& Entering Room
demonstrate accountability for the delivery of standard-based nursing care that is consistent with moral, altruistic, legal, ethical, regulatory, and humanistic principles.
Professionalism
The Nurse of the Future will function effectively within nursing and interdisciplinary teams, fostering open communication, mutual respect, shared decision making, team learning, and development
Teamwork and Collaboration
What does SWIPE in stand for?
S – Self/ role introduction
W – Wash hands (state it out loud)
I – Identify pt. & assess LOC: Name, DOB, Allergies, Date, Location and Why you here? (Check band while completing this entire step) (Note: call registration for name spelling issue(s) or DOB issue(s))
P – Provide privacy (Close Curtains/Door)
E – Explain everything you will be doing and ask for permission to assess!
What are the steps in the nursing process?
ADPOIE
•Assessment
•Diagnosis (NURSING)
•Planning (Plan of Care)
•Objective/Goal (Needs to be measurable & attainable)
•Intervention
•Evaluation
The Nurse of the Future will influence the behavior of individuals or groups of individuals within their environment in a way that will facilitate the establishment and acquisition/achievement of shared goals.
Leadership
The Nurse of the Future will minimize risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance
Safety
What does BRNCOW out stand for?
COMPLETE & STATE ALL BEFORE LEAVING (EACH TIME):
B – Bed in lowest position
R – Rails up
N – Needs met/ neat room
C – Call light within reach
O – Open curtains
W – Wash hands
What does SABC stand for?
SABC's:
Safety
Airway
Breathing
Circulation
demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context of the health care system, and will demonstrate the ability to effectively call on microsystem resources to provide care that is of optimal quality and value.
Systems-Based Practice
The Nurse of the Future uses data to monitor the outcomes of care processes, and uses improvement methods to design and test changes to continuously improve the quality and safety of health care systems.
Quality Improvement
Doug Did Do The Right Patient At Even Every Situation
Doug Did Do The Right Patient At Even Every Situation:
Drug, Dose, Documentation, Time, Route, Patient (name/DOB), Allergies, Expiration, Effect, Situation. If IV, IM or liquid, how much to draw up/measure, how fast to push medication, what size syringe or measuring device, what size needle, what location (IM – where)?
What are the level's of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs starting at the base?
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs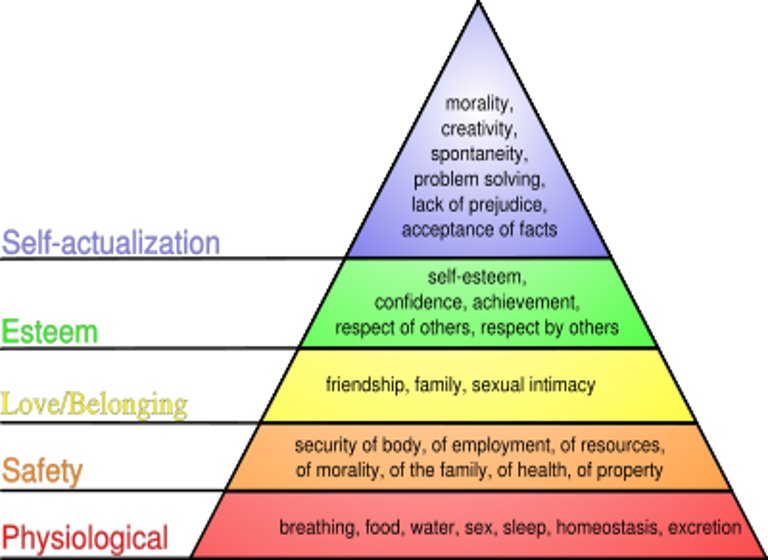
The Nurse of the Future will be able to use advanced technology and to analyze as well as synthesize information and collaborate in order to make critical decisions that optimize patient outcomes.
Informatics and Technology
The Nurse of the Future will identify, evaluate, and use the best current evidence coupled with clinical expertise and consideration of patients’ preferences, experience and values to make practice decisions
Evidence-Based Practice
What does PO stand for?
per oral / by mouth
- Study abbreviations - know the meaning of each!
Which comes first: acute vs. chronic AND expected vs. unexpected
•Acute before Chronic
•Unexpected before Expected
The Nurse of the Future will interact effectively with patients, families, and colleagues, fostering mutual respect and shared decision making, to enhance patient satisfaction and health outcomes.
Communication
The Nurse of the Future will provide holistic care that recognizes an individual’s preferences, values, and needs and respects the patient or designee as a full partner in providing compassionate, coordinated, age and culturally appropriate, safe and effective care.
Patient-Centered Care
The nurse can take Tylenol from the medication cart if s/he has a headache
No! False!
Which should the nurse implement first for the following two scenarios?
1. PO medication vs. IV medication
2. IM medication vs. distraction for confused patient
•Least Invasive or Restrictive to Most Invasive to Restrictive:
PO before IV
distraction before IM medication.