DNA -gene expression--->transcription --mRNA--> translation in ribosome ------> protein folding (function depends on shape // gene sequence is important)
a molecule having a partial negative charge on oxygen with two lone pairs covalently attached to two hydrogens adopting partial positive charges.
What is a water molecule?
can form from other molecules called ampholytes, or amphoteric compounds and can act as both an acid and a base.
What is a Zwitterionic form?
A peptide bond may
not freely rotate
nonprotein compound // used to designate an organic cofactor // necessary for the function of that enzyme
coenzyme
enchance biological rxns, decrease activation energy, NEVER change equalibrium, and don't get used up
What can enzymes do for a biochemical reaction?
good solvents for water
What are polar/charged molecules?
The polypeptide chain bond can freely rotate.
not at the polypeptide bond. phi and psi bonds rotate
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
What are the 4 protein level structure?
the structural unit of an oligomeric protein (subunits are identical)
protomer
delta G = delta H - Temperature in Kelvin delta S is free energy change.
Endergonic
Exergonic
Endothermic
Exothermic
unfavorable
favorable
absorb heat - reaction is cooler than the surrounding
release heat - reaction is hotter than surrounding
hydrogen bonds
ionic interactions
hydrophobic/philic interactions
Van der Waals
What are 4 weak interactions?
proteins coming down a column to purify it based on size using beads.
The large proteins would flow fast down and would not be kept in the column.
what is size-exclusion chromatography?
heat and cold
pH extremes
organic solvents
chaotropic agents: urea and guanidium hydrochloride
What can denature proteins?
nonprotein group // covalently attached cofactors
prosthetic group
-30.5 jK/mol of free energy that allows a reaction to become more favorable
What is ATP?
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
What are the 3 cases that may happen based on the osmolarity?
Using TCEP can break what bonds?
What are disulfide bonds?
btw, what are the two amino acids with S in their R groups?
An experiment using a small protein that contains 8 cystines linked via four disulfide bonds. In the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol and urea the disulfide bonds break and in absence of these chemicals they reform
What is the experiment of ribonuclease refolding experiment?
a functional non amino acid component such as
metal ions or organic molecules
cofactor
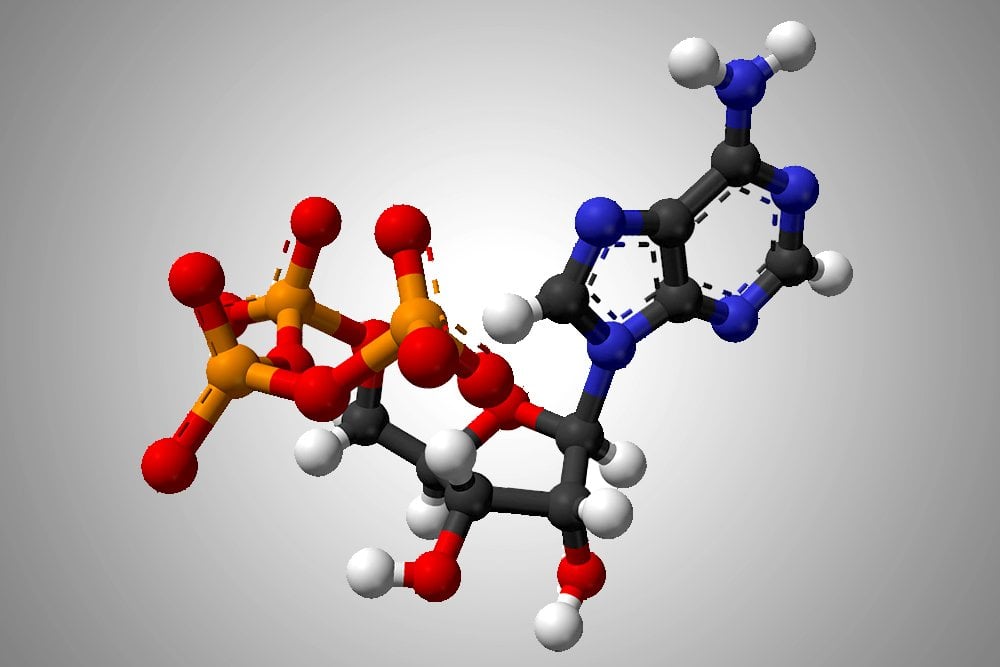
What is ATP?
It equals 14 when added together.
What is pH and pOH?
Successive rounds of Nterminal
What is Edman degradation?
London forces
Electrostatic
Hydrogen bonds
Hydrophobic effect
What are 4 weak interactions in proteins?
not all proteins fold spontaneiously therefore these facillitate correct folding pathways // provided mirco enivrionment for folding
chaperones