A 59 yo gentleman with hx of HFrEF (EF 35%) presents with decompensated heart failure. You auscultate his lungs and astutely tell him that his presentation is consistent with left heart overload. What did you likely hear and in what lung fields?
What are bibasilar crackles/rales. Also acceptable is cardiac wheeze
Commonly obtained in the ED, this imaging modality is relatively inexpensive and can sometimes help distinguish pneumonia from pulmonary edema.
CXR
What are the 4 medications all patients with HFrEF should be on (if no contraindication) which have been shown to improve outcomes including mortality?
What are beta blocker, ACE/ARB/ARNI, MRA, SGLT2i.
Diuretics improve hospital readmission but not mortality.
65yo F with HFrEF (EF 37%), CKD2, HTN presents with decompensated heart failure. Her home diuretic dose is PO lasix 40mg BID. She is HDS and without any electrolyte abnormalities. What is a good starting diuretic, route (IV vs PO) and dose while inpatient?
IV lasix 40mg (at least).
PEARL: Good rule of thumb to try 2-2.5x home diuretic dose. IV lasix = 2*PO lasix
A 65yo M with hx of HFrEF (EF 25%), diet controlled DMII, HTN, HLD presents with progressive weight gain, shortness of breath and leg swelling for 5 days. He has been smoking 1ppd daily x35 years. He has been adherent to his home chlorthalidone 25mg daily, metoprolol xl 50mg daily (decreased from 100mg 2 weeks ago), losartan 50mg daily (increased from 25mg 2 weeks ago), and lasix 40mg BID (recently decreased from 60mg BID). He says he takes all his medications. What is the likely cause of his exacerbation?
What is underdiuresis?
PEARL: always check for changes in medication/doses and assess adherence
Define orthopnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea

This natriuretic hormone was initially identified in the brain but is released in large quantities with elevated ventricular filling pressures. Values are lower than expected in patients with obesity.
What is BNP/NT-proBNP
A 63yo F presents with decompensated heart failure and volume overload. She is HDS without s/s of shock. At home, she diligently takes carvedilol 25mg BID and PO lasix without any recent missed doses. In addition to starting IV diuresis, should you continue her beta blocker?
YES! Always continue beta blocker while inpatient unless they were not adherent, you are worried about cardiogenic shock, or they have bradycardia
While on IV diuretics what 2 electrolytes must be monitored and how often (typically)?
What are potassium and magnesium BID
A 54yo M with h/o uncontrolled HTN, DMII, HLD, 40 pack-year smoking hx, CVA, recurrent osteomyelitis of LLE s/p BKA who presents with s/s new onset heart failure. He reports chronic exertional angina. He also mentions a recent 3 day trip to South America for business. What is the most likely etiology of his heart failure.
Ischemic cardiomyopathy
Partial credit for Chagas Dz
Ultrasound imaging of this great vessel can help you estimate central venous pressure.
What is the IVC?
What is the mechanism of action of Sacubitril/valsartan (entresto)?
What is angiotensin receptor block/neprilysin inhibitor.
PEARL: One reason that we tend to check NT-proBNP over BNP is that BNP will be sky high in anyone taking entresto regardless of volume status.
Today, you are discharging your patient who came in with a CHF exacerbation. At home, she was taking PO lasix 40mg BID. You want to switch her to daily torsemide. What dose of torsemide should you prescribe to achieve the same daily diuretic dose?
What is torsemide 40mg daily.
PEARL: 40mg PO lasix = 20mg IV lasix = 20mg PO torsemide = 1mg bumex
You are asked by the ED to evaluate a patient with known heart failure with progressing b/l leg swelling. He denies shortness of breath, chest pain, orthopnea, PND. He is adherent to his heart failure medications and was recently started on amlodipine for uncontrolled HTN. His vitals are wnl, heart and lung sounds nl. Exam only notable for 2+ pitting edema to shins in BLE. What is the likely etiology of his leg swelling?
AMLODIPINE!
The presence of this heart sound (not a murmur) may increase your suspicion of volume overload.

A 84yo M with HFrEF (EF 10%), HTN, HLD presents with acute on chronic heart failure. His HR is 105, BP 110/85 and labs are notable for a sodium of 128, potassium of 5.1, and a Cr of 2.5 (bl 1.2). Lactate is 1.1 (normal). He is very volume overloaded on exam. Urine studies are consistent with pre-renal azotemia. How do you manage his volume status?
DIURESE. Cardiorenal syndrome
A 84yo M with HFrEF (EF 10%), HTN, HLD presents with acute on chronic heart failure. His HR is 105, BP 90/54 and labs are notable for a sodium of 128, potassium of 5.1, and a Cr of 2.5 (bl 1.2). Lactate is elevated to 4. He is AAOx1-2 (unclear baseline). At home, he is adherent to metoprolol, losartan, spironolactone, and PO torsemide. Which GDMT medications would you continue for admission?
NONE! Hyperkalemia and concern for cardiogenic shock
A 88yo male with HTN, HLD, BPH, HFrEF (EF 35%) presents with decompensated heart failure and is initiated on IV diuresis. For the last 2 days, he has had minimal urine output despite escalating doses of his diuretic. His renal function is normal. What is the next step?
What is bladder scan?
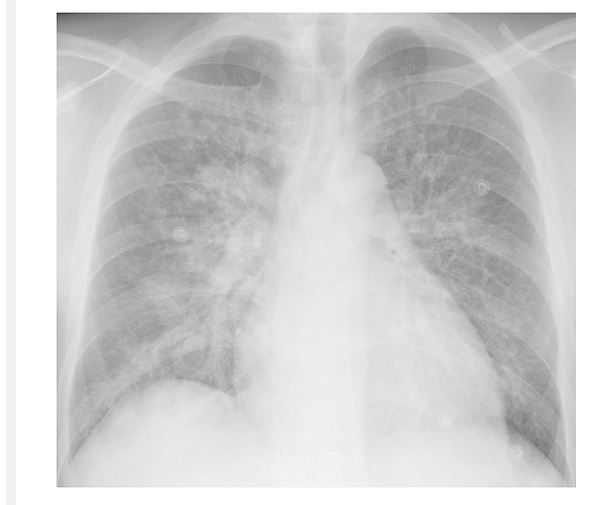 A patient with known HFrEF presents with sudden onset dyspnea requiring BiPAP. His CXR is shown here. His vitals are stable while on BiPAP. Exam is notable for diffuse lung crackles and a loud systolic murmur. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A patient with known HFrEF presents with sudden onset dyspnea requiring BiPAP. His CXR is shown here. His vitals are stable while on BiPAP. Exam is notable for diffuse lung crackles and a loud systolic murmur. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute MR!
Something that patients with heart failure should track daily at home to allow for early intervention and potentially prevent heart failure admissions.
What are daily weights?
PEARL: Always ask you heart failure patients what their "dry weight" is. If they don't know and you can't find it in the chart, document their weight on the day of discharge.
64 yo F with HFrEF (EF 25%) presents with decompensated heart failure. Her labs are notable for a Cr 3.1 (bl 1.9), Na 129, AST 239, ALT 341, Alp 380, T bili 1.9. Lactate 1.2 (nl). Hepatitis panel is negative, HIV neg, RUQ US shows gallbladder wall edema. What is the likely cause of the elevated LFTs?
Congestive hepatopathy!
PEARL: Note "shock liver" usually presents with LFTs usually close to or in the thousands. There have also been several HF patients who underwent unnecessary cholecystectomies due to concerning US findings.
A 84yo M with HFrEF (EF 10%), HTN, HLD presents with acute on chronic heart failure. His HR is 105, BP 90/54 and labs are notable for a sodium of 128, potassium of 5.1, and a Cr of 2.5 (bl 1.2). Lactate is elevated to 4. He is AAOx1-2 (unclear baseline). In addition to diuresis, what other medication would you consider using?
What are inotropes - dobutamine or milrinone (probably dobutamine in this case since patient has an AKI and milrinone is renally cleared)
A 48yo F with hx of HFrEF (EF 28%), CKDIV, HTN, DMII presents with septic shock 2/2 UTI requiring ICU admission. During her stay, she receives 4L IVF and her GDMT and her home diuretics are held. Her course is c/b volume overload, mixed shock and hypoxia 2/2 pulmonary edema. She is maxed out on a lasix gtt but only makes 30cc UOP. She is HDS. PVR is normal. What is the next step for volume management?
What is dialysis (HD vs CRRT)
64 yo F with h/o HTN, HLD, HER2/neu-positive breast cancer s/p chemo now in remission presents with new onset dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, PND and LEE. She gets a TTE showing an EF of 32%. She has a prior history of smoking 1ppd x45 years. She had a recent CTA chest showing minimal coronary calcium. What is the likely etiology of her HF?
Trastuzumab induced cardiotoxicity.
PEARL: This agent causes largely reversible HF but anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity is usually irreversible