What is the name of the most outer layer of a hair called?
cuticle
What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines?
Purines: 2 rings
Pyrimidines: 1 ring
What is the monomer of proteins?
amino acids
When a biopsy is done on a tumor what does it mean if it is benign?
non cancerous
What is a phenotype?
the expressed trait
prokaryotic infectious agent that can be treated with an antibiotic.
bacteria
What is the function of thrombocytes?
What is the common name for thrombocytes?
blood clotting
platelets
What are the 5 manners of death?
homicide, suicide, natural, accident, undetermined
What elements make up carbohydrates?
CHO
what does diploid mean?
2 copies of each chromosome
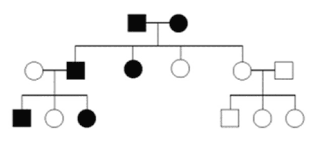
How many males have the trait.
3
How does an antibody help fight infections?
Antibodies are specific to antigens found on pathogens. They are released from B-cells and can disable a pathogen by attaching to it and signaling to send more white blood cells to help fight the infection.
What are the parts of a nucleotide in DNA?
deoxyribose, phosphate, nitrogenous base
What is rigor mortis?
stiffening of the muscles after death
Which pressure number shows the blood pressure when the heart is contracted?
systolic
How does blood sugar raise when you haven't eaten in a long time?
When blood sugar is low, the alpha cells of the pancreas release glucagon. Glucagon travels to the liver and causes glycogen to break down into glucose that is then released into the blood stream
If a heterozygous mom and homozygous recessive dad for a trait have children. What is the probability their children will be heterozygous for the trait?
50%
If a bacteria turns pink after gram staining.
Are they gram positive or gram negative?
Do they have thick peptidoglycan layer or a thin peptidoglycan layer?
negative
thin
If blood clotted with A antibody and B antibody, but not with Rh antibody. What would that blood type be?
What blood type can be donated to this person?
Blood Type:
AB-
Who can donate?:
A-, B-, AB-, O-
What is the function of valves?
keep the blood from going backward
136/90
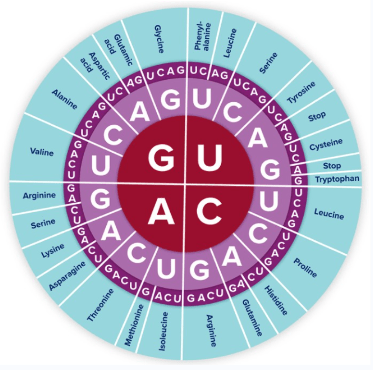
ATACTGCCCGCGAATCCTACAAG
Transcribe and translate the above DNA sequence.
A TAC TGC CCG CGA ATC CTA CAA G
U AUG ACG GGC GCU UAG GAU GUU C
Met-Thr-Gly-Ala
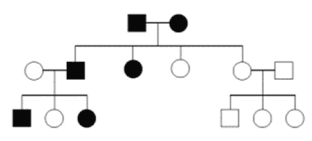
Is this a dominant or a recessive trait?
Dominant
A person comes into the ER and is having pains in their left arm, along with trouble breathing, sweating and feels too fatigued to walk on their own.
What would you triage this patient as and why.
Emergent
trouble breathing and heart problems
How does gel electrophoresis separate DNA? (there are 2 answers needed)
size and charge
Trace the blood flow through the heart starting and ending at the right atrium. Include all valves, chambers and blood vessels.
RA>tricuspid valve>RV>pulmonary valve>pulmonary artery>pick up oxygen at lungs>pulmonary vein>LA>bicuspid (mitral) valve>LV>aortic valve>aorta>give oxygen to body>superior and inferior vena cava>RA
What is the function of high density lipoprotein?
takes cholesterol to the liver to be broken down
Explain 3 differences between mitosis and meiosis.
mitosis:
makes somatic cells
1 division
creates 2 identical cells
PMAT 1 time
pulls apart chromatids
Meiosis:
makes gametes
2 divisions
creates 4 genetically different cells
homologous chromosomes pair up
PMAT 2 times
pulls apart homologous chromosomes and chromatids
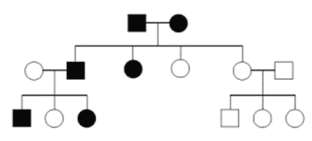
What is the genotype of generation II person 2?
Bb
heterozygous
Draw an example of cell in a hypertonic solution. Write in percentages or show with dots where the solute is located. Show the movement of water. Explain what will happen to the cell (bigger, smaller, same size) in this solution.
water moves out
cell will be smaller
more solute outside