Why do viruses need a host?
What is:
- Their metabolic enzymes are nonexistent.
- They lack ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis.
- Without host machinery, they are unable to replicate.
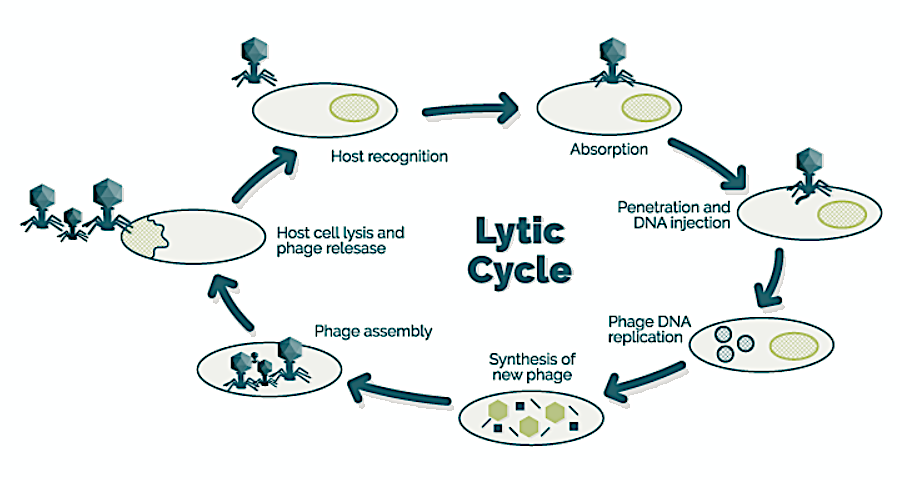
What is the Lytic Pathway?
What is:
- Lytic (also known as frontal assault): In 5/6 key phases, the virus attaches, replicates, and destroys the host cell.
What are some diseases that are caused by viruses?
What is:
Covid 19, Chicken pox, Polio, Hepatitis, Measles.
How can we identify prokaryotes?
What is:
- Prokaryotes have ribosomes, cell walls, necleoid (no nuclear membrane), and cells.
- Prokaryotes are smaller than eukaryotes and lack organelles.
What is vertical gene transfer?
What is:
- In bacterial cells, vertical gene transfer describes the movement of genetic material from a parent cell to its offspring during cell division. The inheritance of genetic traits and the long-term evolution of bacterial populations are both caused by this kind of gene transfer.
- Bacteria reproduce quickly.
- Most organisms reproduce through fission.
- Plasmids can replicate when bacteria do.
What are some characteristics of a virus?
What is:
- Viral organisms are not cells
- Viral particles are much smaller than ribosomes (20–50 nm) in size.
- Viral reproduction is confined to the host cell.
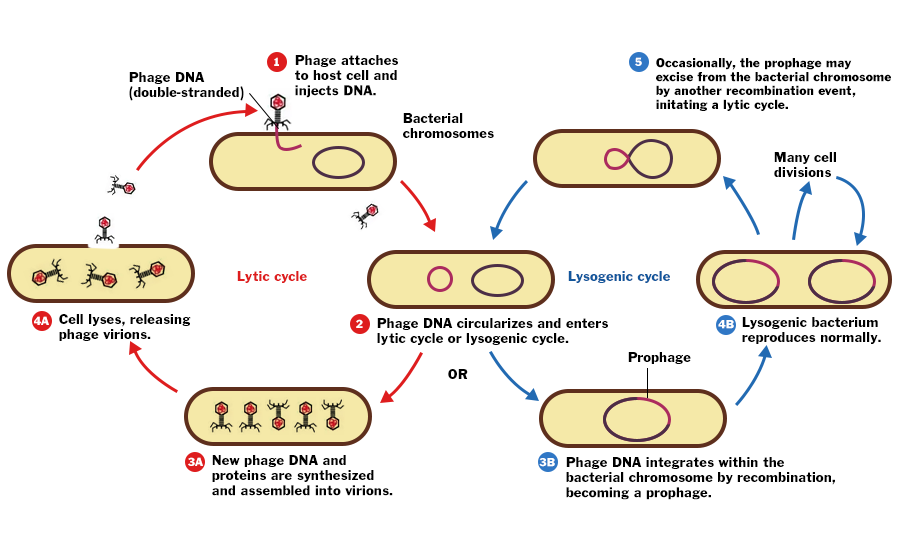
What is the Lysogenic pathway?
What is:
- Lysogenic (also known as a stealth attack): the virus binds to the host and incorporates viral DNA into it; as a result, all newly formed cells become infected. (sun, stressed...)
How do we classify bacteria by shape?
What is:
We can remember to classify bacteria by their shape with the following:
- Bacili (Baguette shaped)
- Cocci (Cookie shaped)
- Spirilli ( Spiral shaped)
What are the parts of a bacterial cell?
What is:
What is horizontal gene transfer?
What is:
- In bacterial cells, horizontal gene transfer describes the exchange of genetic material between several bacterial cells that are not parent and offspring. Via mechanisms like transformation, transduction, and conjugation, this process can take place and lead to the receiving cell acquiring new features.
What parts are found in all viruses?
What is:
- Genome: collection of genetic data that can be either linear or circular and can be made of DNA or RNA.
- Capsid: Protein-coated shell
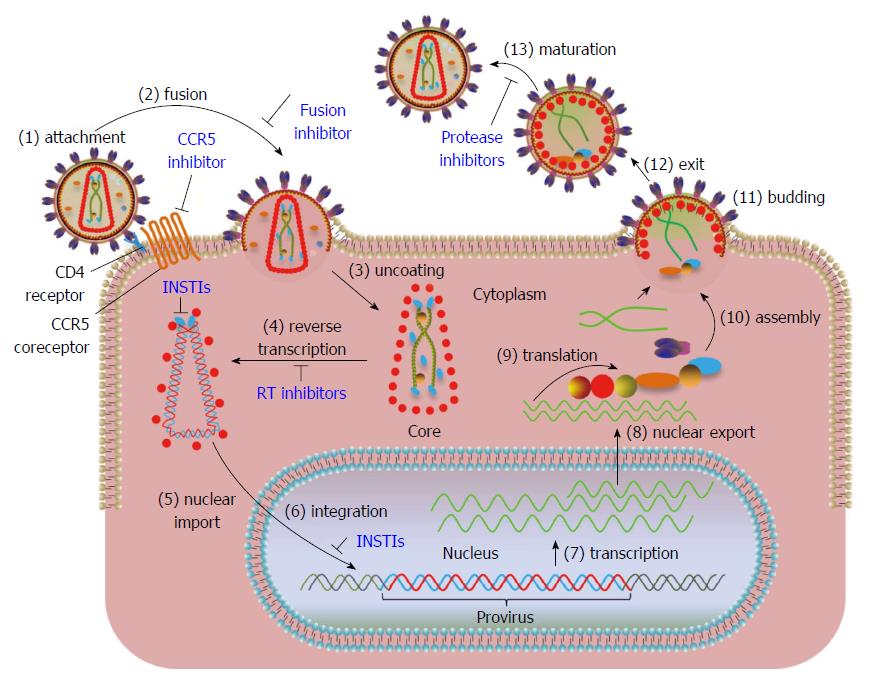
Describe the Retrovirus Pathway.
What is:
- Retroviruses include RNA.
- RNA needs to be changed into DNA.
- The required reverse transcriptase enzyme is present in the virus.
- Retroviruses often have a high rate of mutation.
What are the two types of prokaryotes?
What is:
1. Bacteria, which are the most ancient prokaryotes and contain cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), which are photosynthetic N fixers
2. Archaea - a more recent organism than bacteria Extremophiles and methanogens should be mentioned (like salty, hot, acidic environments)
What are the parts of the bacterial cell that contain genetic material?
What is:
- A loop of necessary DNA is found in the nucleoid.
- Plasmids are tiny DNA circles with supporting properties.
What are the 3 types of Horizontal gene transfer?
What is:
1. Transformation: take on surroundings
2. Conjugation: Exchange with another bacteria that is still alive.
3. Transduction: Viral agents ingest DNA from different bacteria.
What is "host range"?
What is:
- Host range: the different sorts of cells and creatures that a virus can infect.
- Certain viruses, like rabies, have a wide host range (all mammals)
- Some, like rhinoviruses (colds), have a limited host range. - Specific respiratory system cells
What can change the things that can be infected by a virus?
What is:
- The way in which something is infected is limited (host)
- Glycoproteins function as keys and locks.
- Compatibility with membranes
What is is an example of emerging viruses (appeared or are increasing in incidence, geographic range, or severity of disease)?
What is:
SARS, Hantavirus, Covid-19, Ebola.
What parts of the bacterial cell help with movement?
What is:
- Flagellum, which moves the entire cell.
- The Pili, a shorter version of the flagellum that aids in attachment and DNA exchange
What is the name of the technique that allows scientists to selectively modify genes in a particular organism?
What is:
- Genetic engineering: The process of selectively altering an organism's DNA involves adding, removing, or changing particular genes using tools like CRISPR in order to produce desired features or treat genetic disorders.
What parts are found in some viruses?
What is:
- Glycoproteins: surface-bound proteins that aid in host binding
- Separate sections: such as the bacteriophage's head and tail.
- Lipid Envelope: taken from host cell
What are the general 5 steps in the replication of a virus?
What is:
Attachment: The virus identifies and binds to certain receptors on the surface of the host cell to connect to it.
Entry: The virus enters the host cell either by endocytosis, where it is absorbed by the cell, or by fusing its envelope with the cell membrane.
Replication: The virus releases its genetic material (DNA or RNA) once inside the host cell and uses the tools of the host cell to duplicate itself. This entails the replication of the viral genetic material as well as the creation of viral proteins.
- Assembly: The newly synthesized viral components come together to form new virus particles inside the host cell.
Release: The newly assembled virus particles are then released from the host cell, either by budding out from the cell membrane or by causing the cell to rupture and die, and can then go on to infect other cells and repeat the replication cycle.
What process can lead to the emergence of new viral infections and pandemics by allowing viruses to evolve and jump from one species to another?
What is:
- Cross-species transmission, can cause pandemics and novel virus diseases.
Describe the outer layer and and the plasma membrane of the bacterial cell.
What is:
Outer layers
- Slime layer: keeps bacteria wet and sticky to attache to surfaces.
- Capsule: protection, stops some microorganisms from hurting the cell.
- Cell Wall: keeps form.
Plasma Membrane:
- The line dividing a cell and its surroundings
- Facilitates respiration (energy as ATP)
- Facilitates reproduction
How is vertical gene transfer different from horizontal gene transfer?
What is:
- Vertical gene transfer occurs when genetic material is passed down from parent to offspring during cell division or replication, maintaining the genetic continuity of the bacterial lineage. Horizontal gene transfer, on the other hand, occurs when genetic material is transferred between different bacterial cells that are not directly related, such as through conjugation, transformation, or transduction. Horizontal gene transfer can lead to the acquisition of new traits, such as antibiotic resistance, that can rapidly spread through bacterial populations. In contrast, vertical gene transfer is responsible for the gradual accumulation of genetic changes over generations that contribute to bacterial evolution.