Calculate the momentum of a .2 Kg mass traveling at 12 m/s to the right.
2.4 Kg m/s
Which is the cause and which is the effect: Impulse and change in momentum
Impulse causes a change in momentum. Impulse is the cause. Change in momentum is the effect.
An object, initially travelling at 5 m/s, experiences a change in momentum of 25 Kg m/s. What is the impulse on the object?
Impulse is the same as change in momentum. It experiences an impulse of 25 Ns.
The same as the initial. The momentum is conserved. 400 Kg m/s
PFX=12,000 Kgm/s PFY=28,000 Kgm/s
What is the name of Philadelphia's professional Lacrosse team?
Philadelphia Wings
Which has more momentum, a 1 Kg feather going 8 m/s or a .2 Kg feather going 45 m/s?
The .2Kg feather
If you double the impulse on an object how will its change in momentum change?
The change in momentum is the same quantity as the impulse. If you double one you double the other. It will double.
A 2 Kg object feels a force of 5 N for 10 s. What is the change in momentum of the object?
50 Ns
A 2 Kg mass is moving at 10 m/s to the right. It collides with a 4 Kg mass that is moving at 8 m/s to the right. Both objects are on a frictionless surface. After the collision the 2 Kg object moves with a velocity of 9 m/s to the right. What is the velocity of the 4 Kg mass after the collision?
8.5 m/s (R)
A single object is moving and strikes a second stationary object. If the objects have equal and opposite final y-momentum, what can you conclude about the initial direction of travel of the first object?
The first object only travelled in the x-direction to start. The initial and final momentum are the same and the finals objects have no total y-momentum.
Which of the following weighs the most: an average adult bicycle, a cubic foot of water, an adult deer, or all of the air in this room?
All of the air in this room
Bicycle (40 lbs), A cubic foot of water (62 lbs), An adult deer (150 lbs), Air (390 lbs).
Calculate the momentum of a 2 Kg object moving at 5 m/s to the left
Two eggs of the same mass are dropped from the same height. One egg is caught in a bed of cotton. The other eggs is allowed to hit the ground. Which egg is more likely to break and why (reference the impulse-momentum theorem)
The egg that hits the ground. The change in momentum of the eggs are the same. The time of impact is much shorter for the egg that hits the ground and so the average force is much higher.
A 2 Kg mass is initially moving at 4 m/s (R). It feels a force of 13 N for 5 seconds. What is the final velocity of the mass?
36.5 m/s (R)
A 2 Kg mass moving at 12 m/s (R) collides with a 4 Kg mass moving at 5 m/s (R). After the collision the 2 Kg mass is traveling at 10 m/s (R). What is the velocity of the 4 Kg mass?
6 m/s (R)
Two object collide at a right angle and stick together. What is the final x and y velocity that they move with after the collision?
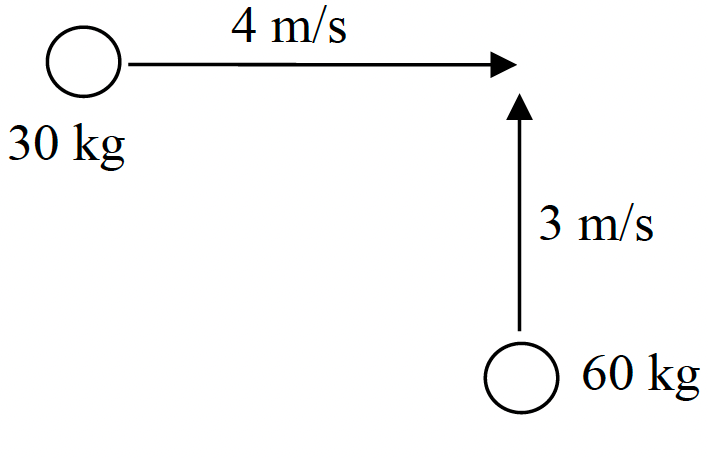
VFX=1.33 m/s. VFY=2m/s
In what decade was Garnet Valley High School built?
1960s (1962-1963)
A 4 Kg mass is moving at 3 m/s. What mass needs to move at 10 m/s to have the same momentum as the 4Kg mass?
1.2 Kg
During a car crash a seatbelt is designed to stretch a little bit. Why do engineers design the seatbelts this way in terms of the impulse-momentum theorem?
The longer you allow the seatbelt to apply a force the lower the average force will be. By letting the seatbelt stretch a little elongates the time and reduces the force on your chest.
A .5 Kg object is traveling at 4 m/s right. A force acts on the mass and causes it to travel at 3 m/s left. The force acted for .5 seconds. What is the force felt by the mass?
-7N OR 7N (L)
A 3 Kg mass is moving right at some initial velocity. It runs into an initially stationary 2 Kg mass. After they collide the 3 Kg mass is moving at 4 m/s (R) and the 2 Kg mass is traveling at 5 m/s (R). What was the initial velocity of the 3 Kg mass? Is the collision elastic (justify your answer)?
7.33 m/s (R).
It is not elastic KI=80.67 J KF=49 J
Two masses collide as shown below. The 200 g object is deflected 60° from its original path at a speed of 2.7 m/s. Find the final velocity of the 500 g object, that is initially at rest.
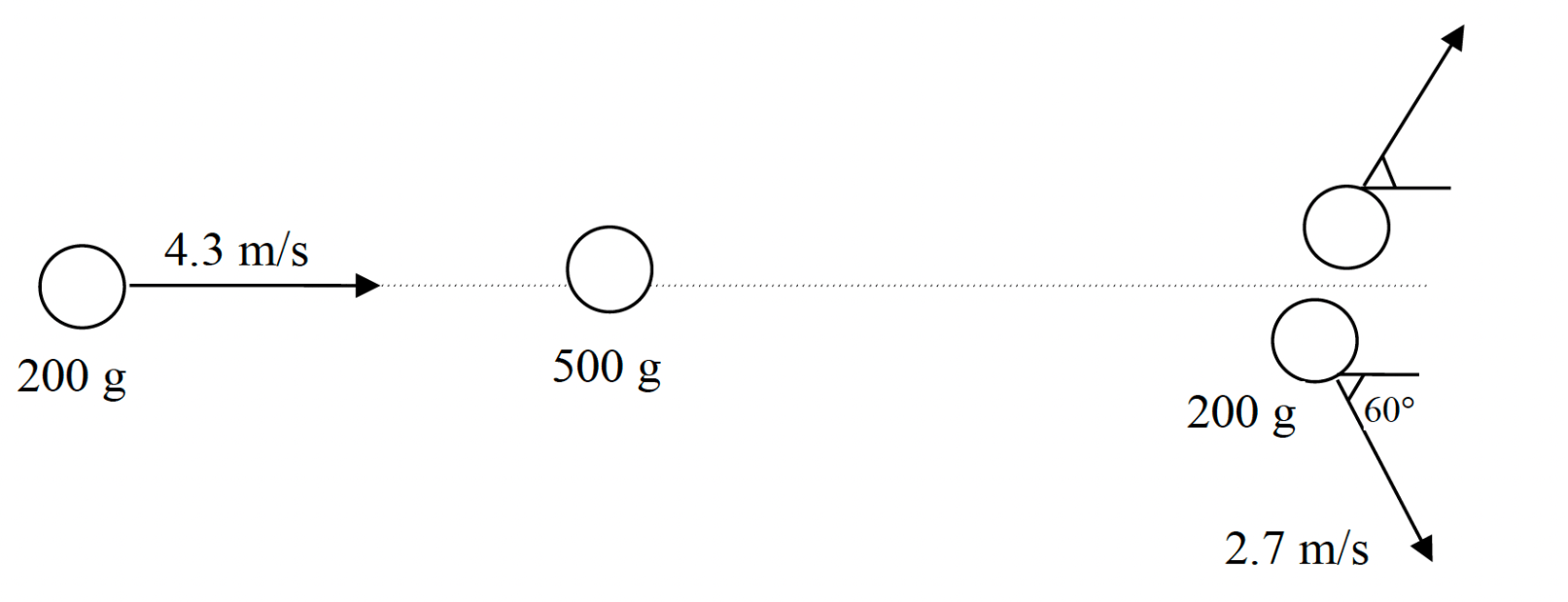
VFX =1.18m/s VFy=-.94 m/s OR .94 m/s down
Which of the following is closest to the area of the high school campus? 100 m2 , 1000 m2 , 10,000 m2 , 100,000 m2 , 1,000,000 m2
The school campus covers approximately 185,500 m2.
Mass A has a momentum of 10 Kg m/s. Mass B has a momentum of 20 Kg m/s. Mass B is twice the mass of mass A. What multiple of mass A's velocity is mass B moving at?
It is moving at the same velocity (1x the speed of A)
You want to close an open door by throwing either a 400-g lump of clay or a 400-g rubber ball toward it. You can throw either object with the same speed, but they are different in that the rubber ball bounces off the door while the clay just sticks to the door. Which projectile will apply the larger impulse to the door and be more likely to close it? Why will that object have a larger impulse?
The bouncy ball. It not only loses all of its initial momentum it gains momentum in the opposite direction. This results in a larger momentum change and so a larger impulse.
-105 Ns.
Equal and opposite impulse. The collision times are the same and the forces are equal and opposite (3rd law).
A .2 Kg object moves at 10 m/s to the left and collides with a 400 gram object moving at 3 m/s to the right. After the collision the .2Kg mass is moving left at 3 m/s. What is the final velocity of the 400 gram object?
.5 m/s (L) OR -.5 m/s
An explosive device, initially at rest, detonates and sends 3 fragments in various directions. Find the velocity of the 30 kg fragment.
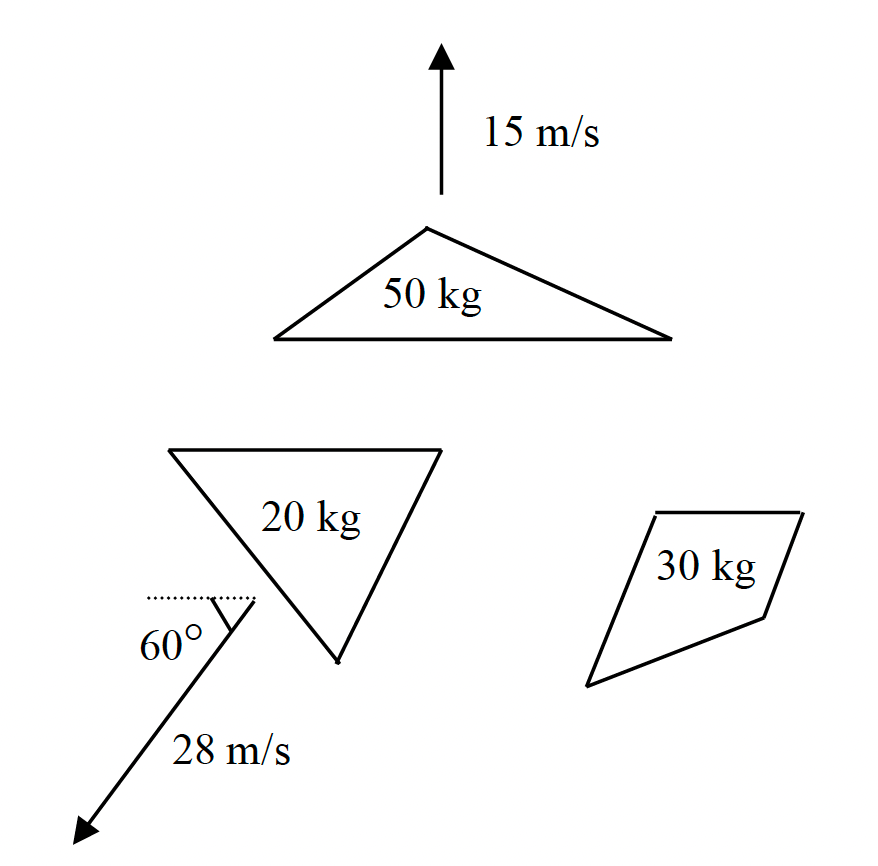
VFX=9.33m/s VFY=-8.83m/s OR 8.83 m/s down
What is the name of the largest desert in the world?
Antarctic Polar Desert