HPV testing is not recommended in women less than 30 years of age because
High prevalence of transient HPV infection at this age
Females <15 years at the time of the first dose How many doses and what should be the schedule
a 2-dose schedule (0, 6 months) is recommended
Please see the cervix after application with acetic acid and diagnose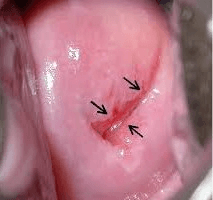
Negative VIA test
What are the three important management components for glandular abnormailities.(AGC)
Colposcopy
endocervical biopsy
endometrial biopsy
What is a key piece of information we as providers need to know about the colposcopy in order to determine treatment modalities?
Whether colposcopy was adequate or inadequate
In the “screen-and-treat approach”, the decision to treat is based on
a positive primary screening test only
How many type of HPV vaccines are available
Bivalent, quadrivalent and Nonavalent
A 40 years old patient attends gynecology clinic with history of intermenstrual and post coital bleeding. Please see the cervix after application of acetic acid. What is your diagnosis?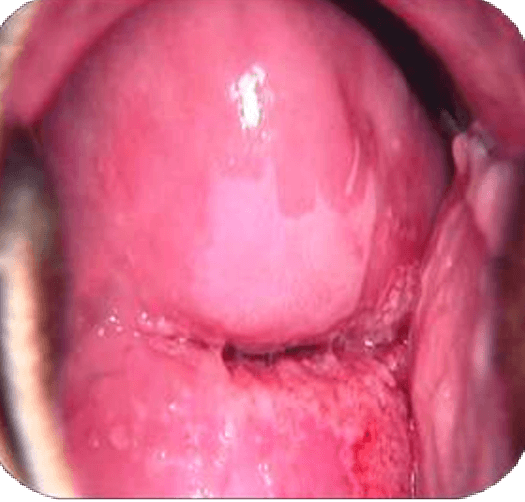
VIA positive and suggestive of HSIL
Your patient is 32 years old with HPV positive on primary screening. For triage she underwent VIA which is positive. She is not eligible for ablative treatment.
what should be the next step?
LLETZ
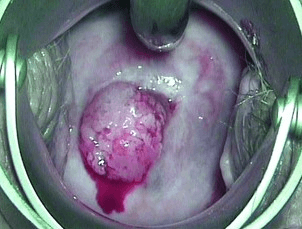 A 49-year-old multiparous woman attends the screening clinic with the complaint of postmenopausal bleeding per vaginum. Below is the finding on her speculum examination. what should be the next step?
A 49-year-old multiparous woman attends the screening clinic with the complaint of postmenopausal bleeding per vaginum. Below is the finding on her speculum examination. what should be the next step?
suspicious of cervical cancer so needs histopathological examination
In the “screen, triage and treat approach”, the decision to treat is based on
a positive primary screening test followed by a positive second test (a “triage” test), with or without histologically confirmed diagnosis.
If primary screening with HPV is negative how should we follow
Rescreen with HPV test in 5 to 10 years for the general population of women and in 3 to 5 years for women living with HIV
When should a VIA positive woman undergoing cryotherapy have repeat screening?
One year
what percentage of women with LSIL will have CIN 2 and 3 on cervical biopsy?
15-20%
what percentage of women with HGSIL will have CIN 2 and 3 on cervical biopsy?
70-75%
In Screen-and-treat approaches which two screening tests are used.
HPV and VIA
Females ≥15 years at the time of the first dose what is the dosing schedule
a 3-dose schedule (0, 2, 6 months) is recommended.
VIA is appropriate to use in women upto which age and why?
in women whose transformation zone is visible (typically in those younger than 50 years).
This is because once menopause occurs, the transformation zone, where most pre-cancer lesions occur, frequently recedes into the endocervical canal and prevents it from being fully visible
Should cryotherapy using a double versus single freeze technique be used in women with histologically confirmed CIN?
Double freeze using a 3 minute freeze, 5 minute thaw, 3 minute freeze cycle
For the managemnt of CIN 2 and 3 Cone biopsy is recommended.
what are the three types of Cone biopsy?
cold knife cone biopsy
LLETZ Cone Biopsy
Laser cone biopsy
- Women living with HIV are how many times more likely to develop cervical cancer compared to women without HIV.
Six times
A 27 year old woman is found to be HPV positive and a VIA triage result is positive.
what are the management options?
Cryotherapy at the same visit
Colposcopic guided biopsy followed by treatment based on biopsy report
Colposcopy followed by LLETZ at the same visit if high grade lesions are suspected
what are the three types of transformation zones
Type 1: The entire transformation zone is visible. The transformation zone is entirely visible and only ectocervical.
Type 2: The entire transformation zone is visible. The transformation zone is entirely visible and has an endocervical component.
Type 3: The transformation zone is not entirely visible. The transformation zone extends into the endocervical canal and is not fully visible.
What are the criterias for eligibility for ablative treatment
There is no suspicion of invasive cancer or glandular disease (i.e. adenocarcinoma or adenocarcinoma in situ, AIS).
The transformation zone is fully visible, the whole lesion is visible, and it does not extend into the endocervix.
The lesion is type 1 transformation zone.
A 19 year old woman, sexually active since the age of 15, has a Pap smear result as “ ASC-H
colposcopy suggests CIN2
For CIN 2- Observation is preferred in adolescent ( as long as colp is satisfactory)
Colposcopy and cytology at 6 month intervals for upto 2 year
Treat only if CIN 2 persists for 2years