change from a liquid to a solid
What is freezing?
particles are in rigid, fixed structure
What is a solid?
rank states of matter from slowest to fastest particle motion
What is solid, liquid, and gas?
 Occurence at D
Occurence at D
What is evaporation or boiling?
an upward force exerted on an object immersed in or floating on a fluid
buoyancy
change from a gas to a liquid
What is condensation?
particles in this state has most kinetic energy and have weakest intermolecular attraction
What is a gas?
The kinetic theory of matter assumes this about particle motion if temperature decreases
What is particle motion slows down?
The state for the particles shown in the following diagram
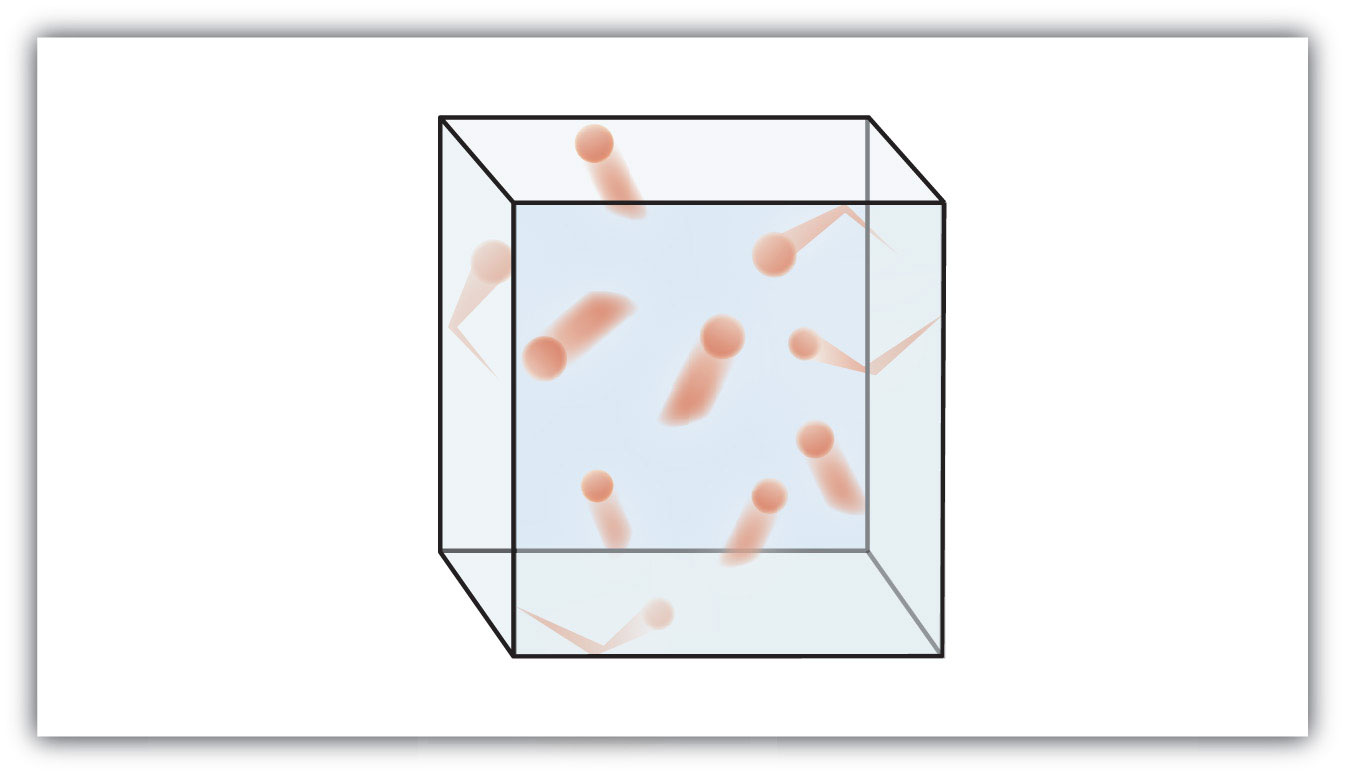
What is a gas?
The law represented by a balloon that shrunk after being placed in the freezer for a couple of hours
What is Charles' Law?
change from a solid to a liquid
What is melting?
DAILY DOUBLE
these particles have broken down and become charged or ionized
What is plasma?
DAILY DOUBLE
The kinetic theory of matter's assumption about particle size and speed
What is larger particles move slower than smaller particles?
Change of state pictured
What is melting?
If temperature is constant, and a sample of gas increases in volume, this is the result
What is decrease in pressure?
Change from a solid to a gas
What is sublimation?
The particles slide past each other, but are still packed together
What is a liquid?
The common factor that the kinetic theory states among all phases of matter
What is all atoms and molecules are always in motion?
 Endothermic, exothermic, or no change in energy
Endothermic, exothermic, or no change in energy
What is exothermic?
Two factors that affect the speed of a fluid in a pipe
change from a liquid to a gas
What is evaporation?
The resulting state in deposition
What is a solid?
the meaning of conservation of matter in a phase change
 Hoarfrost occurs when vapor changes directly to a solid. This is what phase change?
Hoarfrost occurs when vapor changes directly to a solid. This is what phase change?
What is deposition?
resistance to flow
What is viscosity?