In what direction does a DNA polymerase polymerize?
A) 5'-3'
B) 3'-5'
C) it starts with Guanine and ends with methionine
D) None of the above
A) 5'-3'
What is the central dogma of biology?
DNA->RNA->protein
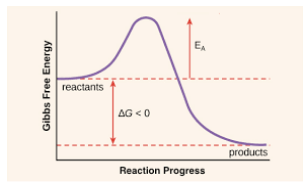
True or false. Enzyme do not effect the Delta G of the reaction.
True. Enzymes only change the Ea, not the delta G
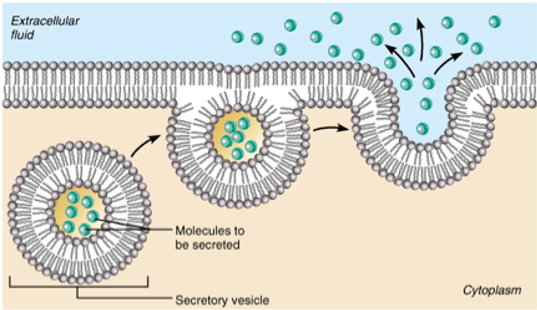
What is this process called?
Exocytosis
Which of the cytoskeletal structure is the largest?
A) Actin
B) Microtubules
C) Intermediate Filaments
D) none of these
B) Microtubules
True or false: Wee1 is a inhibitor kinase and Cak is a activating kinase. When both of these are present, the M-Cdk complex is inactive.
True
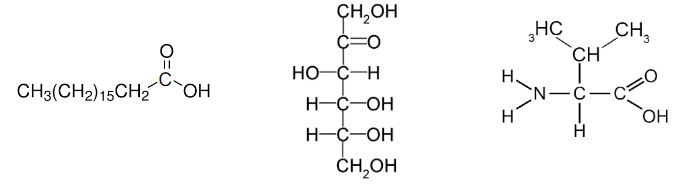
What type of macromolecules best describe these 3 molecules?
From left to right: Lipids, carbohydrates, amino acids/proteins
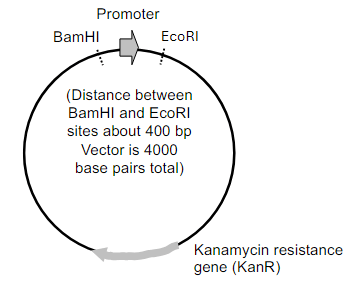
If you were to digest this plasmid with EcoRI and BamHI, how many fragments would you get?
2 fragments
Which of the following si the most widely used activated carrier molecule?
A) GTP
B) ATP
C) hydrogen ion pumps
D) hydrolysis reaction
B) ATP
A) Golgi apparatus
B) Nucleus
C) Lysosomes
D) Endoplasmic reticulum
E) Mitochondria
A) Golgi apparatus
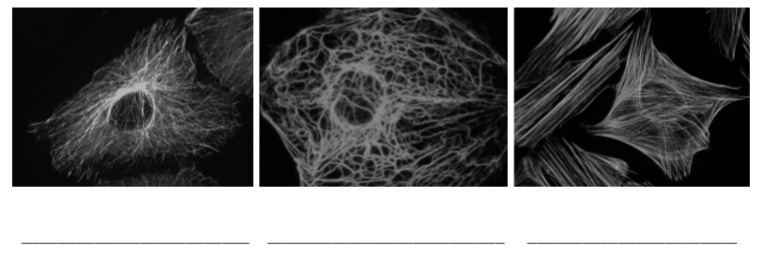 Name each of these cytoskeletal structures.
Name each of these cytoskeletal structures.
microtubule
intermediate filaments
actin
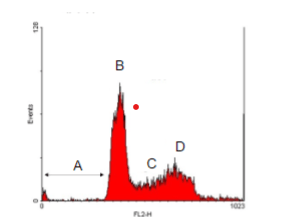 What stage of the cell cycle is represented in the histogram above. (name each stage A-D)
What stage of the cell cycle is represented in the histogram above. (name each stage A-D)
A) Apoptosis
B) G1
C) S
D) G2 + M
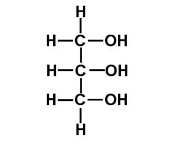 What is the molecular weight of this molecule?
What is the molecular weight of this molecule?
92 g/mol
O= 16 g/mol
C= 12 g/mol
H= 1 g/mol
What is the amino acid sequence for this DNA template strand?
3'TAC TTC AAA CCG ATT5'
DNA template 3'TAC TTC AAA CCG ATT 5'
DNA Compliment 5'ATG AAG TTT GGC TAA3'
mRNA 5'AUG AAG UUU GGC UAA 3'
Protein Met Lys Phe Gly stop
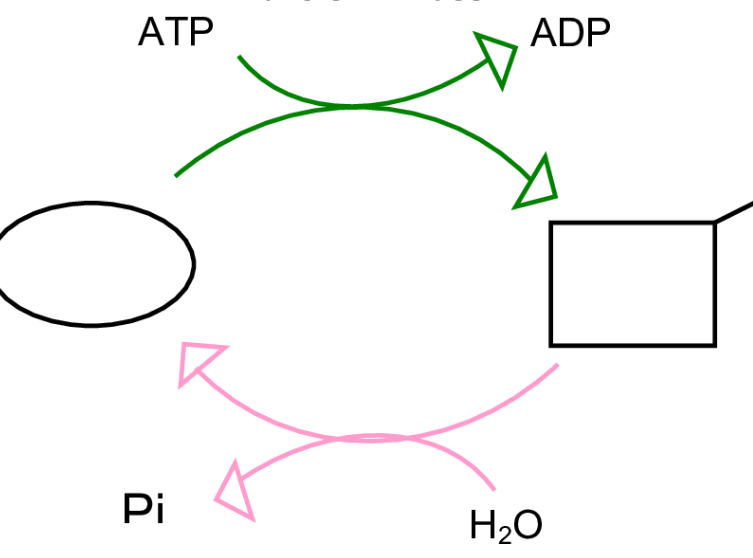
what are the two enzymes involved with this reaction?
Top is kinase
bottom is phosphatase
True or False, proteins that are embedded into membranes or secreted are typically made in the ER
True. ER makes lipids and if a protein has hydrophobic regions, it will need lipids to surround.
True or False: Dynein and Kinesin are motor proteins but dynein move to the negative end and kinesin move to the positive end of a microtubule
True
What protein is involved with regulating the cell cycle. Specifically it checks for DNA damage.
P53
What separates the strands of DNA for PCR and cellular DNA replication?
A) Helicase (PCR), Topoisomerase (DNA)
B) Taq polymerase (PCR), Topoisomerase (DNA)
C) DNA Polymerase (DNA), Taq polymerase (PCR)
D) Helicase (DNA), Heat (PCR)
D) Helicase (DNA), Heat (PCR)
If protein X is very abundant in a cell, which one of the following is most likely true?
A) There is only one copy of gene x in the genome
B) mRNA for protein x is abundant in the cell
C) the promoter of gene X is not accessible by the polymerase
D) mRNA for protein X is rapidly degraded
B) mRNA for protein X is abundant in the cell
mRNA is what drives protein production because we translate from mRNA to protein
Pick the correct statement about GTPases.
A) GTPases are like ATP where the phosphate is added to a GDP-bound protein
B) A bound GDP to a binding protein is considered off and the only way to turn it on is to replace GDP with GTP
C) GTP bound to a binding protein is inactive and GTP is phosphorylated, it is active
D) GTPases are superior than ATP and are more abundant
B) A bound GDP to a binding protein is considered off and the only way to turn it on is to replace GDP with GTP
Which of these statements are true about endocytosis?
A) Endocytosis is when the cell is moving molecules out of the cytoplasm and into the extra cellular matrix
B) Pinocytosis is involved with the ingestion of fluid and small molecules by a vesicle
C) Phagocytosis is the ingestion of large particles such as foreign cell or cellular debris
D) limocytosis is the secretion of small signaling molecules that leave the mitochondria but not the cell
E) Both B and C
E) Both B and C
The major type(s) of enzyme-linked receptors are couple to: (select all that apply)
A) dehydrogenases
B) Kinases
C) polymerases
D) GTPases
E) Isomerase
Both B and D
How does loss of Retinoblastoma (Rb) allow for the formation of tumors?
RB is bound to an inactivated transcription regulator (E2F). When RB is phosphorylated, it will cause a confirmation change and release E2F which will then lead to cell proliferation. The loss of RB will lead to E2F freely activate and make the cell go through cell division abnormally.
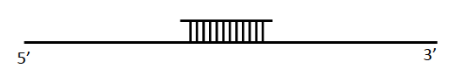
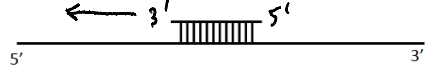
If a DNA polymerase and dNTPs were added to the template and annealed primer above, which direction would the polymerase travel?
Insulin is made by beta cells in the pancreas, myoglobin is made by muscle cells. If you genetically replaced the promoter for myoglobin with the promoter for insulin, what would happen?
The promoter is needed to start synthesizing the mRNA for that protein. All cells have the same promoter but not the same activators available.
1) The pancreas would not make Insulin and muscle cells would not make myoglobin unless the same activators are available.
2) if all the activators are available, the pancreas would start to create myoglobin and muscle cells would start making insulin.
you have 3 proteins in a vial. One that has a high affinity for Nickel, one that is 30 kd, and one that is negative. The protein you are interested in has an overall negative charge. How would you separate the other two proteins from the one you are interested in?
Ion exchange chromatography
Which of these molecules is a classic example of a receptor mediated endocytosis?
A) Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
B) Dynamin
C) v and t SNARE
D) none of the above
E) All of the above
A) LDL
Kinases are important signaling proteins because they can: (select all that apply)
A) amplify pathways
B) rapidly be turned off or on
C) efficiently degrade proteins
D) hydrolyze GTP to GDP
E) freely pass through membranes to initiate signaling
A, B and C
What would happen if Bcl2 gene was expressed at all time and at high levels?
A) Bcl2 does not contribute to the cell cycle and is involved with expression of lipid bound proteins
B) Bcl 2 regulates the cell cycle by creating proteins that block apoptosis. high expression levels would result with the cell to grow indefinitely
C) Bcl 2 turns on apoptosis when it detects an abnormality in the cell cycle. High expressions would lead to immediate cell death.
D) High Bcl 2 expression would result the cell to become arrested during mitosis and won't allow the cell to continue until it has corrected the issue.
B