Define flow
The movement of matter or energy from one storage to another, or into/out of the system.
Define ecosystem

a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system.
Define climate

The weather conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, and winds, in an area over a long period of time.
Define lithosphere

the outer part of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle, approximately 100 km (62 miles) thick.
Define salinity

total quantity of dissolved salt
Define energy

The ability to do work or give off heat.
define renewable energy

energy from sources that are constantly being formed.
Outline the inputs and outputs of a forest
Inputs: dust, wind, rain, CO2, sunlight etc.
Outputs: oxygen, erosion, harvesting, fire etc.
Outline components of ecosystem

The Abiotic, biotic factors and a geographical area. (Accept: Living and nonliving)
Outline where Taigas are located.

The northern coniferous forest stretches across the Northern Hemisphere just below the Arctic Circle.
list the types of collisions between boundaries

convergent, divergent and transform
Outline the water cycle

water evaporates into water vapor, then condenses to form water droplets and drops water as rain or precipitates.
Outline the main problems of depending on fossil fuels.

1. The supply of fossil fuels is limited.
2. It has environmental consequences.
3. There are several environmental alternatives.
Outline the process of generating wind energy

1. Wind spins turbine
2. Generator converts energy to electricity
3. The electricity flows down the shaft.
Describe this picture in scientific terms.

Accept any answer that includes 4 of the following:
Boundaries, flow, transfer, input, output, storage, organisms, and open system.
Describe Abiotic and Biotic factors

Biotic factors are the living and once living parts of an ecosystem, including all of the plants and animals. Biotic factors include dead organisms, dead parts of organisms and the organisms’ waste products.
The Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of the ecosystem. Abiotic factors include air, water, rocks, sand, light, and temperature.
Describe how plants determine the name of a biome.

Plants in a particular biome have characteristics, specialized structures, or adaptations that allow the plants to survive in that biome.
Describe when does a transform boundary occur

This occurs when the boundary between tectonic plates are sliding past each other horizontally; often called transform faults.
Describe the process of condensation

Water vapor forms water droplets on dust particles.
Describe the different uses of fuel.

Fuel is used for transportation, for manufacturing, for heating and cooling buildings, and for generating electricity to run machines and appliances.
Describe passive solar heating

Using the sunlight's energy to heat something directly without storing the energy.
State the term for a process in which the outputs are circled back and used as inputs.
Feedback Loop
State the term for: any heritable trait that helps an organism

Adaptation
State the word for tropical and subtropical areas near the equator and between tropical rain forest and desert biomes.

Savannas
State the term for a plate boundary where two plates move toward each other

convergent boundary
State a term for:
This bottom layer extends from the base of the thermocline to the bottom of the ocean. The temperature in this zone averages 2°C.

The ocean deep zone
State all forms energy can take

Energy can take the form of chemical, heat, light, electric and kinetic.
state the technology use to:
convert the sun’s energy into electricity

Photovoltaic cells
Analyze the components that make a closed ziplock a closed system.

Matter cannot enter or exit the zip lock bag.
Energy in the form of sunlight can enter and exit the bag.
Analyze the relationship between abiotic and biotic factors.

Biotic and abiotic factors make up an ecosystem. To survive, biotic factors need abiotic factors such as water, air and soil.
Analyze how temperature affects which plants grow in an area.

Temperature and precipitation determine which plants grow in an area because if it rains a lot and is not very cold, big trees and a lot of plants will grow, but if it is no rain and hot, then the plants will be cacti.
Analyze two pieces of evidence for plate tectonics

Evidence from fossils, glaciers, and complementary coastlines helps reveal how the plates once fit together.
Fossils- there evidence of some animals having their fossils in a different continent which proves that all continents were once connected.
coastlines: they connect to each other like puzzle pieces
Analyze the affect of wind on oceans.

Surface currents are wind driven and result from global wind patterns.
Analyze what is the relationship between natural gas and petroleum?

Fossil fuels were formed millions of years ago from the remains of plants and animals. The fossil fuels are petroleum, natural gas, and coal. All types of fossil fuels aren't renewable and natural gas is the cleanest-burning fossil fuel.
Analyze the benefits of a hydroelectric dam

1. They don't release air pollutants.
2. They last longer than fossil fuel power plants
3. About 25% of the world's electricity is generated from dams.
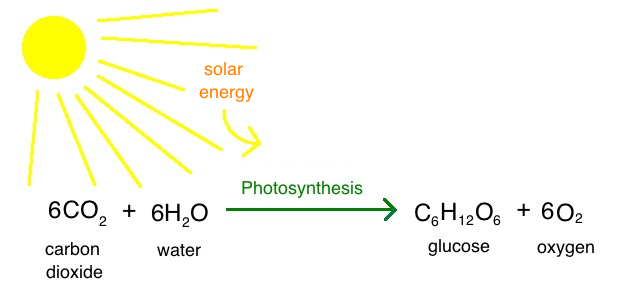
Apply Neuton's law of conservation of energy/mass to a process in nature.

Ex. Photosynthesis
Apply natural selection to an animal

Camel
Can stay up-to 3 days on its water storage.
Apply the concept of adaptations to two desert animals and the adaptations that help them survive.

Cacti and camels can thrive with little water throughout the seasons.
Apply Alfred Wenger's theory to the shape of the continents

Based on his theory, the continents were once connected hence, South America and Africa can be connected like pieces of puzzles.
Apply the concept of temperature zones to an ocean

The surface of the ocean is warmed by the sun. In contrast, the depths of the ocean, where sunlight never reaches, are very cold and have a temperature only slightly above freezing.
Prize: Triple the score!!!!!(3000)
Give an example of direct use of fossil fuels

Ex.
An oil fired furnace.
Making steel
fertilizers and pesticides
Apply geothermal energy to a house's heating system

During the winter, the ground is much warmer than the air. Heat in the ground can be transferred to warm the house.
Distinguish between a steady state equilibrium and a stable equilibrium.

Steady state equilibrium is an open system with inputs and outputs of energy/matter but it remains the same.
Stable equilibrium tends to return to the same equilibrium after disturbance.
Distinguish between food chain and food web

Food chain has energy flowing in 1 direction from prey to predator. Food web has multiple interactions.
Distinguish two ways in which the forest biomes of the world are being threatened.

intensity and timing of fire events, hurricanes, droughts, ice storms and insect outbreaks are shifting as a result of human activities and global climate change, making forest ecosystems even more prone to damage
Distinguish rifts and trenches

A rift valley is a depression that develops at a divergent plate boundary. A trench is a long, narrow, steep-sided depression of the seafloor formed where a sub-ducting oceanic plate sinks into the mantle causing the seafloor to bend downward.
Distinguish between ocean water and fresh water

Ocean water contains more salts.
Distinguish nuclear fission with nuclear fusion.

Nuclear fission is the process in which the nuclei splits and releases energy. On the contrary, nuclear fusion occurs when two nuclei combine and this only occurs in the sun.
Distinguish cogeneration from conservation

Energy conservation means saving energy. Cogeneration is the production of two useful forms of energy from the same fuel source.
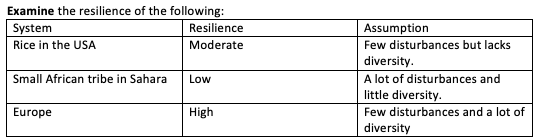
Explain why diversity causes resilience.

The higher the diversity, the more resilient a system becomes because there are multiple solutions and alternatives to a disturbance.
Ex. Amazon Rainforest
Explain how insects can developed resistance against pesticides

The insects that aren't affected by the pesticides are those who survive. Then, they would give birth and their offsprings would also be resistant to pesticides.
Explain how tropical grasslands differ from temperate grasslands.

Tropical grasslands have dry and wet seasons that remain warm all the time. Temperate grasslands have cold winters and warm summers with some rain
Explain the process of carbon dating.

Carbon has several isotopes that are responsible for the process of decay on all organisms. By measuring radioactivity of the isotope, the age of a bone or rock can be determined
Explain what is the recharge zone.

Water cannot reach an aquifer from places where the aquifer is covered by impermeable materials. The area of the Earth’s surface where water percolates down into the aquifer is called the recharge zone.
Explain how petroleum fuels pollute the environment

When petroleum fuels are burned, they release pollutants. Internal combustion engines in vehicles that burn gasoline pollute the air in many cities. These pollutants contribute to the formation of smog and cause health problems.
Explain the concept of tidal power

Tidal power plant works much like a hydroelectric dam. As the tide rises, water flows behind a dam; when the sea level falls, the water is trapped behind the dam. When the water in the reservoir is released, it turns a turbine that generates electricity.
Compare and contrast resilience and tipping points.

Both of them are related to a disturbance or a change in a system. However, resilience the measure of how it responds to disturbances and tipping point is the point at which a system experiences a new shift with significant changes.
Compare and contrast decomposers and detritivores.

Both receive their nutrition from dead matter. Decomposers break down complex organic matter into simpler. Detritivores consume the decomposing organic matter.
Compare and contrast the plants that live in deserts with the plants that live in the tundra biome.

Both of them survive in areas of little liquid water supply. Plants in a tundra must adapt to the cold winters while plants in the summer must adapt to the hot summers.
Compare and contrast oceanic and continental crust.

Both oceanic and continental are part of the lithosphere. The oceanic crust rocks are younger than the continental crust rocks. Oceanic crust is composed of basalt and the continental crust is made up mostly of granite.
Compare and contrast aquifers with oasis.

Aquifers is an underground layer of water permeable rock. Oasis a small lake storing water that leaks from underground or rivers. They both store fresh potable water.
Infer what might have caused the increased demand for oil in the 1950.

Post world war 2, the demand increased as most countries around the world began industrializing. Adding to this, the increase in automobiles and human population further increased the demand.
Compare and contrast wind energy and solar energy

Both wind and solar energy are considered forms of renewable energy. However, Wind is a more efficient power source than solar. Compared to solar panels, wind turbines release less CO2 to the atmosphere, consume less energy, and produce more energy overall.
Discuss why a human body adapting to a temperature change is a negative feedback loop.

The equilibrium returns to its original state with minimal change. (A human body maintains its temperature by sweating when its too hot and it shivers when its too cold.
Discuss mutualism

A relationship in which both animals benefit. An example would be a shark and smaller fish that clean the shark's teeth.
Discuss why are tall trees found in taiga biomes but not in tundra biomes.

The taiga has a thick forest of conifers such as pine and spruce, while in the tundra trees are absent completely. This is due in part to the lack of water available in the tundra, but also is a result of permafrost. Trees have great difficulty growing stable roots in frozen ground.
Discuss the theory of plate tectonics movement

the plates of Earth are in motion every moment. The forces that control this motion of the plates create the surfaces on our planet such as mountains, ocean basins and volcanoes.
Discuss the process of water treatment

1. Collection of water
2. screening
3. Chemical added
4. Coagulation (liquid to viscous)
5. filteration
6. disinfecting
7. storage and distribution
Discuss the process of generating electricity through nuclear power plants.

The splitting of uranium atoms generates heat to produce steam, which is used by a turbine generator to generate electricity. Since nuclear power plants do not use combustion, they do not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
Discuss ways to conserve energy (5 at-least)

1. Use energy efficient light bulbs, washing machines and other appliances.
2. Use smart sensors to turn on and off light
3. Use the AC for fewer hours
4. Use cold water more frequently
5. Walk or cycle instead of using an automobile

Examine the differences in habitats

Every habitat has specific characteristics that the organisms that live there need to survive.
Ex. A coral reef contains sea water, coral, sunlight, and a wide variety of other
organisms. If any of these factors change, then the habitat changes.
Examine as moisture decreases, what happens to the amount of vegetation in an area?

The more humidity, the more the plants are going to thrive and prosper. However, if the weather is quite dry, there will be less vegetation.
Examine the results of plate tectonics moving.

Diverging: sea-floor spreading occurs when the plates move away from each other.
Subduction: old lithosphere is destroyed when the new lithosphere is created and a trench mark is left.
Transform: the friction caused by the plates sliding past each other may cause an earthquake.
examine the ocean's role as a temperature regulator.

The world ocean absorbs over half the solar radiation that reaches the planet’s surface. The ocean both absorbs and releases heat more slowly than land does. As a consequence, the temperature of the atmosphere changes much more slowly than it would if there were no ocean on Earth. If the ocean did not regulate atmospheric and surface temperatures, the temperature would be too extreme for life on Earth to exist.
Examine the history of fuel until the present day. (Hint: wood)

The first records of combustion was the burning of wood which was used to scare animals and keep humans warm. Then, coal was discovered during the industrial revolution and it was used to power machines and transportation. Next, oil and gas were discovered to power automobiles and generate electricity. The most recent type of fuel is hydrogen but it is yet to be implemented in society.
Examine the future uses of hydrogen

Hydrogen is an energy carrier that can be used in internal combustion engines or fuel cells producing virtually no greenhouse gas emissions when combusted with oxygen.
(Cars and machinery)
Evaluate the Sahara Desert as a system.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Conclusion
Evaluate the importance of competitive relationship between animals

Strengths: survival of the fittest, only the best will survive hence animals will have to adapt. This implies that competition causes adaptations
Weakness: lack of animals and diversity will stress the ecosystem and might put it in danger of extinction.
conclusion:it is important as the strengths outweigh the weaknesses
Evaluate which would be better suited for agricultural development: the soil of a tropical rain forest or the soil of a temperate deciduous forest?

The temperate deciduous forest because the leaves and seeds fall to the ground during the change of seasons, leaving the soil extremely fertile.
Evaluate Alfred Wenger's theory

Strengths: continents; the distribution of ancient fossils, rocks, and mountain ranges; and the locations of ancient climatic zones.
Weakness: tidal force is not strong enough to move continents and if the tidal force existed the Earth wouldn't spin.
Conclusion: His theory was correct to some extent. However, it definitely lacked a reasonable force.
Evaluate the construction of a dam

Strength: Power production, irrigation, storing water and controlling floods.
weakness: High costs, damages wetlands (river natural filters), less fertile soil due to the blockage of sedimentation and prevents fish form migrating.
Conclusion: *Must be supported by pros and cons*
Evaluate the use of nuclear energy

Strengths: low cost energy, releases zero carbon emissions, reliable stable source of energy and promising future.
Weaknesses: accidents (hiroshima and chernobyl), produces radioactive waste, limited amount of uranium and could be used to make nuclear bombs.
Conclusion: *Claim must be supported*
Evaluate wind energy

Strengths
1. No green-gas emission
2. No boiling water to produce steam--> water conserving
3. Efficient and reliable source of energy
4. Has a huge potential, 35% of the world energy demands will be fulfilled by wind energy by 2050
Drawbacks:
1. Require vast empty land
2. Noisy mechanism
conclusion: *Must be supported by claims*