Dividing a population into homogeneous groups before taking random samples from each group is known as this type of sampling.
What is stratified sampling?
sum_(i=1)^n x_iP(X=x_i)
What is the mean or average of x-values?
A data point with a very large residual is referred to by this term.
What is an outlier?
Every one unit increase in the explanatory variable corresponds to a change in the response variable by some number of units is an interpretation of what parameter in linear regression?
What is the slope?
The explanatory variables in an experiment are also referred to by this term.
What are factors?
A sampling method is called this if in some critical way it consistently results in samples that do not represent the population.
What is biased?
r frac(s_y)(s_x)
What is the slope of the prediction equation in LSR?
Making predictions using values far outside of the range of values of the explanatory variable is referred to as this.
What is extrapolation?
To interpret this, I might say the response variable has this value when the explanatory variable is zero.
What is the intercept?
When their effects on the response variable cannot be distinguished, an explanatory variable and another variable are said to be this.
What is confounded?
In this type of study, data are gathered without disturbing the population.
What is an observational study?
sum_(i=1)^n (x_i-\mu)^2P(X=x_i)
What is the sample variance?
If r=-0.5 , what percent of variability in the response is explained by the model?
What is 25%?
The prediction equation either under- or overestimates values of the response by some number of units, which is an interpretation of this term in linear regression.
What is a residual?
In an experiment to test the effect of caffeine on pulse rates, a caffeine-free herbal tea is used. Observing a raised pulse rate after administering the herbal tea is sometimes referred to by this two-word term.
What is the placebo effect?
A nice characteristic of this sampling method is that every possible sample of a desired size has an equal chance of being selected.
What is simple random sampling?
overline(y)-b overline(x)
What is the intercept of the prediction equation in LSR?
The association between weight and quarter mile time of 32 cars is summarized in the output below. Give the strength and direction of the linear relationship between weight and quarter mile time.
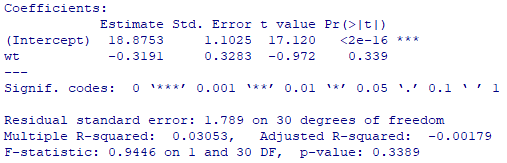
What is weak and negative?
Interpret the residual plot below to decide on the appropriateness of a linear model.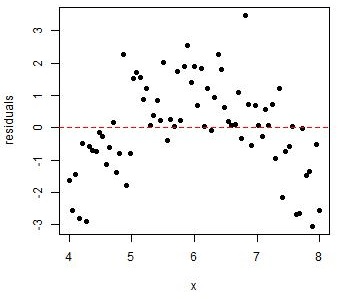
What is a linear model is not appropriate?
Examples of this type of experimental design include experiments on mice of the same litter, or even before/after measurements on the same person.
What is a matched pairs design?
Let's say I wanted to gauge student opinion on the outcome of the state championship football game. I go into the study hall and randomly select tables and proceed to survey every student at the selected tables. I am employing this method of sampling.
What is cluster sampling?
frac(1)(n-1)sum_(i=1)^n(frac(x_i-overline(x))(s_x)cdotfrac(y_i-overline(y))(s_y))
What is correlation?
A point is said to be this, if when omitted the regression model results in a much different slope.
What is influential?
The proportion of variation in the response variable that is explained by the model is known as the interpretation of this three word term.
What is the coefficient of determination?
What the objects receiving treatments are people, they are often referred to by this term.
What are subjects?