and Social Responsibility (2)
Business (4)
organization that provides goods or services to earn
profits
What is business
beliefs about what is right and wrong or good and bad
in actions that affect others
What is ethics
the government agency charged with assisting small
businesses
What is SBA ( Small Business Administration)
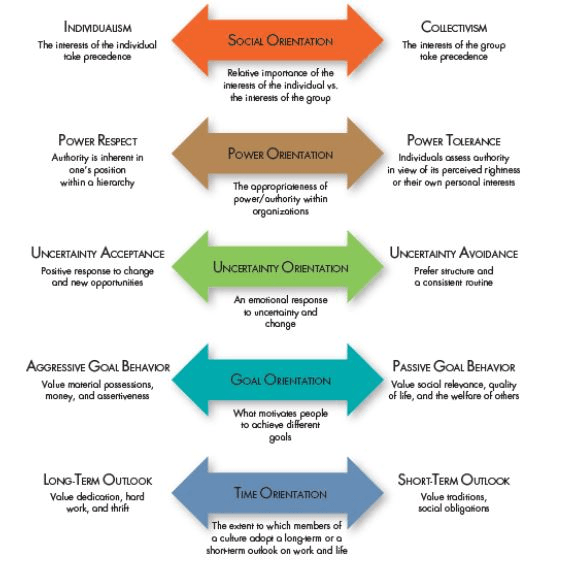
What is
Hofstede’s Five Dimensions of National
Culture
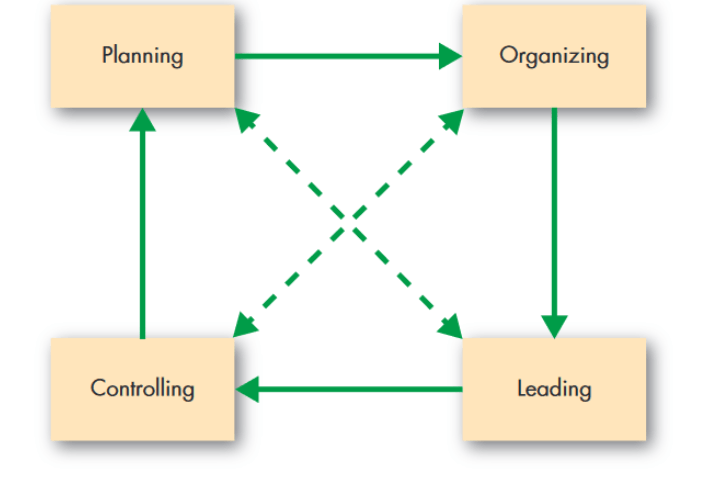
What is the management Process
specification of the jobs to be done within an organization and the ways in which they relate to one another
What is Organizational Structure
1. Gather relevant factual information.
2. Analyze the facts to determine the most appropriate moral values.
3. Make an ethical judgment based on how right or
wrong the proposed activity or policy is.
How do you assess ethical behavior?
the difference between revenue (income or sales) and expenditure (cost of goods or services sold).
What is a profit
* Personal taxation of business income
* Problems managing all aspects of the business
*Problem of personal liability for bank loans
What are the characteristics of a sole proprietorship
document in which the entrepreneur describes her or
his business strategy for the new venture and
demonstrates how it will be implemented
What is a business plan
tax levied on imported product
What is a tariff
1. Paperwork
2. Telephone calls
3. Meetings
4. E-mail
What are the leading causes of wasted time
*characteristic of decentralized companies with
relatively few layers of management
What is a flat organizational structure
Advantages
– Proven business opportunity
– Access to management expertise
• Disadvantages
– Start-up costs
– Ongoing payments
– Management rules and restrictions
What are the advantages and disadvantages of franchising
* Labor
*Capital
* Physical resources
What are factors of productions
those groups, individuals, and organizations that are directly affected by the practices of an organization and who therefore have a stake in its performance
Who are organizational stakeholders
strategic alliance in which the collaboration involves ownership of the new venture
What is a joint venture
1. High-income countries
2. Upper-middle-income countries
3. Lower-middle-income countries
4. Low-income countries
What are the Distinctions Based on Wealth
Helps firms allocate resources
Helps to define corporate culture
Helps managers assess the performance
What are the reasons we set goals
the process of identifying the specific jobs that need to be done and designating the people who will perform them
What is job specialization
The purchase of one firm by another for a price that is paid to the purchased firm’s owner(s)
What is acquistion
1. all firms in an industry must be small, and
2. the number of firms in the industry must be large
What are the conditions for perfect competition
* Commitment
* Independence
* Risk-takers
What are the characteristics of an entrepreneurial
Bank loans
Venture capital companies
SBA financial programs
How do you finance a small business
he ability to produce some products more efficiently
than others
What is comparative Advantage
*Top management begins to formulate a vision of a new company.
*The firm sets up new systems for appraising and compensating employees who enforce the firm’s new values.
What are the steps in managing change
1. Assigning responsibility - the duty to perform an assigned task
2. Granting authority - the power to make the decisions necessary to complete the task
3. Creating accountability - the obligation employees
have for the successful completion of the task
What is the delegation process
agreement among major European nations to eliminate
or make uniform most trade barriers affecting group
members
What is the EU
is demand where significant increases in the price of a product or service will have little effect on the quantity of the product or service demanded. (Example: Dental cleaning price went up slightly)
What is Price Inelastic Demand
A hybrid form of corporation that has limited liability but is taxed as a partnership and therefore avoids double taxation of earnings; also known as a Subchapter S corporation
What is an S-corporation
a segment of a market that is not currently being
exploited
What is a niche
1. Promote trade by encouraging members to adopt
fair trade practices
2. Reduce trade barriers by promoting multilateral
negotiations
3. Establish fair procedures for resolving disputes
among members
What are the goals of the World Trade Organization
organization’s statement of how it will achieve its
purpose in the environment in which it conducts its
business
What is a mission statement
informal communication network that runs through an
organization
What is a grapevine
Step 1: Setting Strategic Goals
Step 2: Analyzing the Organization and the Environment: SWOT Analysis
Step 3: Matching the Organization and Its Environment
What are the steps in formulating strategy