The amino acid whose side chain only contains a single methyl group
What is Alanine?
The type of inhibition that decreases Vmax, but leaves Km unaffected
A tightly bound group to an enzyme that is not made of amino acids, but still critical to the function of that enzyme.
What is a prosthetic group?
Cooperativity explains this phenomenon in hemoglobin.
What is hemoglobin's ability to bind oxygen easier as more oxygen bind?
The two structures associated with secondary protein structure
The amino acid that looks like this:

What is glutamine?
The enzyme will experience these changes to Km and Vmax when bound to an uncompetitive inhibitor
What is a decreased Km and Vmax?
The enzyme that utilizes a catalytic triad
What is chymotrypsin?
This specialized molecule can stabilize the "T" state of hemoglobin
What is 2-3-BPG?
A pathogen that solely consists of amino acids
What is a prion?
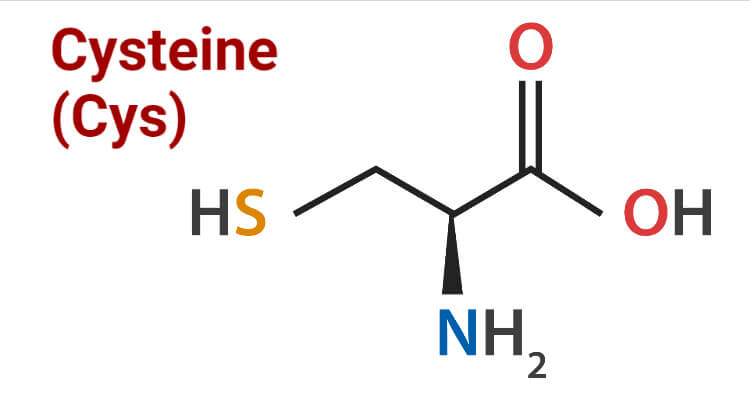
The amino acid responsible for disulfide bonds
What is Cysteine?
The site in which a noncompetitive inhibitor will bind to
What is the allosteric site?
The maximum speed at which a given enzyme will catalyze a reaction.
What is Vmax?
Hemoglobin can bind and release oxygen much easier in this state.
What is the "R" state?
The change in entropy as a protein folds.
What is -deltaS?
The group of amino acids that generally have a protonated side chain at physiological pH
What are basic amino acids?
The condition in which a competitive inhibitor will bind
What is when substrate is not bound to the enzyme?
The role of histidine in the chymotrypsin mechanism. (think nucleophile/electrophile, acid/base)
What is a base and acid?
The condition that causes sickle-cell hemoglobin to polymerize.
What is the exposing of a hydrophobic patch in sickle cell hemoglobin during the "T" state?
The type of secondary structure represented by shading in the top left region of a Ramachandran plot
What are alpha helices?
The one-letter code equivalents to this peptide chain:
What is RVY?
Uncompetitive inhibition will cause Km to decrease, which by itself will result in this effect on enzyme velocity.
What is increased enzyme velocity?
The definition of Km conceptually.
What is the substrate concentration [S] at 1/2 of Vmax?
This structure can freely move once an oxygen binds to a hemoglobin monomer, affecting R and T state equilibrium.
What is the alpha helix attached to the heme group?
What is when change in enthalpy is negative?