Molecules are made of these.
What are atoms.
The branch of science concerned with the classification of living things.
What is taxonomy?
This is the broadest level of classification.
What is a domain?
A tool used to identify a particular species.
What is a dichotomous key?
What is homeostasis?
Fill in the blank: atom -> molecule -> _________ -> tissue -> organ -> organ system -> organism
What is cell?
This is the two part naming system used to identify species.
What is binomial nomenclature?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
What are the 3 domains?
This is used to verify information on a cladogram.
What is DNA?
True or False: All living things move.
The brain is an example of this level of organization.
What is an organ?
The genus plus species.
What are the two levels of classification used to form a scientific name?
The primary difference between Bacteria and Eukarya.
What is a nucleus?
Plants that have vascular tissue, seeds, but do not have flowers. 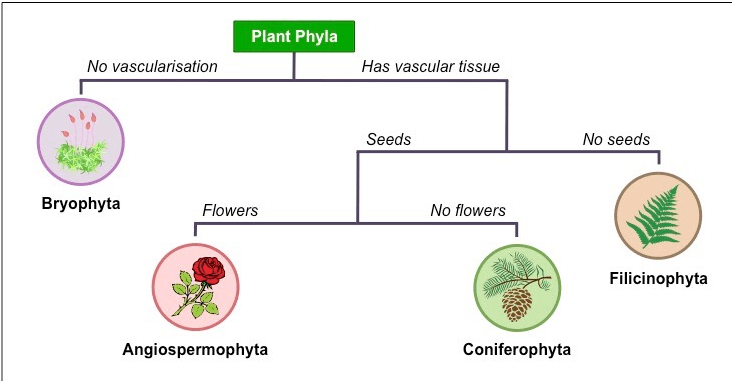
What are Coniferophyta?
What is responding to stimuli?
A prokaryote goes up to this level of organization.
What is a cell?
The level of organization where organisms are most closely related and can produce offspring.
What is a species?
A unicellular, autotrophic eukaryote
What is a Protista?
The organisms most closely related to the humans on the cladogram shown. 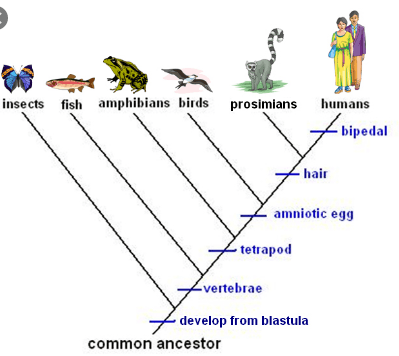
What are prosimians?
There are many different types of tissues that make up the human body. This is true of all tissues.
What is -- they are made of cells?
Organs working together to do a specific function are an example of this level of organization.
What is an organ system?
This is how organisms are classified and organized within the Linnaean system of taxonomy.
What are shared characteristics?
A multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryote that has a cell wall made of chitin
What is a Fungi?
These organisms all have amniotic eggs. 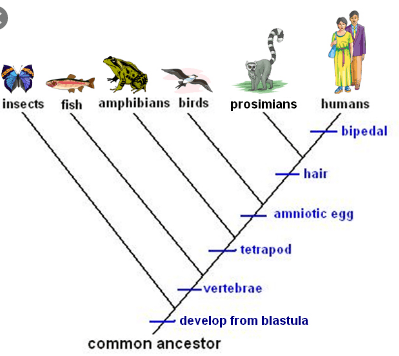
What are birds, prosimians, and humans?
In order for a species to survive over time, it must have this characteristic of life.
What is the ability to reproduce?