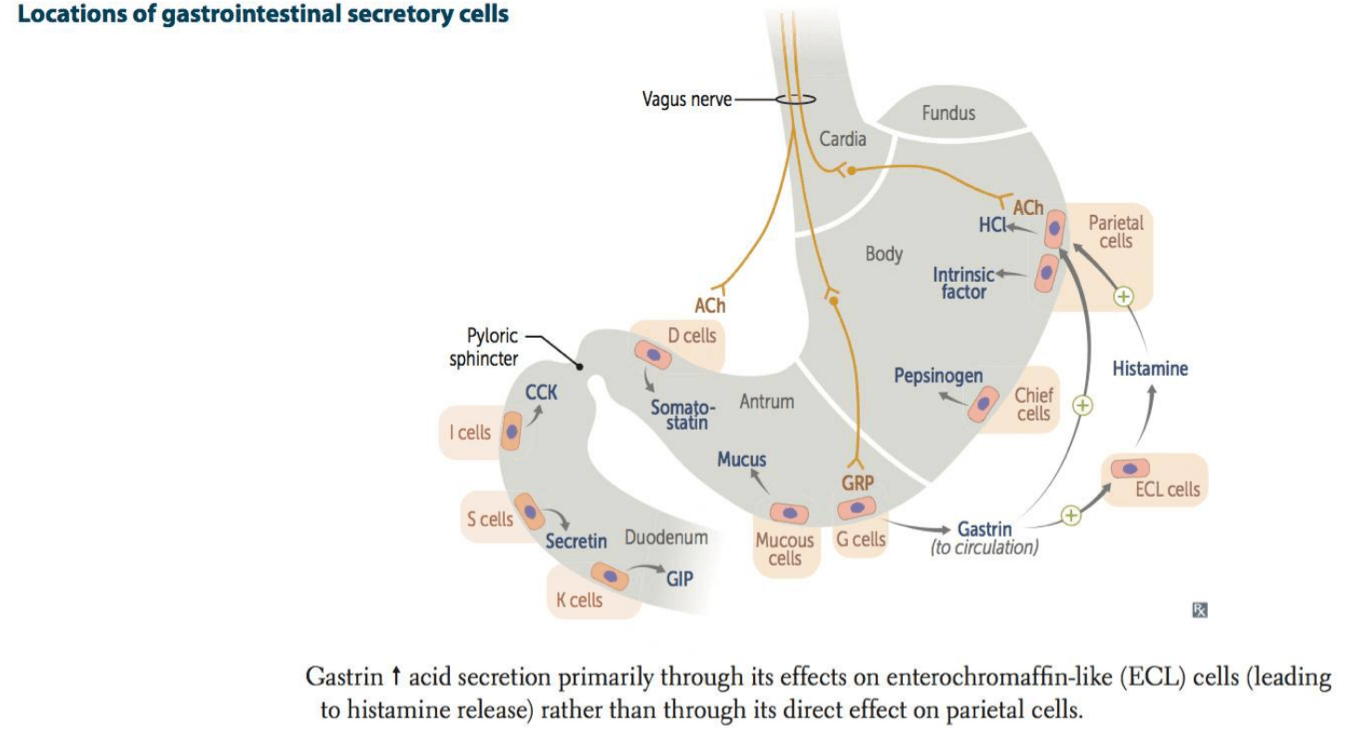
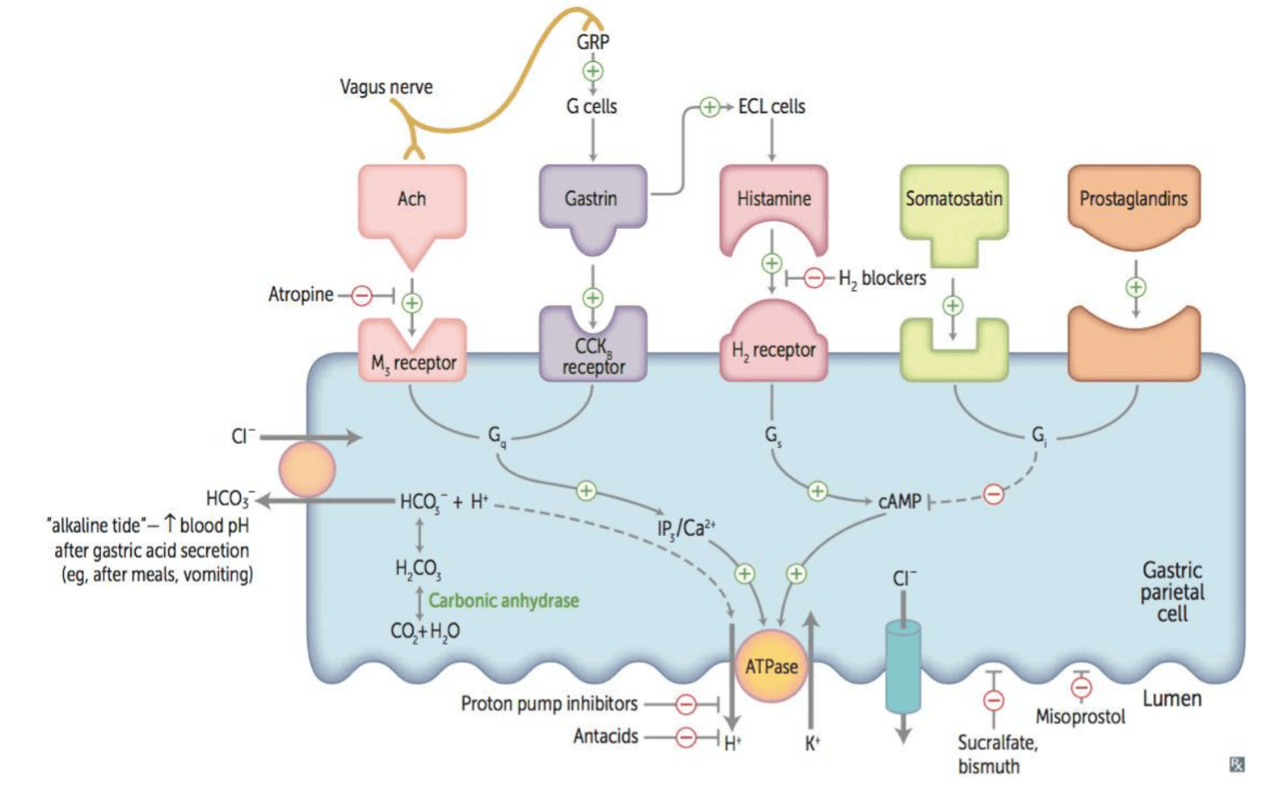
Histamine and gastrin both work to increase H+ secretion from this GI cell.
What are parietal cells?
This condition involved dilated submucosal veins in the lower esophagus.
What is esophageal varices?

What is gastroschisis?
CN VII (chords tympani branch) provides parasympathetic innervation to these 2 glands for salivation.
What are the submandibular and sublingual glands?
This is the most common cite of ectopic thyroid tissue.
What is the tongue?
This plexus in the gut primarily controls motility.
What is the myenteric nerve plexus (Auerbach)?
Teenagers boys are at risk of sterility from this virus that infects parotid glands.
What is the mumps?
these type of cells are known to be in diffuse gastric carcinoma?
what are signet ring cells?
In western countries, this is the most common cause of portal hypertension.
What is cirrhosis?
This is an anterior, midline neck mass that moves with swallowing or protrusion of the tongue.
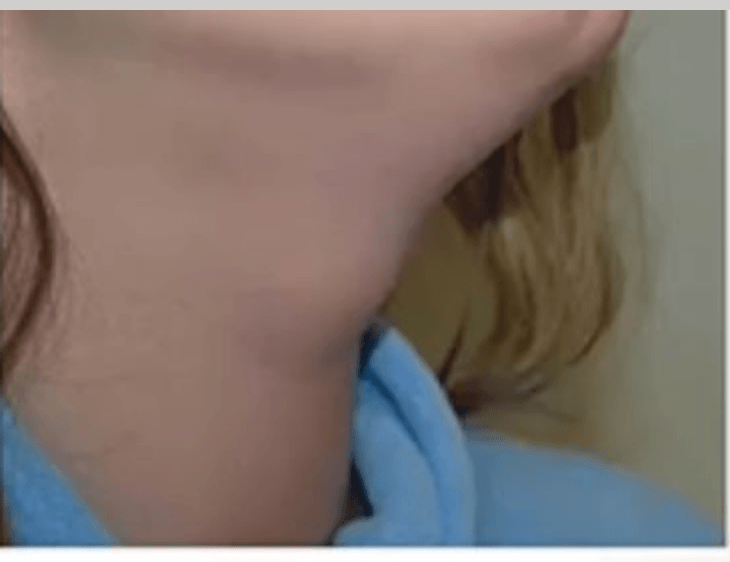

What is a thryoglossus duct cyst?
What is the CCKB receptor?
Behcet syndrome is assoiciated with these ulcers.
What are apthous ulcers?
peptic ulcer disease in the duodenum shows hypertrophy of this.
What are Brunner glands?
Cutting this nerve will cause the tongue to deviate towards the lesion.
What is the hyoglossal nerve (CN XII)?
If the 2nd-4th pharyngeal clefts are not obliterated, this will happen.
What is a persistent cervical sinus?

Gastrin secretion is inhibited by this regular substance (secreted by D cells).
What is somatostatin?

What is achalasia?
"olive-like" mass in the abdomen
what is pyloric stenosis?
These 2 arteries branch off of the common hepatic artery.
What are the proper hepatic artery and the gastroduodenal artery?

A failure of the stylopharengeus to develop could be blamed on the malfunctioning of this arch.
What is the 3rd arch?

Babies use this molecule instead of pepsin for a lil right after they are born.
What is rennin?
Achalasia is associated with a lack of these 2 molecules.
What is VIP and NO?
Autoimmune chronic gastritis is this type of hypersensitivity reaction.
What is type IV?