What happens to red litmus paper in an alkali?
Changes to blue
 What is the name of the structure marked with the letter D?
What is the name of the structure marked with the letter D?
Left Bronchi
True or False
Pitfall traps are used to measure the population of plants in an area
False
True or False
Sound travels in a vacuum
False: sound needs particles to travel
Mention an acid and an alkali commonly used in the lab
HCl and NaOH
Capillaries help deliver ___________ (nitrogen/oxygen/carbon dioxide) to cells and pick up _____________ (nitrogen/oxygen/carbon dioxide) as a waste product.
oxygen, carbon dioxide
Sacs where gas exchange occurs.
Alveoli
The pH of the soil in Malta is approximately:
pH 7.5/8
 Mention the structure in the digestive system that:
Mention the structure in the digestive system that:
a. prevents food from entering the trachea
b. where HCl acid is added to digest food
a. epiglottis
b. stomach
Fill in with suitable words
______________ (opaque/transparent/translucent) objects block all light passing through, creating darkness behind them called _________________ (beam/shadow/strand).
Opaque
Shadow
A solution with a pH 6 is a:
Strong Acid, Mild Acid, Strong Alkali, Mild Alkali, Neutral.
Mild Acid
Name the piece of equipment used to estimate the number of plants in an area
Quadrat (Quadrat Sampling)
Why do we need proteins in our diet? Mention 1 function
For hormones
for immune system
The part of the eye where an image is formed
Retina
Explain, giving a reason, what happens to your heart rate when you exercise.
Heart rate increases since the body needs more oxygen to be delivered to the cells. Oxygen is needed to convert stored glucose to energy in a process called respiration.
Mention 2 activities that are not allowed in protected Natura 2000 sites
using motorbikes
hunting
cutting down trees
campfires
trapping organisms
Mention the 7 basic food substances
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats, Vitamins & Minerals, Fibre (roughage), Water.
Explain why we can see a yellow flower as "yellow"
Yellow objects absorb all colours of the visible spectrum except for yellow which is reflected back
Give a word equation for the reaction between a metal and an acid
metal + acid 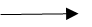 salt + hydrogen
salt + hydrogen
Mention three factors that can lead to heart disease
Smoking, not exercising enough, unhealthy diet (sugars, cholesterol, junk food), family history, underlying medical conditions (diabetes, high blood pressure)
Mention an adaptation of flowers that are insect pollinated
Mention an adaptation of plants growing in hot climatesbrightly-coloured petals/scented
Thick waxy leaves
Mechanical and physical breakdown of food starts in the oral cavity (mouth)
a. What brings about the mechanical breakdown of food (physical change)?
b. What brings about the chemical breakdown of food?
a. teeth
b. enzymes
Which part of the ear:
a. collects sound waves?
b. amplifies sound?
c. changes sound waves into electrical energy?
a. pinna
b. 3 bones
c. cochlea
Match the universal indicator colour change to the solution
red - yellow - green - blue - purple
neutral strong acid strong alkali
weak acid weak alkali
red: strong acid
yellow: weak acid
green: neutral
blue: weak alkali
purple: strong alkali
John's typical breakfast includes: eggs, sausages, bacon, beans & toast.
Suggest an alternative filling breakfast giving reasons why this healthier version is ideal (mention substances in your breakfast etc.)
whatever mentioned if relevant and with appropriate reasons
e.g. wholemeal cereal fortified with vitamins
wholemeal: for fibre
vitamins: needed to prevent diseases
lower in fats but high in starch (carbohydrates) to provide energy stores needed to start the day.