What is Economics?
The study of how individuals allocate scarce resources among many competing users.
Draw a demand curve and label the axes.
See board.
Draw a supply curve and label the axes.

Due to a trend, people have started buying leather chairs in the Sherwin-Williams color Lupine. What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity?
Equilibrium price and quantity increase.
Define Opportunity Cost.
The value of the next-best option.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Production_Possibility_Frontier_PPF_Apr_2020-01-b1778ce20e204b20bf6b9cf2a437c42e.jpg)
Describe points X, Y, and B.
B = attainable and efficient
X = attainable but inefficient
Y = unattainable
Chairs and tables are complements. The price of tables increases. What happens to the demand curve for tables?
There is a movement up and to the left on the demand curve.
The government imposes taxes on sellers of chairs. What happens to the supply curve? What if the government give chair producers subsidies?
It shifts to the left.
With a subsidy, it would shift to the right.
The market equilibrium is at $20 and 200. Is a price floor of $21 binding or non-binding?
Binding
Define Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Microeconomics: small-scale, examining individuals and specific markets
Macroeconomics: large-scale, examining total output, price level, and other aggregate measures
Quantity Total Cost
0 3.00
1 8.00
2 11.00
3 13.00
4 14.50
5 16.00
What is the Marginal Cost (MC) of the 4th good?
MC of 4th good = $1.50
A change in consumer income results in people buying more chairs. Are chairs a normal or inferior good?
Normal good
The supply curve shifts left.
Dr. Neuroscientist buys plastic to create her brain-improving helmet. However, the price of plastic increased. What happens to equilibrium price and quantity?
Equilibrium price increase, quantity decreases
A binding price ceiling intersects the supply curve at a quantity of 20 and the demand curve at a quantity of 45. Does this create a shortage or surplus? How big is it?
This creates a shortage of 25.
You are choosing between three jobs.
1. Pays $15 - $4 of gas.
2. Pays $13.
3. Pays $16 - $4 in fees.
What is the opportunity cost of the 2nd job?
$12
There is a decrease in the price of Gatorade. What happens to the demand curve for Powerade?
The demand curve for Powerade shifts to the left (down).
A farmer plows his field by hand. However, he is able to buy a tractor after a few years. After a few years of use, the tractor breaks, and the farmer goes back to plowing his fields by hand. What happens to the supply curve in both situations?
The supply curve shifts to the right, then back to the left.
See PowerPoint for Graph.
Consumers Pay: $13
Producers Pay: $4
The cost of a chair is $20. The TB is as follows:
Q: TB:
2 11
4 29
6 60
8 100
How many chairs should you buy to maximize output?
8 chairs

What is the opportunity cost of 1 bike?
1 bike = 1/2 car
Name the determinants of demand.
Income, Price of related goods, Expectations of prices, Number of buyers, Tastes and preferences
Name the determinants of supply.
Technology, Resource Price, Number of Sellers, Price Expectations, (Taxes), (Subsidies)
Due to a shortage of tea leaves, the price of tea rose. At the same time, another coffee shop opened up in Stillwater. What happens to the equilibrium price (P) and quantity (Q) in the market for coffee in Stillwater?
Q increases, P is indeterminate
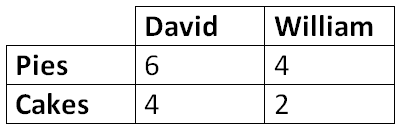
Who has the comparative advantage in producing pies? Who has it in producing cakes?
Pies: William
Cakes: David