Consider the following reaction:
NH3 = N2 + H2 ∆H = 30.1 kJ/mol
Which way will the reaction proceed if there is an increase in pressure? What about an increase in temperature?
2 NH3 = N2 + 3 H2
An increase in temperature will cause the reaction to proceed right towards products.
An increase in temperature would cause the reaction to proceed right towards products.
What is the biochemical standard state?
pH 7
298 K/25°C
1M of all species
What is a characteristic of a "high energy" bond?
Consider the following reaction:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2. ∆G = 5 kJ/mol
Will this reaction proceed spontaneously. If not, what would make it proceed spontaneously? Give an example.
No, it cannot proceed on its own since it has a positive ∆G and thus it would need to be coupled with another reaction that is spontaneous in order to yield a net negative ∆G. An example of a reaction that could suffice would be ATP hydrolysis.
Consider the following two acids:
Acid A: Ka = 6E3
Acid B: Ka = 2
What are the pKas and which acid is the stronger acid?
Acid A: pKa = -log(6E3) = -3.77815
Acid B: pKa = -log(2) = -0.30103
Acid A is the stronger acid
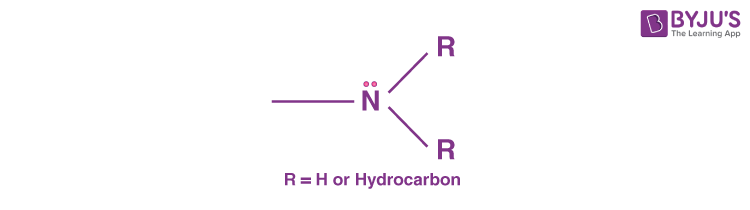
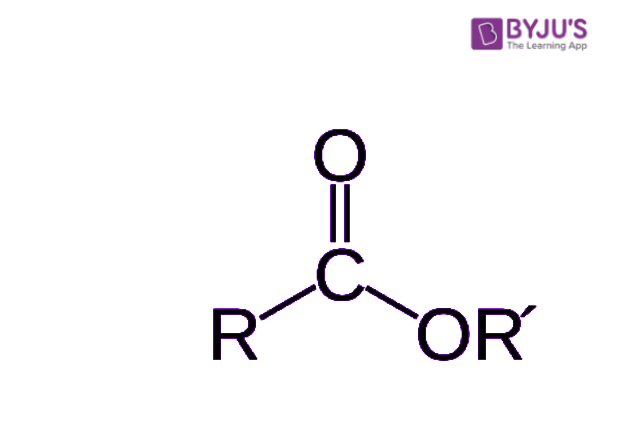
What functional groups are these?


1. Ether
2. Amine
3. Carboxylic Acid
4. Ester
Keq' = 6 x 10-5 and ∆G = 5 x 10-12 J/mol
Which way will the reaction proceed?
Hint: ?
Keq = e-∆G°/RT
6x10-5 = e-∆G°/8.314(298)
∆G° = 24084.9 J/mol
∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ
5x10-12 = 24084.9 + 8.314(298)lnQ
Q = 6 x 10-5
The reaction is already at equilibrium!
We want to work at a pH of 7.5 at 25°C. Which buffer would work best?
TEA: pka = 7.80
Trizma: pka = 8.06
TAPSO: pka = 7.6
TAPSO
DOUBLE JEOPARDY! - Surprise Thermodynamics
Without doing a calculation...
∆H = -5 J/mol
∆S = -2 J/K
T = -250 K
Is this reaction spontaneous?
Yes, but only because this is at a very low temperature
Consider the following reactions:
2 NH3 = NH2 + 3H2 Keq'=.2
NADH = NAD+ + H+ Keq'=10.8
What is the ∆G°'? Is the reaction spontaneous?
Net Keq' = (.2)(10.8) = 2.16
Keq' = e-∆G°'/RT
2.16 = e-∆G°'/8.314(298)
∆G°' = -1907.999 J/mol
The reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions
This molecule has a pKa of around 10.07. Draw its dominant form at pH 4 and pH 12. The molecule shown is at pH 7.
At pH 4, the molecule still has its hydroxide protonated.
At pH 12, the hydroxide has been deprotonated.
Which carbon is more likely to be electrophilic?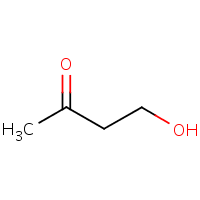
The carbonyl carbon
You have 300.26 moles of CH3COOH (MM = 60.052 amu), .002M CH3COO- and .05M H3O+. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, which side is favored? Find the final concentrations of all species and ∆G at equilibrium.
CH3COOH + H2O = CH3COO- + H3O+
Keq' = 1.75E-5
CH3COOH + H2O = CH3COO- + H3O+
5 M .002M .05M
-x +x +x
5 - x .002+x .05+x
((.05+x)(.002+x))/(5-x) = 1.75E-5
x = .005
Final Concentrations:
CH3COOH = 4.995 M
CH3COO- = .007 M
H3O+ = .055 M
∆G = ∆G°' = -RTlnQ
= -8.314 (298)ln(1.75E-5)
= -.04335751 J/mol
Molecule A has a pKa of 4. What is the percentage of Molecule A's conjugate acid and base at a hydroxide concentration of 1E-7M? Which is the predominant species?
pOH = -log (1E-7) = 7
14 = pH + 7
pH = 7
pH = pKa + log (A-/HA)
7 = 4 + log (A-/HA)
3 = log (A-/HA)
A-/HA = 1000/1
A- = 1000/1001 * 100 = 99%
HA = 1/1001 * 100 = .099%
Conjugate base is the predominant species.
Which molecule is acting as an acid? As a base? As an electrophile? As a nucleophile?
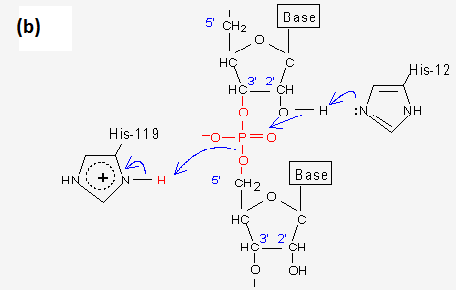
His 12 is acting as a base
The deprotonated oxygen is the nucleophile
The phosphate is the electrophile
His 119 is acting as an acid
