Pathophysiology
What is the most common symptom of HSP?
Palpable purpura
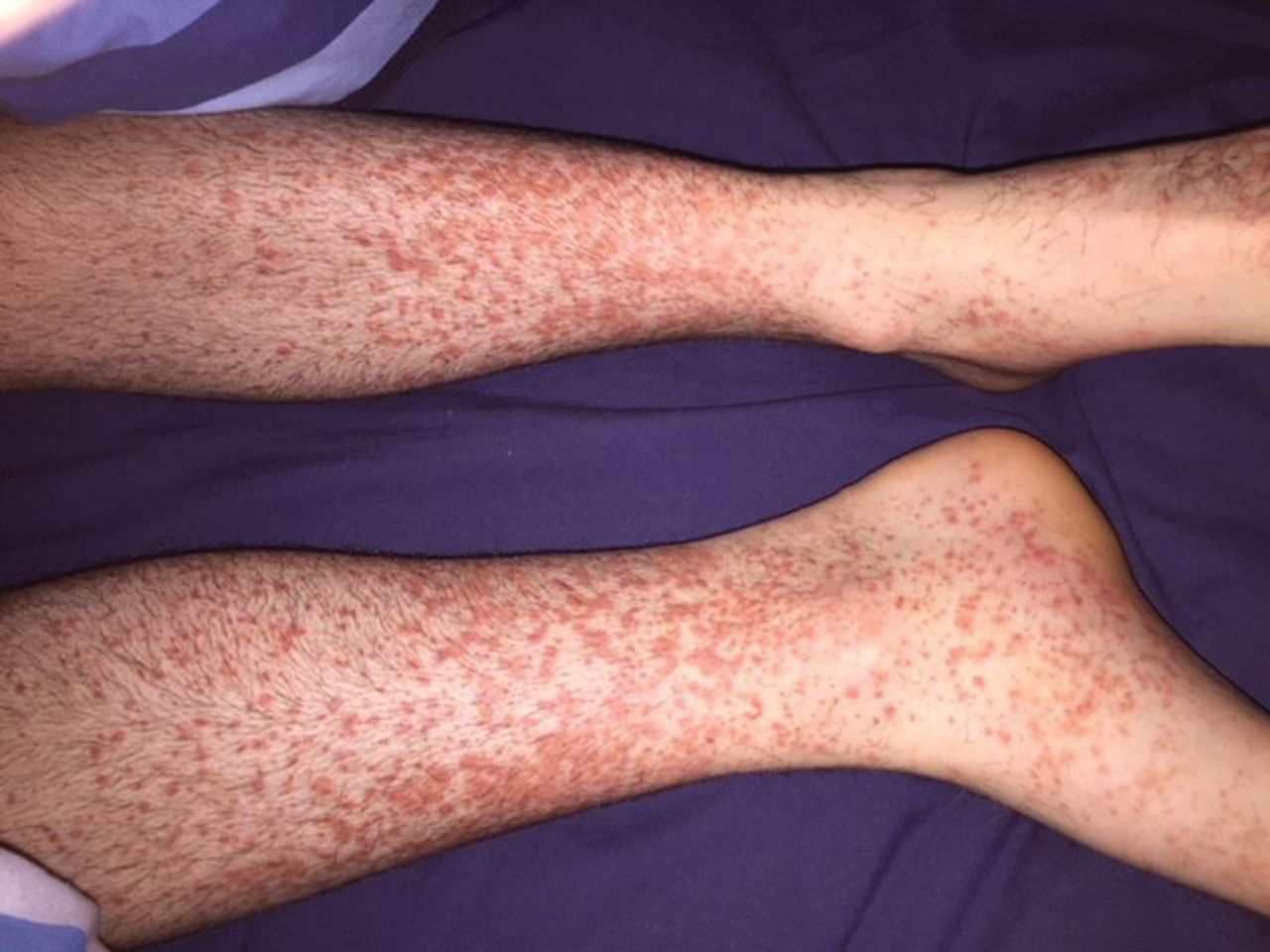
In addition: Joint pain. abdominal pain, vomiting, subcutaneous edema, rectal bleeding, scrotal edema, headache, fever, diarrhea, hematemesis, fatigue.
HSP is the most common systemic vasculitis in _______?
Children
How is HSP most commonly diagnosed in children?
The diagnosis of IgAV is typically based upon clinical manifestations of the disease.
The prognosis for most HSP patients is _______?
A) Excellent
B) Poor
A) Excellent!
A patient with HSP presents to the ED with abdominal pain, vomiting and stool mixed with blood and mucous. Which complication of HSP is most likely to be the cause?
Intussusception
True or False:
HSP is more common among males than females.
True!
When is a skin biopsy indicated?
Patients with incomplete or unusual presentations.
Adult patients
Can HSP recur?
Yes!
The recurrence rate of HSP is 2.7%–30%.
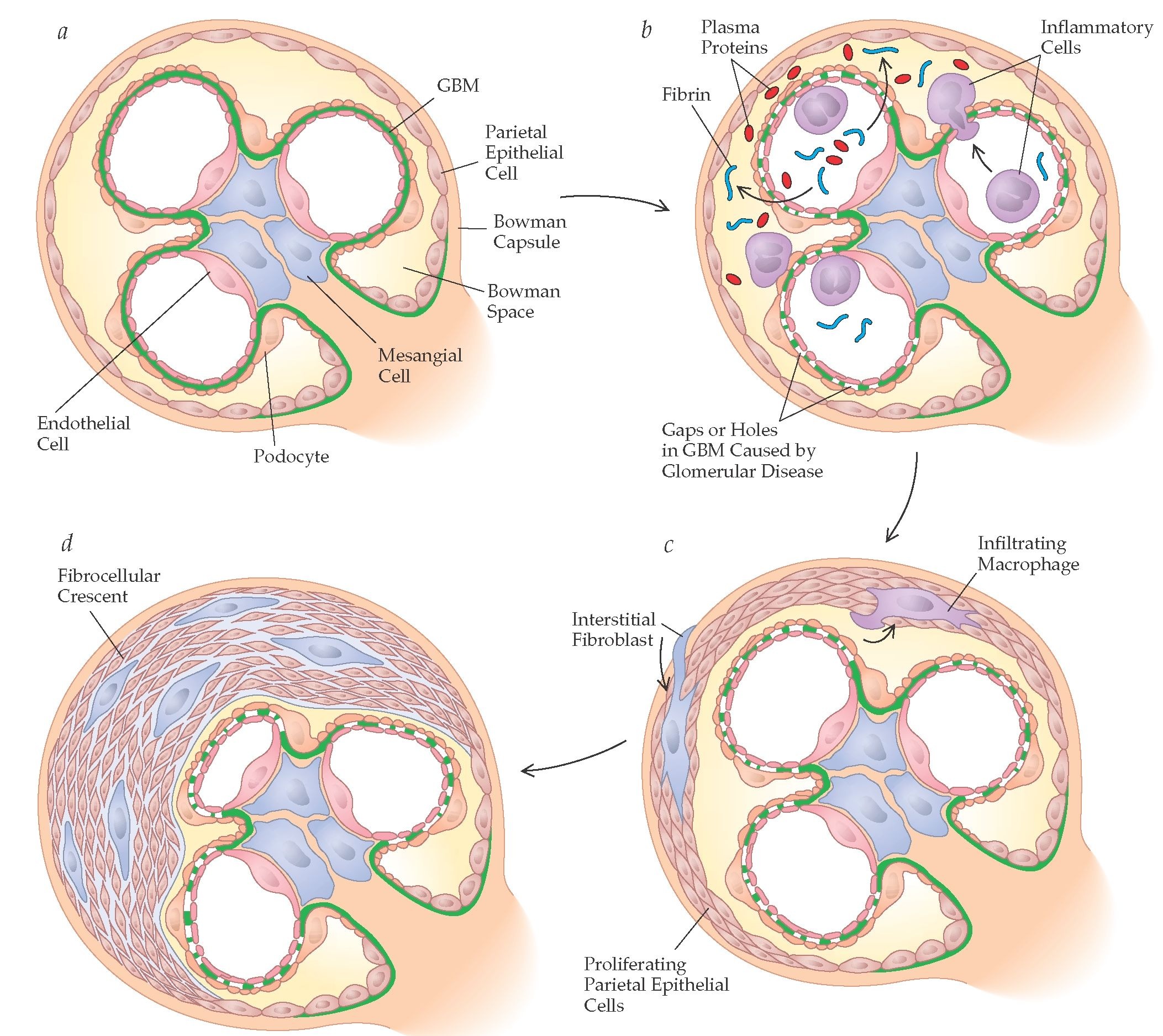
What is the cause of HSP nephritis?
The tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, which filter blood to remove extra water, salt and waste into the urine, become inflamed. This causes the kidneys to 'leak' blood cells and proteins into urine.
__________ caused by antigenic exposure from an infection or medication deposit in the small vessels of the skin, joints, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
IgA-antibody immune complexes
When is a kidney biopsy indicated and what should you look for?
Kidney biopsies are indicated if the diagnosis is uncertain or if there is extensive renal impairement.
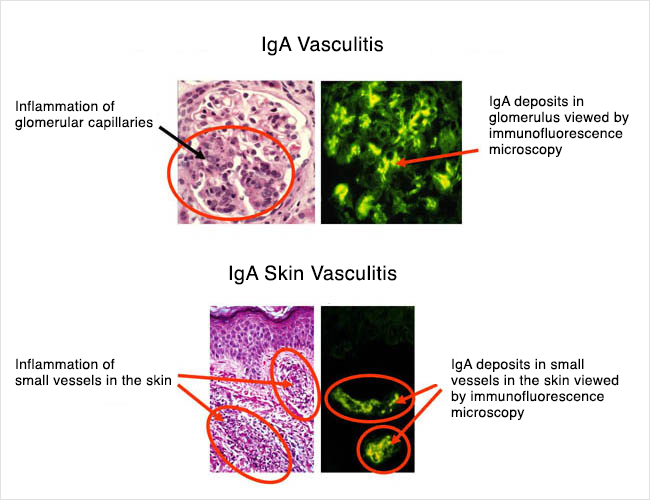
Immunofluorescence: Globular mesangial IgA deposits.
Light Microscopy: Range from isolated mesangial proliferation to severe crescentic glomerulonephritis.

How long does HSP last on average?
4-6 weeks.
Many patients with HSP get acute arthritis. What are the two most commonly affected areas?
Knees and ankles.
Who described the first cases of HSP? Which year? Which country?
Dr. William Heberden, a London physician, described the first cases of Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) in 1801.
In describing HSP, Heberden wrote of a 5-year old boy who “…was seized with pains and swellings in various parts…He sometimes had pains in his belly with vomiting…and the urine was tinged with blood. Presently, the skin of his leg was all over full of bloody points” (purpura).
How is intussusception diagnosed?
Ultrasound
Death (a rare complication of HSP) is caused mostly due to _________?
Kidney disease.
List some of the rare symptoms/complications of HSP.
Neurological Symptoms
Pulmonary Symptoms
Urological Symptoms
Occular Symptoms
Just for fun!
Where does the name Henoch Schönlein Purpura come from?
Johann Schönlein (1837) and Edouard Henoch (1874) reported additional cases decades after Heberden.
They recognized that the disorder often followed upper respiratory tract infections and was not always self-limited, sometimes progressing to serious kidney involvement.
What is one lab test that you should always perform on patients with HSP?
Urinalysis