What two compartments is total body water divided into?
Intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF)
What serum sodium defines hyponatremia?
<138 mEq/L
What serum sodium defines hypernatremia?
>145 mEq/L
What serum potassium define hypokalemia and what is the most common cause of hypokelamia?
Insufficient dietary intake
What test is necessary in all hyperkalemia patients?
Name 5 signs or symptoms of dehydration
Dark urine or decreased urine output, dizziness (orthostasis), dry axilla, tachycardia, neurologic impairment, sunken eyes, skin tenting, dry mouth
Two main causes of hypoosmolar hyponatremia?
SIADH and cerebral salt wasting syndrome
What are the most common symptoms of DI?
Thirst, polydipsia, and polyuria
Treatment of severe hypokalemia (<2.5 mEq/L) or symptomatic patients with moderate (2.5 to 3 mEq/L) hypokalemia
IV potassium
What serum potassium defines hyperkalemia and what is the most common cause?
[K+] of >5.5 mEq/L
Most common cause = factitious hyperkalemia caused by hemolysis during phlebotomy
What percentage of body weight is total body water?
60%
Rate of correction of sodium for chronic hyponatremia?
6 mEq/24 hours for high risk patients and 12 mEq/24 hours for low risk patients
What is the difference between central diabetes insipidus and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus?
Central diabetes insipidus (also called neurogenic) is due to inadequate ADH secretion. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (also called nephrogenic) occurs because the v2R receptors of the kidney’s collecting duct cells do not respond appropriately to ADH.
What electrolyte abnormality typically coexists with severe hypokalemia?
Hypomagnesemia
A 67-year-old man presents with generalized weakness. He has had poor oral intake for several days. An ECG is performed as seen above. Which of the following medications should immediately be administered?
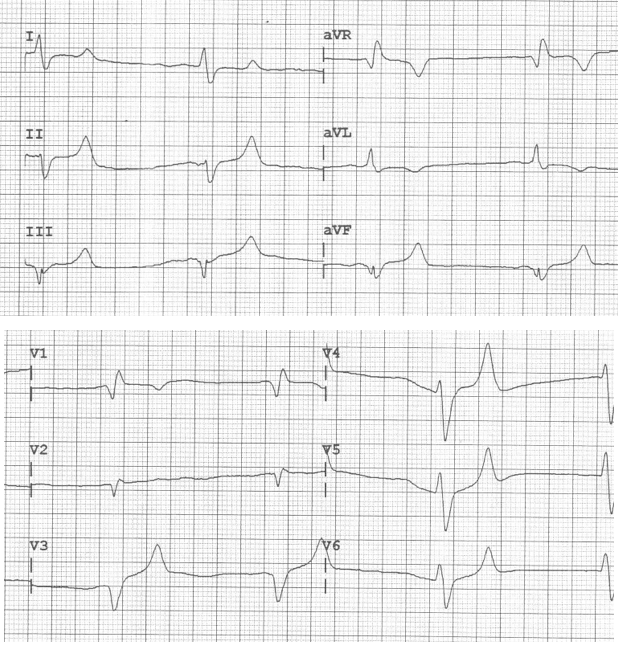
What test
- Aspirin
- Calcium
- Dextrose
- Sodium bicarbonate
Equation for osmolality
2 × [Na+] + glucose/18 (normal range, 275 to 290 mOsm/L)
Treatment of seizing patient with hyponatremia?
The initial treatment includes infusion of 100-150 mL 3% hypertonic saline over 15–20 min, May repeat 150 mL of 3% hypertonic saline up to 3 total doses,or a total of 450 mL IV of3% hypertonic saline
Rate of sodium correction for hypernatremia?
Acute: 1 mEq/L/h
Chronic: 0.5 mEq/L/h or 10 to 12 mEq/24 h
Prolonged QTc, flattened T wave, U wave
Treatment for hyperkalemia with mechanism of action of each step in treatment
1. Calcium (chloride or gluconate) - stabilizes the cardiac membrane
2. Sodium bicarb - shifts potassium intracellularly
3. Insulin and glucose - shifts potassium intracellularly
4. Albuterol - upregulates cyclic adenosine monophosphate and shifts potassium intracellularly
5. Lasix - increased renal secretion of potassium
6. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) or
sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma) - increases GI potassium secretion
7. Hemodialysis
What is the difference between osmolarity an osmolality?
Osmolarity is the measure of solute concentration per unit volume of solvent. Osmolality is the measure of solute concentration per unit mass of solvent.
What are 5 symptoms of osmotic demyelination syndrome?
Dysarthria, dysphagia, lethargy, paraparesis or quadriparesis, seizures, and coma.
What can occur if you correct chronic hypernatremia to quickly?
Cerebral Edema
Name 5 signs or symptoms of hypokalemia
Hypertension, orthostatic hypotension, malaise, weakness, fatigue, hyporeflexia, cramps, paresthesias, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention
What are the main EKG changes based on different potassium levels?
6.5–7.5 = Prolonged PR interval, tall peaked T waves, short QT interval
7.5–8.0 = Flattening of the P wave, QRS widening
10–12 = QRS complex degradation into a sinusoidal pattern