CHANGES IN THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE IS CHARACTERISTIC FOR RHEUMATISM
mucoid swelling
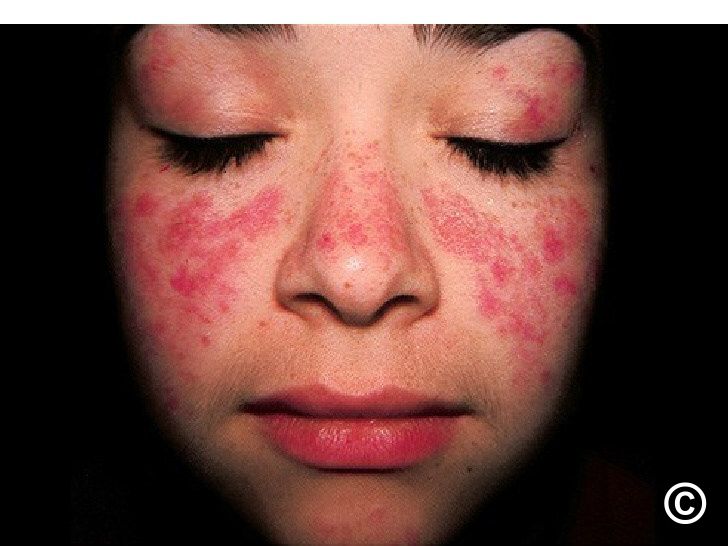
SLE
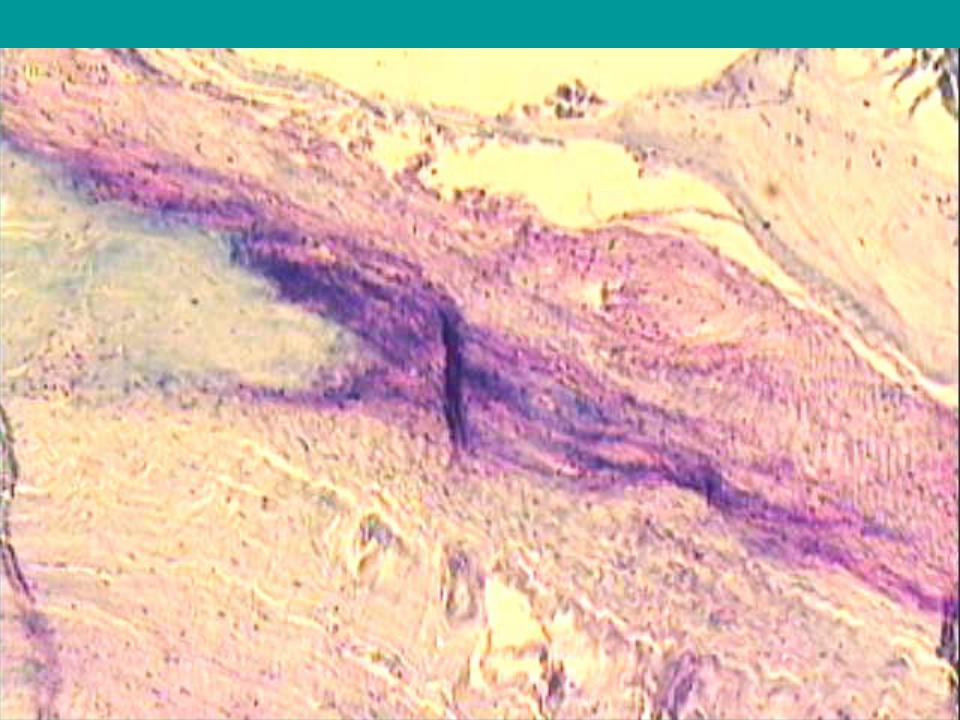
Mucoid swelling of the endocardium in rheumatism: the unchanged part of the valve is colored bluish-blue (1), the focus of mucoid swelling of the endocardium and deeper areas of the valve tissue is purple (2) (the phenomenon of metachromasia).
A 40-year-old woman complained of focal changes in the skin of the shoulder in the form of a pale gray, parchment-like seal. A skin biopsy was performed. The diagnosis of systemic progressive sclerosis has been established.
1 Name a synonym for the disease.
2 Describe microscopic skin changes.
3 Name the manifestations of systemic disorganization of connective tissue.
1) scleroderma
2) fibrosis of the dermis, atrophy of the epidermis
3) mucoid swelling, fibrinoid necrosis, sclerosis
A pathologist must go to what kind of school?
medical school
CLINICAL AND ANATOMICAL FORM OF RHEUMATISM
heart and vessels

Muscat liver: chronic venous fullness: the liver is enlarged in volume, dense consistency, the capsule is tense, smooth, the anterior edge of the liver is rounded. On the incision, the liver tissue appears mottled due to the alternation of small foci of red, maroon and yellow, resembling a nutmeg pattern on the incision
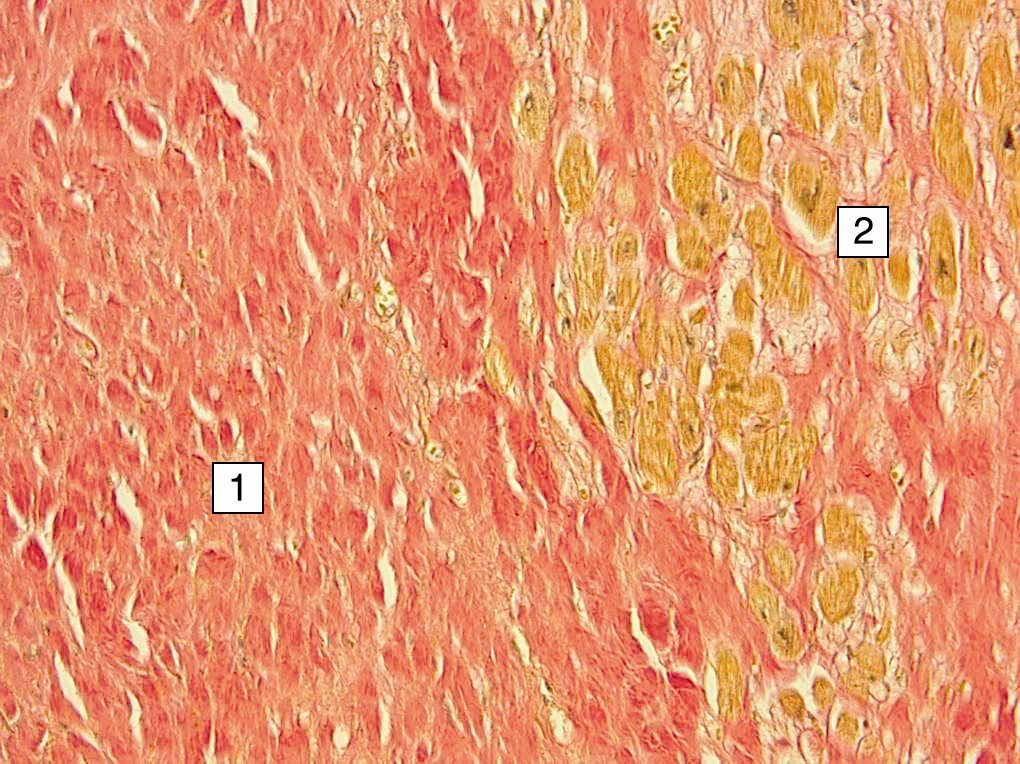
Rheumatic myocarditis cardiosclerosis: foci of sclerosis and myofibrosis of different sizes, when stained with picrofuxin, connective tissue is colored red (1), cardiomyocytes (hypertrophied) - yellow
In a 19-year-old girl operated on for mitral heart disease, granulomas were found in the biopsy of the auricle of the heart, in the center of which there are foci of fibrinoid necrosis, along the periphery – clusters of macrophages.
1 What disease are we talking about?
2 What is the stage of granuloma development?
3 Specify the etiological variety of this granuloma.
4 Name the outcomes of the process in the myocardium.
1) rheumatism
2) blooming granuloma
3) infectious-allergic (rheumatic)
4) diffuse small-focal cardiosclerosis
Medical pathology comprises ________ and __________ pathology.
anatomical, clinical
WHICH STRUCTURAL CHANGE IS CHARACTERISTIC FOR RA
diffuse disorganization of connective tissue

Acute warty endocarditis of the mitral valve in rheumatism: the size and weight of the heart are not changed, the mitral valve flaps are moderately thickened, edematous, with small (2-3 mm), dark red, crumbling, dull, easily separated thrombotic overlays (in the form of warts) along the free edge of the flaps (in foci of endocardial damage of the valve flaps)

Productive (granulomatous) rheumatic myocarditis: Aschoff-Talalaev granulomas in the myocardial stroma (perivascular) with large hyperchromic macrophages, lymphocytes, with fibrinoid necrosis (1)
A 50-year-old man has suffered from combined mitral heart disease since childhood. He was admitted to the clinic with signs of active rheumatism. Against the background of increasing cardiac decompensation, left- sided paralysis developed, death occurred.
1 What clinical and anatomical form of rheumatism are we talking about?
2 What changes in the heart valves characterize the exacerbation of rheumatism?
3 What brain changes caused the development of left- sided paralysis?
4 What is the mechanism of these changes?
5 Explain the concept of "combined" heart disease
1) cardiovascular
2) recurrent warty endocarditis (foci of fibrinoid necrosis , fresh thrombotic overlays)
3) cerebral infarction
4) thromboembolism of the cerebral arteries
5) combination of orifice stenosis and mitral valve insufficiency
What is the definition of pathology?
the scientific study of disease
WHAT DISEASES OF THE JOINTS DOES RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS APPLY TO?
the immune system reaction
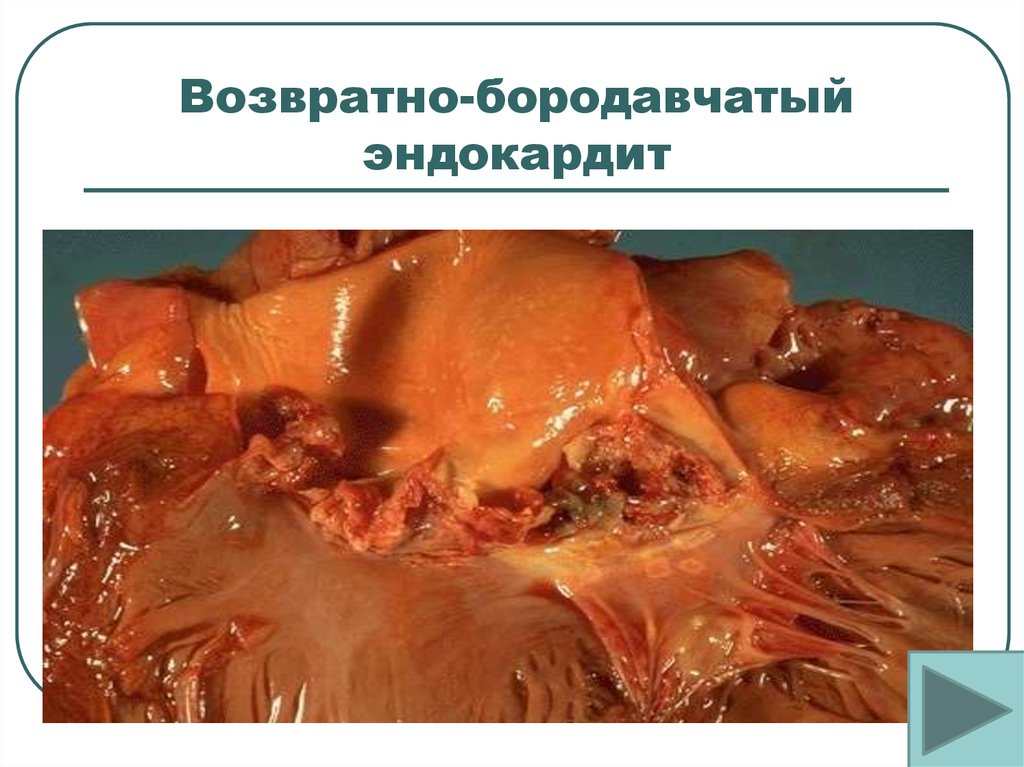
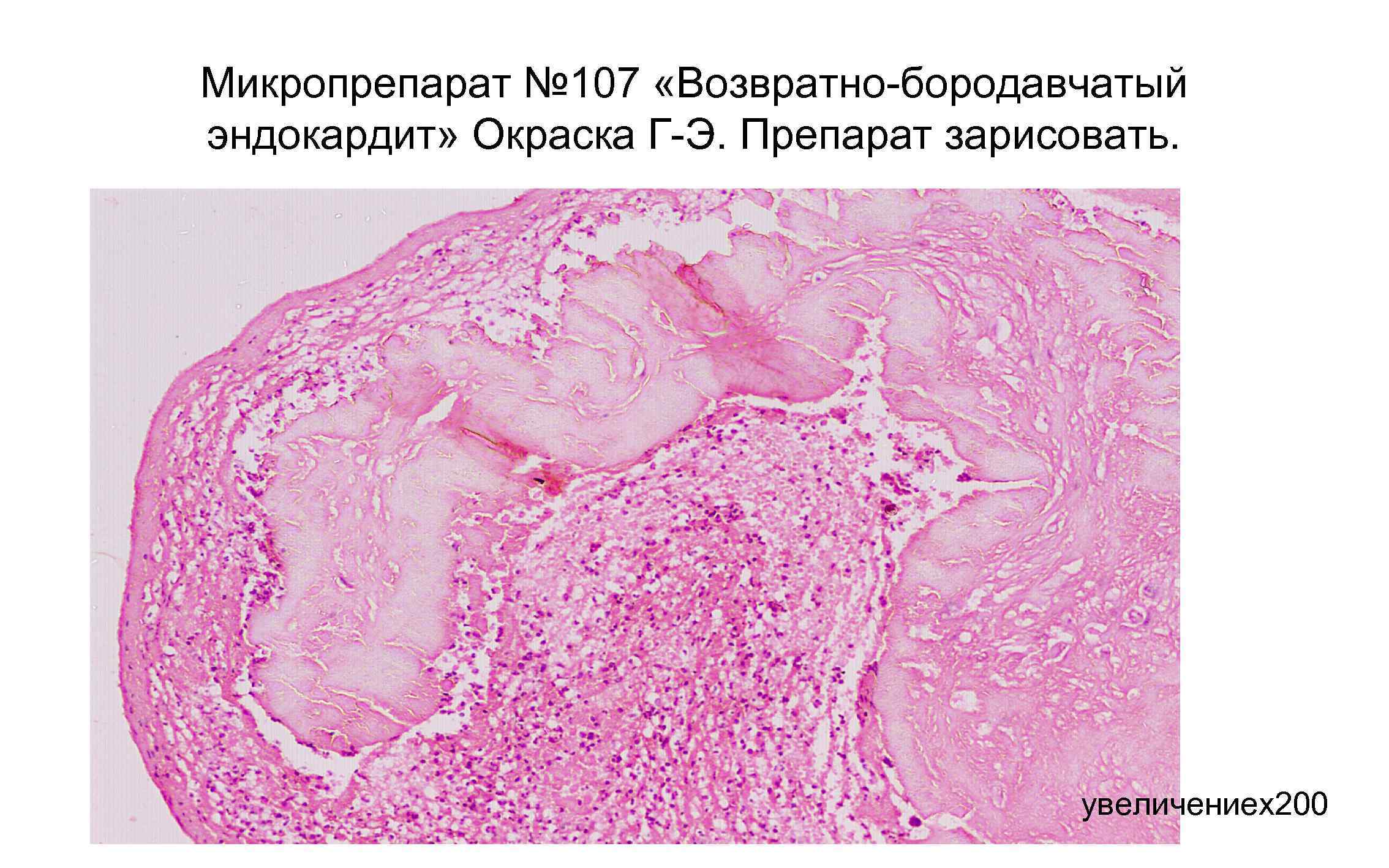
Recurrent warty endocarditis of the mitral valve in rheumatism: the size and weight of the heart are increased (myocardial hypertrophy). Small thrombotic overlays of red color (in the form of warts) along the free edge of sclerosed, deformed, partially fused and petrified mitral valve flaps (in foci of endocardial damage to the valve flaps). Chords are thickened, spliced, shortened (rheumatic heart disease)
Recurrent warty endocarditis in rheumatism: the valve leaf is sclerosed, hyalinized, vascularized, with foci of mucoid swelling and fibrinoid necrosis, with weakly expressed lymphomacrophagal infiltration (1). A mixed thrombus is attached to the areas of damage to the endocardium and destruction of the endothelium (2)
A 10-year-old child died from rapidly progressing rheumatism with severe allergic reactions. An autopsy revealed pancreatitis.
1 List the characteristic changes of the endocardium. 2 Describe the macroscopic changes in the heart muscle.
3 Specify the features of myocardial changes during microscopic examination.
4 Determine the essence of the pericardial change.
5 What type of immune reaction prevailed in the patient?
1) endocarditis (acute warty)
2) flabby, mottled
3) diffuse exudative myocarditis
4) pericarditis (serous, fibrinous)
5) immediate type hypersensitivity reaction
Pathology is seperated in to groups based on what?
anatomical/ structural
WHICH CELL IS IN THE RHEUMATIC GRANULOMAS
component of the mononuclear phagocytic system that regulates immunity

a- normal
b- hypertrophy of the myocardium(left ventriculum)
c- excenrtic hypertrophy of the myocardium
Fibrinoid changes of the endocardium in rheumatism: 1- destruction of collagen fibers

SURPRISE!!!!!
The vast majority of cancer diagnoses are made by _______.
Pathologists