What are the two main characteristics of DNA structure? Is DNA charged?
Double helix and antiparallel.
Yes, Negative
Proteins used in the initiation of replications and their functions?
Topoisomerase: Relieves overwinding strain ahead of replication forks.
Helicase: Unwinds parental double helix at replication forks by breaking H bonds.
Single-Stranded Binding proteins: Binds to and stabilizes single-stranded DNA until it is used as a template
Primase: Synthesizes an RNA primer at 5′ ends of the leading strand and at 5′ ends of each Okazaki fragment of a lagging strand
What are the steps of gene expression for Eukaryotic cells? Where does each step take place?
NUCLEUS Transcription: DNA --> pre-mRNA
NUCLEUS RNA processing pre-mRNA: --> mRNA
CYTOPLASM Translation: mRNA --> Protein
What is an operon?
A unit of genetic function found in bacteria and phages. Consisting of a promoter, operator, and regulatory section of a gene.
What is a nucleotide made of? What is the backbone called?
Phosphate group, deoxyribose (sugar), nitrogenous base.
Sugar-phosphate backbone.
What is the leading strand template direction and lagging strand direction
Leading Template: 5' --> 3'
Leading strand: 3' --> 5'
Lagging Template: 3' --> 5'
Lagging strand: 5' --> 3'
Things needed for transcription? In what direction is the RNA strand created?
1. Promoter sequence (TATA Box) + Transcription factors + RNA Poly II = Transcription Initiation Complex
DNA 3' --> 5'
mRNA 5' --> 3'
What are the repressor and the corepressor?
repressor: inhibits gene transcription. Bind near the promoter.
Corepressor: binds to the repressor and changes its shape allowing it to bind to the operator.
Purines: G, A. Pyrimidines: T, C, U (RNA).
Hydrogen bonds.
A=T (2 H bonds), C=G (3 H bonds)
Remaining enzymes for actual replication and their functions?
DNA Polymerase III: synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the RNA primer.
DNA Polymerase I: Removes RNA nucleotides of primer from 5′ ends and replaces them with DNA nucleotides added to 3′ ends of the adjacent fragment
DNA Ligase: Joins Okazaki fragments of lagging strand; on the leading strand, joins 3′ end of DNA that replaces primer to rest of leading strand DNA
NO
For prokaryotes: terminator sequence stops RNA poly II
Eukaryotes: Polyadenylation signal. Protein-bound to this poly-A-Tail cuts the mRNA from the polymerase.
What is Euchromatin and Heterochromatin?
Euchromatin: a less condensed form of chromatin; available to transcribe.
Heterochromatin: chromatin is very condensed; NOT available to transcribe.
Chromatin: complexes (nucleosomes) of DNA wrapped around histone proteins (positively charged proteins)
What are the three models of DNA replication? Which one do we think is correct nowadays?
Conservative, semiconservative, dispersive
You have a drug that blocks the activity of Primase. How will this drug affect DNA replication?
Synthesis of both complete lagging and leading strands will stop.
Three things to remember about RNA processing (What is added to both ends and what is actually changed)
Addition of a 5' cap (modified guanine)
Poly-A-tail: 50-250 A sequence to 3' end
RNA splicing: RNA cut and paste
How can chemical modifications regulate gene expression?
1. Histone acetylation: addition of acetyl group to histone tails (neutralize the positive charge of histones); promotes transcription by opening chromatin up.
2. DNA Methylation: addition of methyl group on DNA bases (mostly C); promote or inhibit translation
Difference between DNA and RNA
1. RNA has a ribose, while DNA has deoxyribose sugar
2. RNA single-stranded, DNA double-stranded
3. RNA has Uracil, rather than Thymine in DNA
Two types of mistakes repair of DNA replication
Mismatch repair: other enzymes remove and replace incorrectly paired nucleotides.
Nucleotide excision repair: a nuclease (DNA-cutting enzyme) removes and correctly replaces damaged segments of DNA.
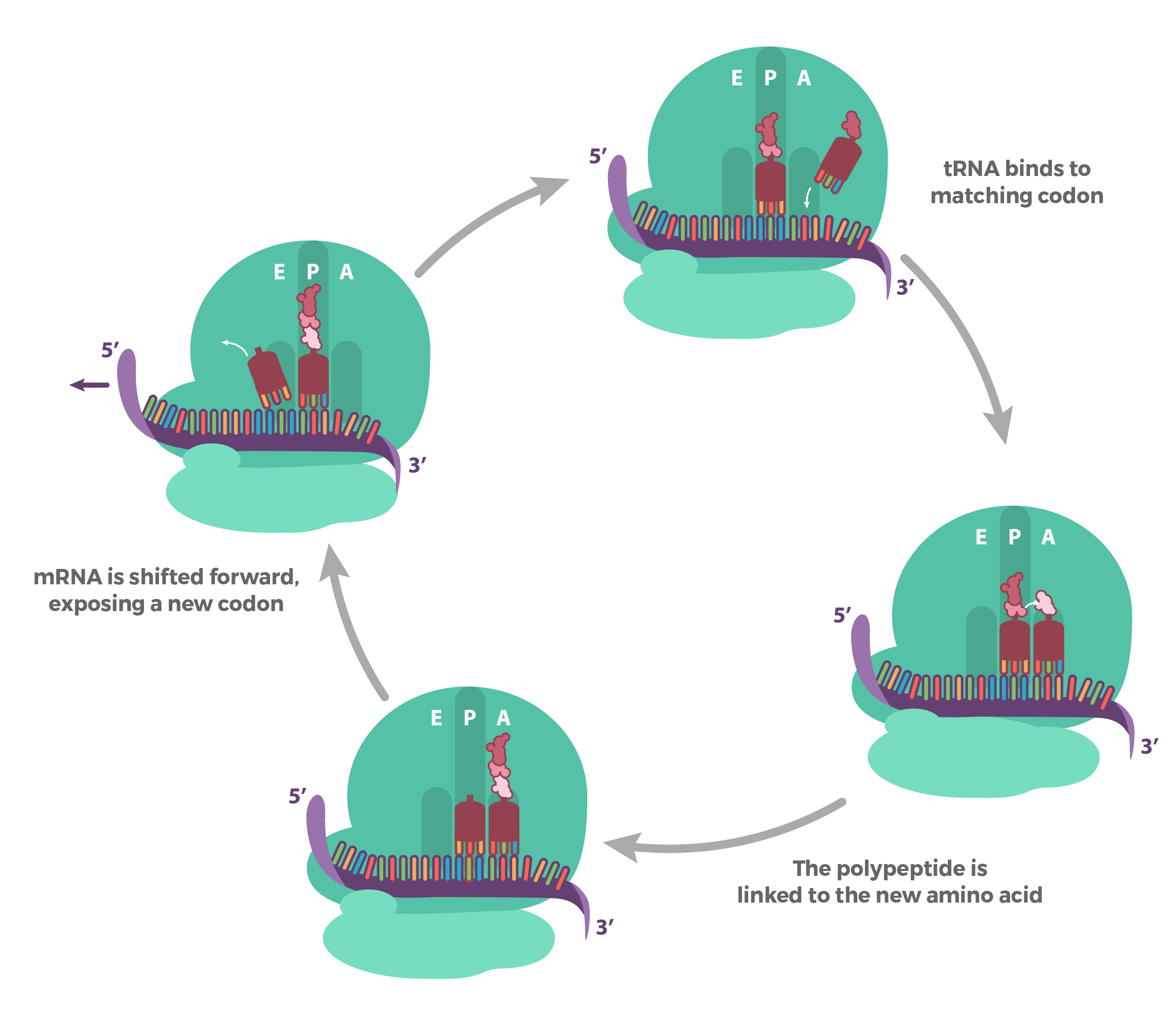
What are the binding sites of the ribosomes in translation?
EPA sites
Inducible operons: off can be turned on. (i.e. lac operons (metabolism starts when allolactose is detected); catabolic (break down)
Repressive: on but can be turned off when the corepressor binds to the repressor; anabolic (building up)