Build up of electric charge
What is static electricity
North and South
What are the poles of a magnet?
Size of the charge and the distance between the charges
What two factors affect the electrostatic force?
Mass of the object and the distance between each object
What are the two factors that affect the gravitational force?
The smallest basic unit of matter
What is an atom?
Electric charge flows through easily
What is a conductor?
Repelling magnetic forces
N-N or S-S
Charging by contact
What is conduction?
Increasing the size of the object or decreasing the distance between the objects
What are ways to increase the gravitational force?
Attracted to protons
What are electrons?
Electric charge does not flow through easily
What is an insulator?
Attractive magnetic forces
N-S or S-N
Charging by rubbing
What is friction?
Proportional relationship
What is the relationship between the mass of an object and the gravitational force?
Attracted to electrons
What are protons?
Wood, plastic, glass, and rubber
What are insulators?
The magnetic force gets weaker
What happens when the distance between two magnets increase?
Charging without touching
What is induction?
Inversely proportional relationship
What is the relationship between distance and the gravitational force?
Attract each other
What do protons and electrons do?
Copper, Steel, and Aluminum
What are examples of conductors (metals)?
The magnetic force gets stronger
What happens when the distance between two magnets decrease?
Conduction and friction
What are two ways to charge an object using contact?
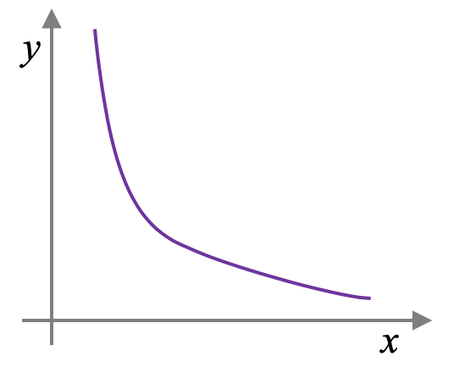
What is an inversely proportional relationship?
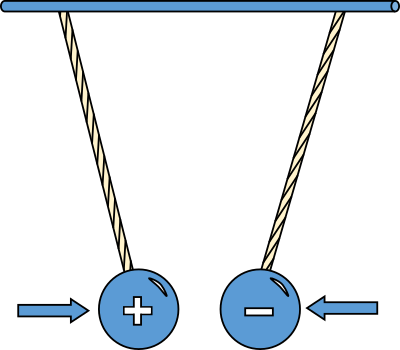
What is attraction?