The Profit Maximizing Quantity AND Price
What is:
Quantity = 3
Price = 4
What is the Profit - Maximizing Point?
MR = MC
What kind of firms are perfectly competitive firms?
a) Wage Takers
b) Price Takers
c) Price Makers
B!
Define: Long Run
A period of time in which all resources can change
Define: Short Run
A period of time in which at least one resource is fixed
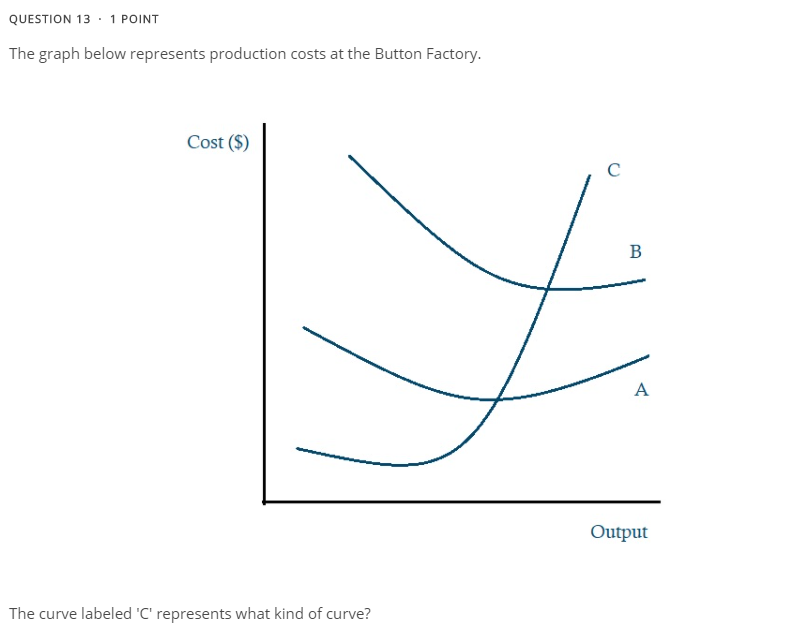
Name the cost curves from A - C
What is
A = Average Variable Cost
B = Average Total Cost
C = Marginal Cost
At what unit does Diminishing Marginal Returns set in?![]()
At the 3rd worker
Wheat Ltd. must also sell at $6
What type of profit do firms make in the long run?
Short run marginal costs eventually increase because of the effects of...
Diminishing Marginal Products
What type of market is this

Perfect Competition Market
Define: Diminishing Marginal Returns
As you add variable resources to fixed resources, the additional output will eventually decrease
(Give two answers)
What is a factor that makes it difficult for firms to enter called? What kind do perfectly competitive firms have?
1. Barrier to entry
2. Low barriers to entry
Which of the following must be true of the long run?
A) All factors of production are fixed
B) Factors of production are not considered
C) At least one factor of production is fixed
D) All factors of production are variable
D!
A profit-maximizing firm will shut down in the short run any time the firm’s total revenue is less than its:
Total Variable Cost
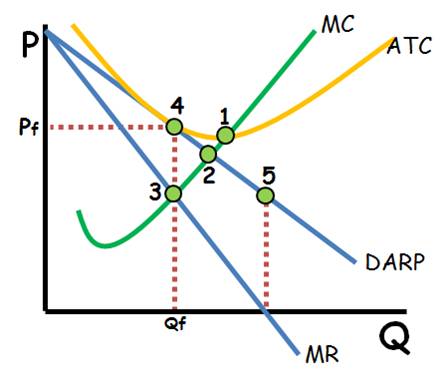
What is the shaded region?
What is:
A Loss
A firm expands its fixed resources and its overall costs of production go up. It is experiencing...
Negative returns to scale
The elasticity of a perfectly competitive demand curve is:
Perfectly Elastic
What's must be true if a firm is in economies of scale?
A) The LRATC decreases as output increases
B) The LRATC increases as output increases
C) The LRATC shifts right, towards the output
D) The LRATC shifts left, away from the output
A!
Assume that a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm has economic losses in the short run. If the firm continues to produce and sell its goods, then which of the following must be true?
The firm is covering its variable costs but failing to cover all of its fixed costs
Answer only 1a and 1b
Tony opens up a hot chocolate stand for two hours. He spends $10 for ingredients and sells $60 worth of tasty beverages. In the same two hours, he could have provided Uber services and earned $40. Tony's accounting profit is ____ and an economic profit of ____.
Accounting Profit: $50
Economic Profit: $10
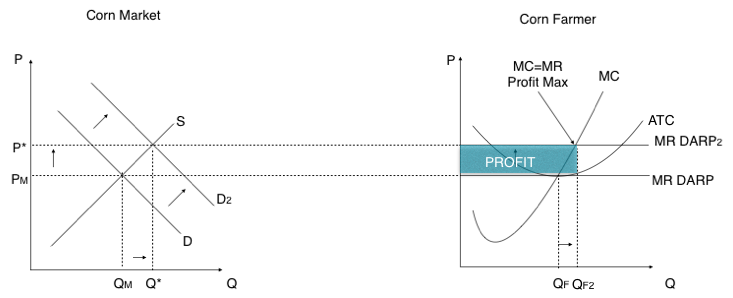
At Price G, the area of which rectangle represents total revenue for the profit-maximizing competitor?
0GKC
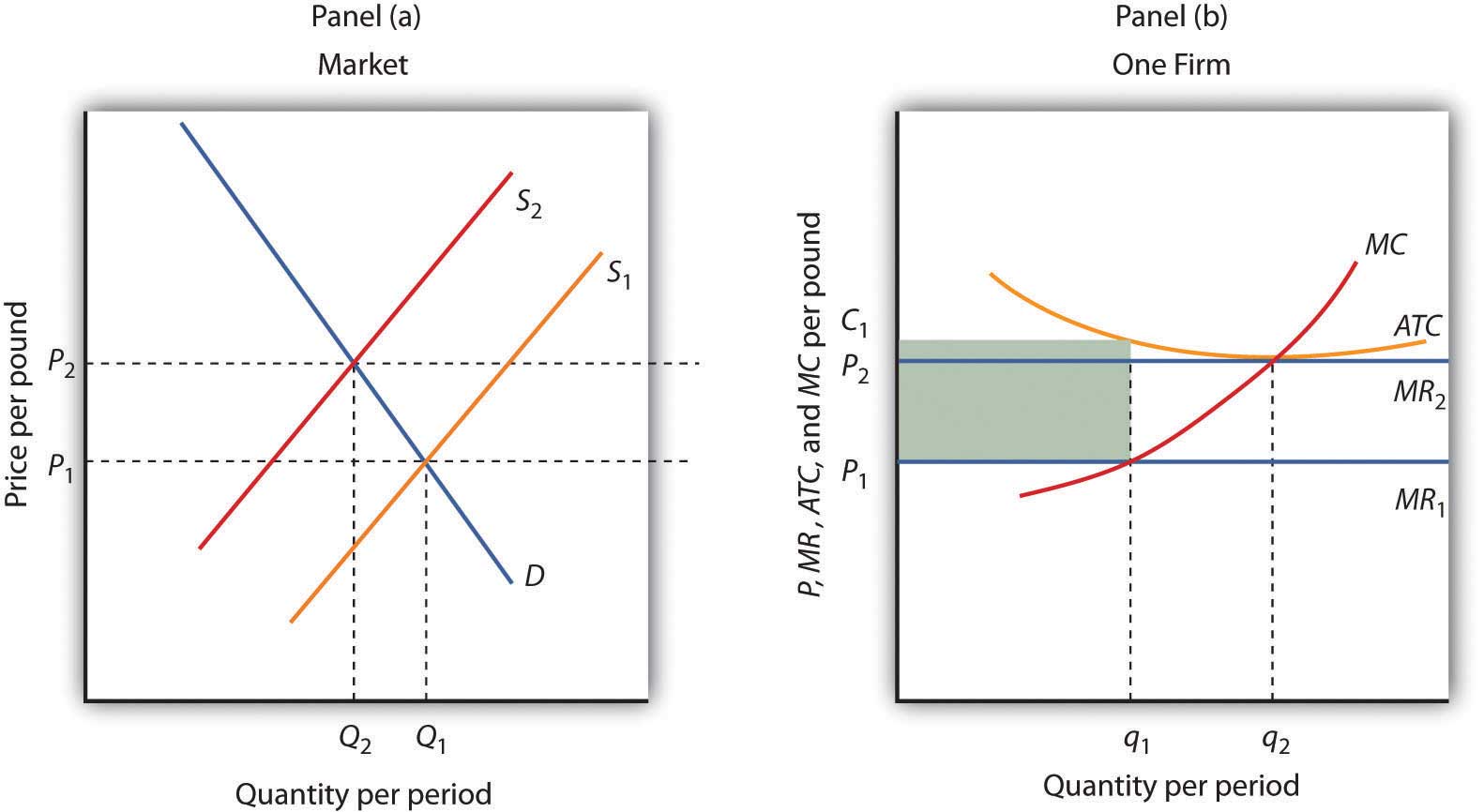
Assume that Mrs. Andes' firm is one of many that produce AP Micro Topic worksheets in a constant cost, perfectly competitive industry which is currently in long-run equilibrium. If the current price for worksheets is $.50, and demand is increasing, how will the price change in the SR and LR?
A) SR= greater than $.50 | LR= greater than $.50
B) SR = greater than $.50 | LR = equal to $.50
C) SR = greater than $.50 | LR = less than $.50
B!
Suppose that price in a perfectly competitive industry decreases and it is now below minimum average total cost but remains above minimum average variable cost. Which of the following will occur in the short run?
Firms will produce the output at which marginal cost equals the new price.