How many ST-A Units do we have?
- 1
In this CXR, the (Left lung compressed [arrowheads]; Trach shifted to right [arrow]; Heart shifted to contralateral side [redline]; Depressed left hemidiaphragm [orange line]). 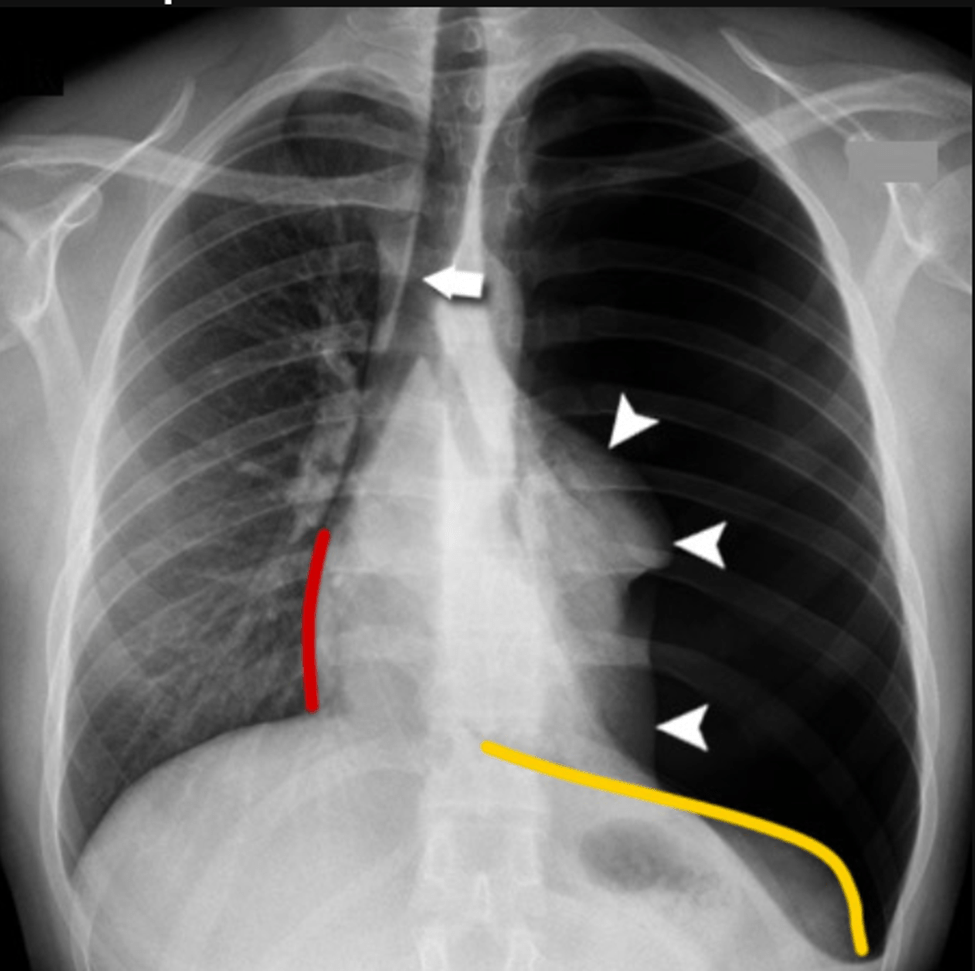
- What is Tension Pneumothorax
- Two factors of the lung that impact volume delivery to the patient via mechanical ventilation ______ and _____
What is resistance and compliance
- This is a classic sign of pediatric Asthma
what is wheezing?
We use this to diagnose pneumothorax in babies
What is CXR?
What is Transillumination?
This Resmed unit/mode provides the equivalent to "auto-cpap"
What is autoset
In this CXR, (From Left ventricular failure; enlarged heart and upper zone levels appear prominent). A procedure used to treat is Thoracentesis.
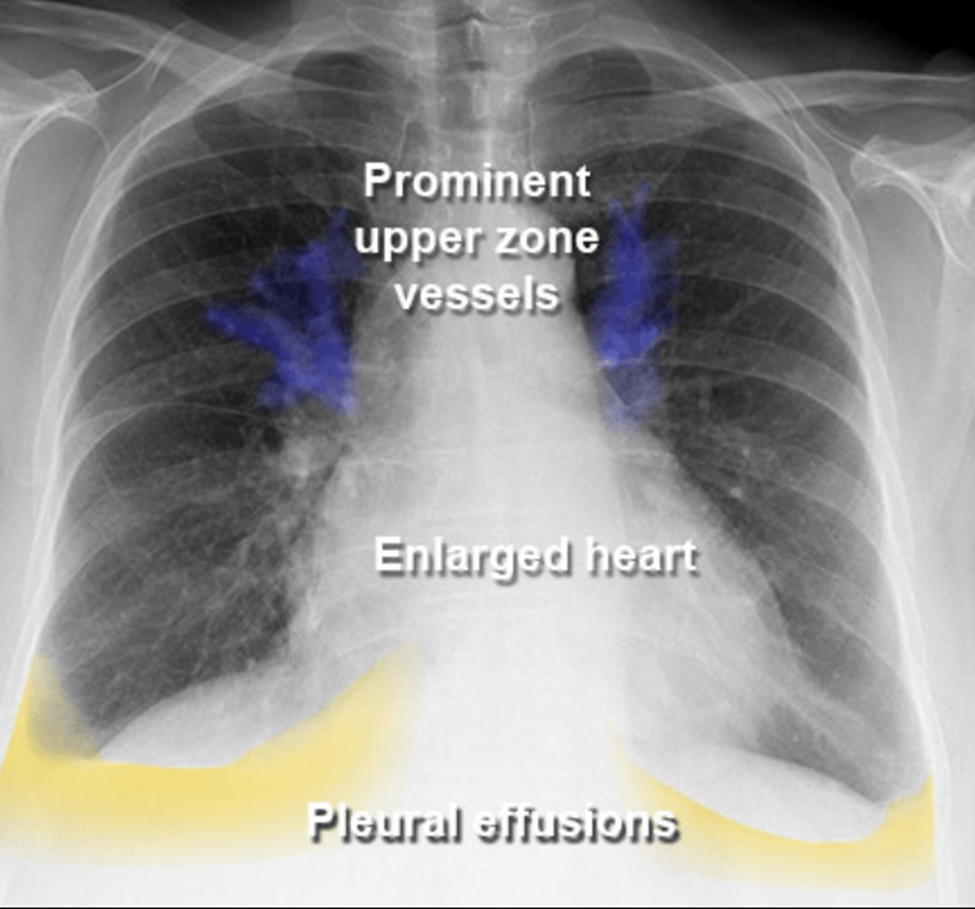
- What is Pleural effusion
A cardiovascular effect of increased PEEP
What is decreased venous return
- Most frequent non-environmental trigger of pediatric asthma
what is viral respiratory infection?
- Term infant ventilation is started with ___% FiO2
What is 21% FiO2/RA?
The AirCurve 10 _____ learns, predicts, responds to and optimizes pressures to suit each patient’s own unique breathing pattern.
What is Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV)

In this CXR, there is a (flattened diaphragm; green line is normal diaphragm). Part of the treatment is maintenance corticosteroids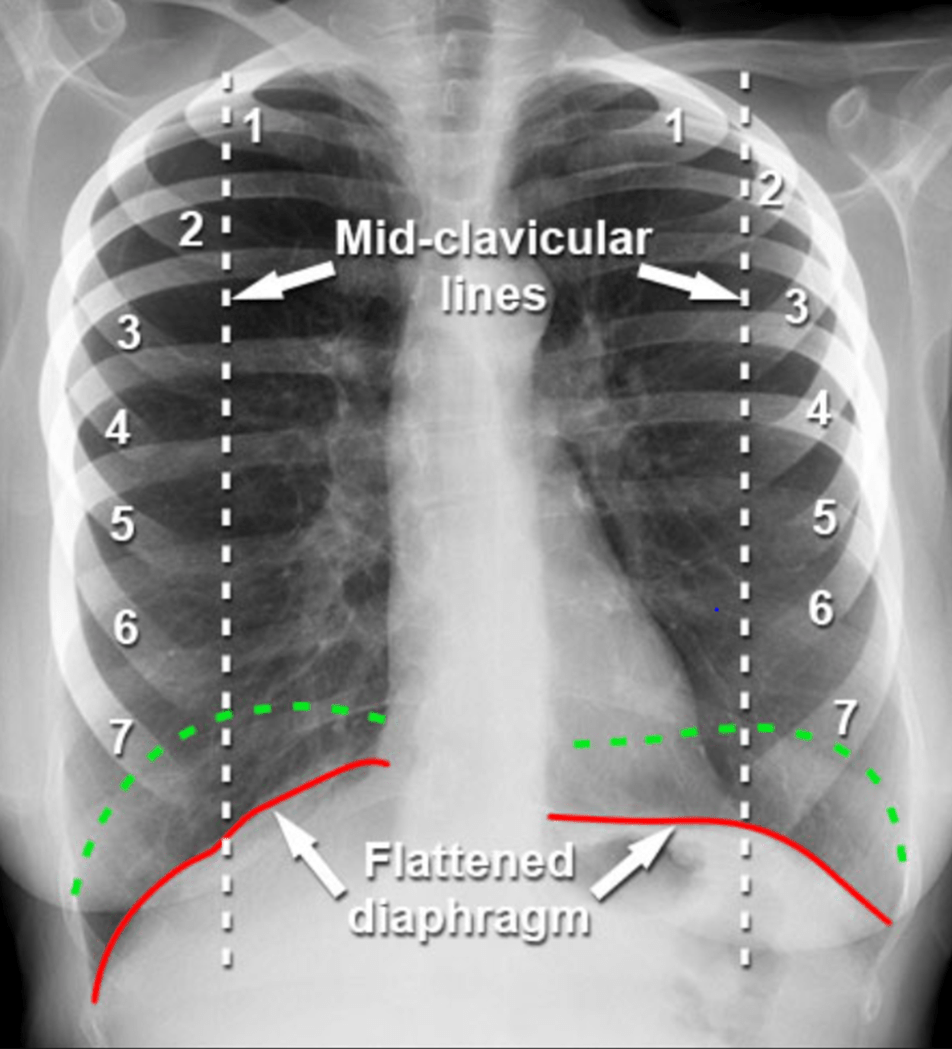
- What is COPD?
- This mode on the Hamilton G5 ventilator allows spontaneous breathing with full support during inspiration and expiration, adapting to patient effort.
What is Adaptive Pressure Ventilation (APV)?
- Plan of care developed by physician that details home management of asthma
What is Asthma action plan?
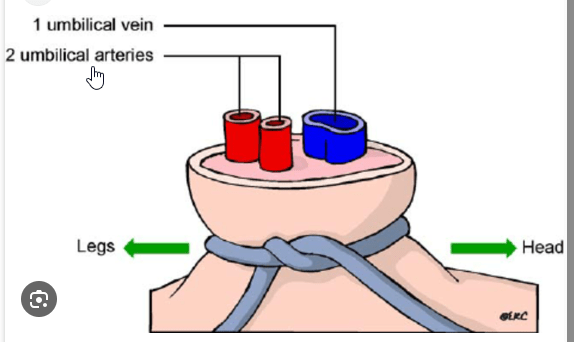
The umbilical cord is composed of:
a)3 arteries
b)3 veins
c)2 arteries 1 vein
d)2 veins 1 artery
What is c) 2 arteries 1 vein
one vein that carries food and oxygen from the placenta to your baby and two arteries that carry waste from your baby back to the placenta
ASV adjusts this setting to respond to a patient's breathing pattern.
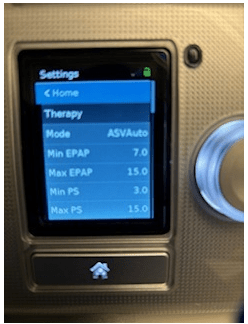
What is pressure support?
In this CXR, there is a Right middle lobe consolidation. Part of the treatement is antibiotics.
What is Pneumonia?
An example of one thing that could be wrong if the high pressure alarm continuously alarms
What is either: 1- Obstruction 2- increased lung resistance 3- decreased lung compliance 4- dyssynchrony 5-Increased airway resistance
- A common chest infection in babies younger than 12 months. The infection causes inflammation and mucus to build up in the airways and makes it more difficult to breathe. Often treat it with HFNC
What is bronchiolitis?
- 32 wk premie has dyspnea, RR of 80 w/ nasal flaring. CXR shows ground glass appearance with air-bronchograms and atelectasis. Diagnosis?
What is Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
This mode is contraindicated in patients with chronic, symptomatic heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF ≤ 45%) and moderate to severe predominant central sleep apnea
What is ASV?
In this CXR, there seems to be a combination of (ILD + Wet lung). What condition could this be? It requires lung protective ventilation.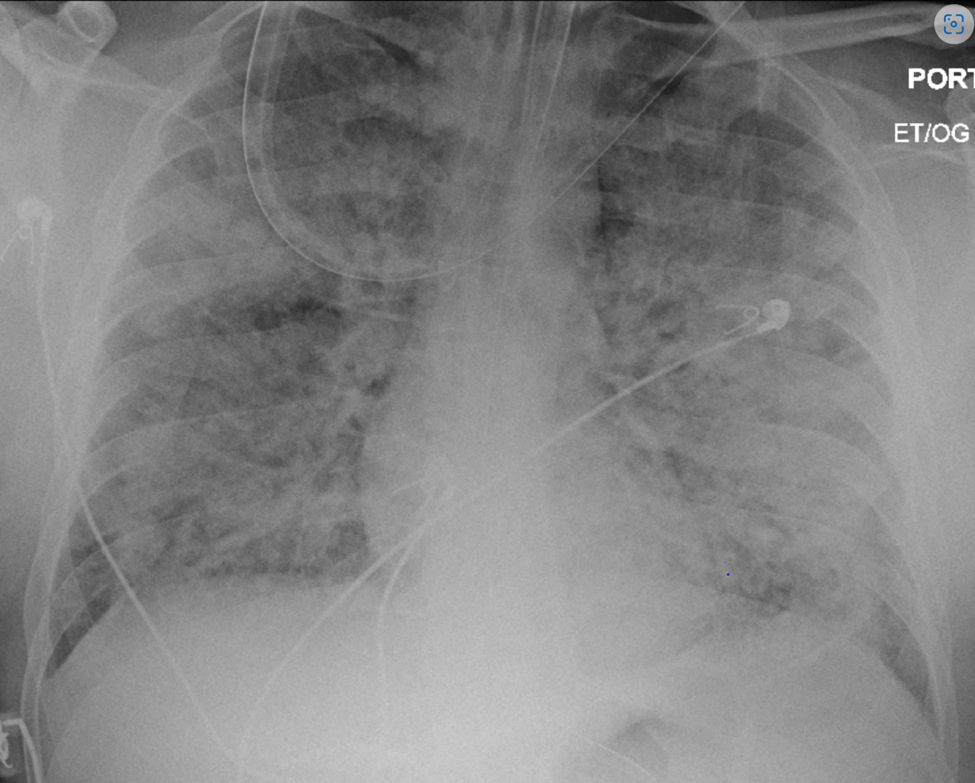
What is ARDS?
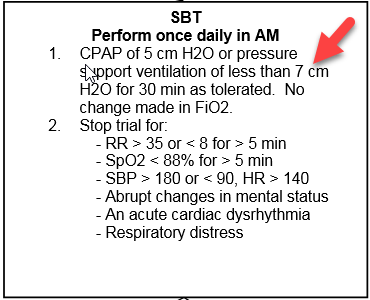
Patient is off sedation, has passed SAT and SBT safety screen. RT changes vent settings to: PS 9; PEEP +5; FiO2 50%. Per KSRO Ventilation Liberation Protocol, is this patient on an SBT trial?
No. Per KSRO protocol, PS settings for an SBT is 7 or less.
- Sound usually caused by a blockage or narrowing in your child's upper airway. May require nebulized epinephrine.
what is stridor?
- 32 wk premie has dyspnea, RR of 80 w/ nasal flaring. CXR shows groudxnd glass appearance with air-bronchograms and atelectasis. Treatments include bubble CPAP and ____?
What is surfactant