Changes in temperature, light, sound, chemical composition of surroundings, humidity or moisture levels, touch or contact.
What are stimuli?
These make up everything.
What are atoms?
The powerhouse of the cell.
What is the mitochondria?
The main source of energy for cells.
What is ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)?
The movement of a molecule down a gradient to reach equilibrium
What is diffusion?
Cells with specialized compartments called organelles and have a nucleus storing DNA.
What are Eukaryotic cells?
These molecules love water and are hydrophilic.
What are polar molecules?
The shape of a plant cell.
What is a rectangle?
The form of energy stored in ATP
What is chemical energy?
The movement of water from low solute concentration to high solute concentration through a membrane.
What is Osmosis?
The process in which characteristics that help organisms live and reproduce are passed to offspring.
What is natural selection?
This reaction occurs when a monomer breaks off from a polymer.
What is hydrolysis?
In the plant cell to hold water and maintain the cell's proper pressure.
What is the large central vacuole?
Theses are three parts of ATP.
What are Adenine, ribose, and triphosphate?
This process moves a molecule across a membrane up its concentration gradients while this process uses a protein to move a molecule across a membrane down its concentration gradient.
What is the difference between active transport and facilitated diffusion?
The term used to describe all living things in earth and is the largest of all organization of life.
What is a biosphere?
These are comprised of a phosphate group, sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base.
What are nucleotides?
These are rod shaped organelles specific to animal cells that are important in carrying genetic information for cell division.
What are Centrioles?
This is where plants get their carbon from to build their own carbon molecule in their cells.
What is inorganic carbon dioxide?
This is when a cell brings water and "drinks."
What is pinocytosis?
Large molecules made up of small molecules and atoms.
What are macromolecules?
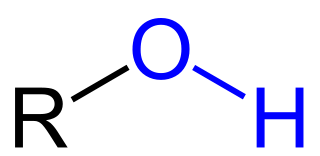 The blue group.
The blue group.
What is a hydroxyl (or alcohol) group?
These allow cells to "talk" to each other.
What are signaling proteins?
These organisms put ATP together using light and need to consume organic carbon molecules.
What are Photoheterotrophs?
This is where the sodium comes from to facilitate the glucose-sodium Symport.
What is the sodium-potassium pump?