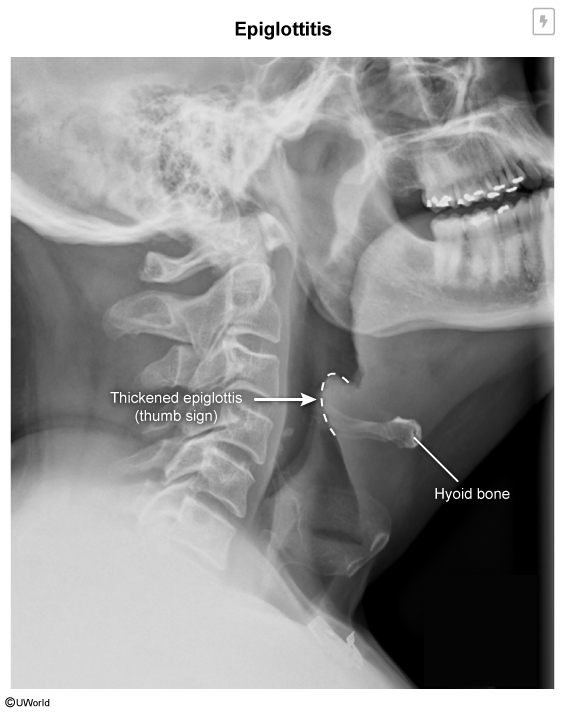
An unvaccinated 3-year-old presents with sudden onset fever, drooling, and is sitting leaning forward. What is the diagnosis?
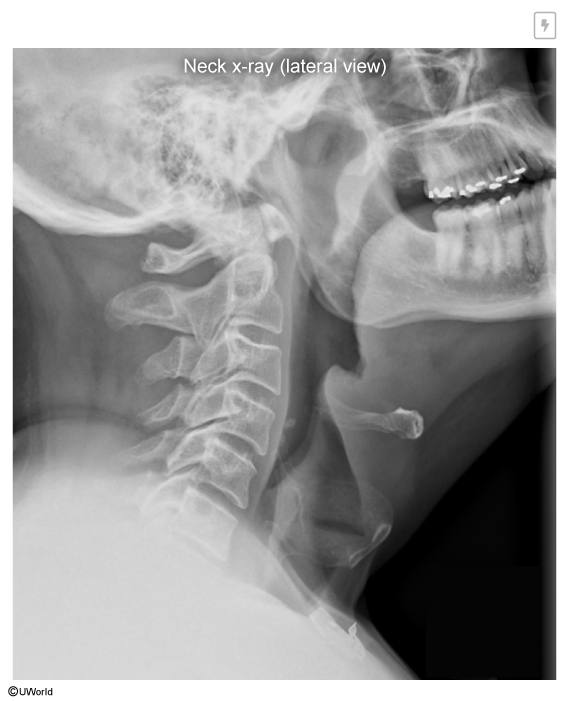
Epiglottitis
Typically presents with stridor, drooling, muffled voice, tripod positioning
A 10-year-old presents to the clinic with the rash seen below. He was visiting family in Massachusetts 2 weeks ago. He does remember pulling a tick off of his skin, but doesn't know how long it was there or what it looked like. The rash is not itchy. They tried using steroid ointment without improvement.
What is the name of the rash and what causes it?
Diagnosis: erythema migrans
Cause: Borrelia burgdorferi causing lyme disease
Treatment: doxycycline
2 years. Rule of 2's - 2 word phrases, 1/2 of speech understandable, knows 2 body parts

Name the 3 most common causes of acute suppurative otitis media in children. What is the first-line treatment?
Streptococcus pneumoniae, nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis.
Treatment: high-dose amoxicillin
Observation can be considered for afebrile children age ≥6 months with unilateral disease and no/mild pain.
Complications: TM perforation, conductive hearing loss (the most common cause in young children), mastoiditis, meningitis
What are the 5 major diagnostic criteria for Kawasaki Disease?
Fever over 100.4 for greater than 5 days
1. Polymorphous exanthem
2. Bilateral conjunctival injection (without drainage)
3. Anterior cervical LAD greater than 1.5 cm
4. Changes in the lips and oral cavity (red, cracked lips, strawberry tongue)
5. Extremity changes (swollen or painful hands or feet, or red or peeling skin)
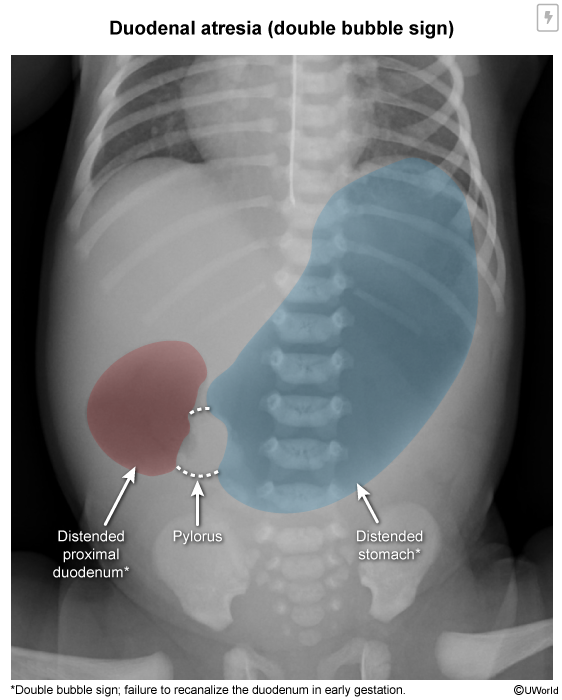
A newborn presents with vomiting and has a "double bubble" sign on x-ray. What is the diagnosis?
What genetic abnormality is commonly associated with this diagnosis?
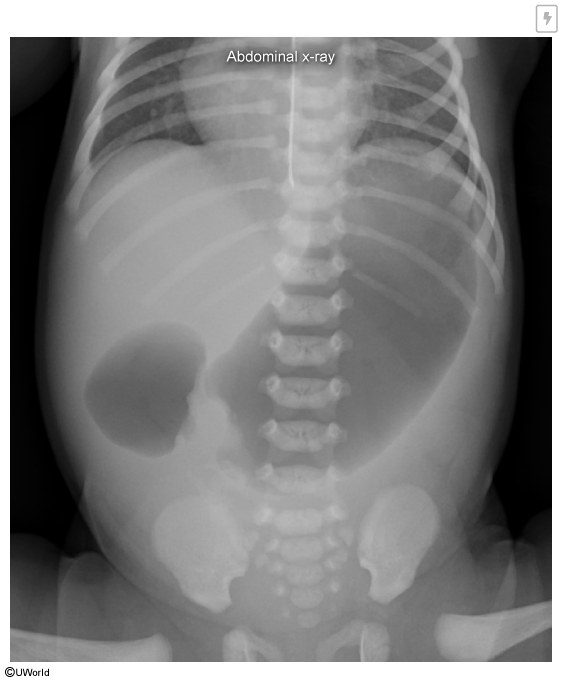
Duodenal atresia
The "double bubble" sign corresponds to air trapped in the stomach and proximal duodenum (atresia prevents air from passing distally).
Trisomy 21 is associated with duodenal atresia
A 4-year-old presents to the ER with a 1 day history of abdominal pain and complaining of ankle pain. The parents noticed that he developed a rash on the back of his legs. On exam, he had swelling of bilateral ankles and a rash on his legs.
What is the diagnosis?

Diagnosis: HSP (IgA vasculitis. Complex immune-mediated vasculitis)
Presentation: palpable purpura, gastrointestinal complaints, arthralgias, and renal involvement.
HSP typically doesn't require treatment and will resolve on its own. Still, children should be monitored for the first six months after diagnosis (BP and urine) to monitor for renal involvement (glomerulonephritis).
12 months

Which 2 bacteria are the most common causes of neonatal sepsis, meningitis, and pneumonia?
Group B Streptococcus (colonizes the genital tracts of some women and can be transmitted to baby during delivery)
Escherichia coli (present in stool that contaminates the delivery field)
Neonatal clinical presentation - temperature instability, poor feeding, respiratory distress (grunting, tachypnea), CNS signs (irritability, apnea, lethargy), jaundice
Treatment: ampicillin and gentamicin
A premature newborn has cessation of respirations for > 20 seconds with associated bradycardia and desaturations. The infant is normal between episodes.
What is the diagnosis? What is the treatment?
Dx: apnea of prematurity (immature central respiratory center in preterm infants)
Treatment: caffeine, noninvasive ventilation (CPAP), typically resolves by the expected due date
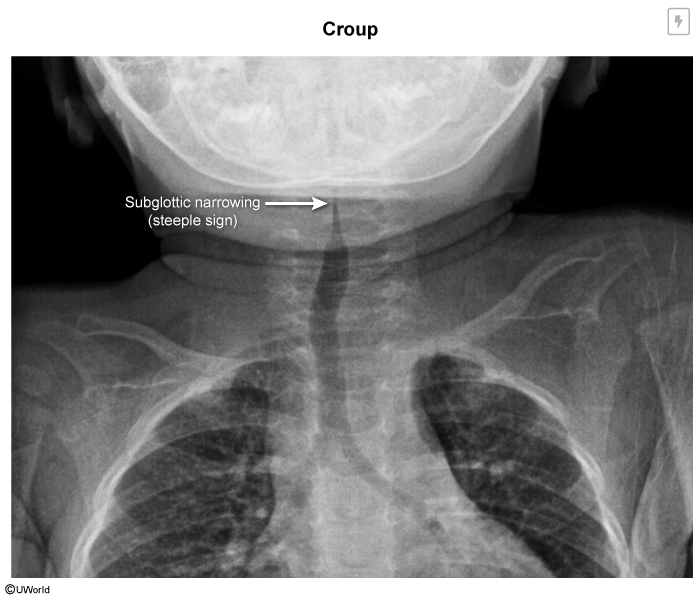
A 2-year-old has a 2-day history of runny nose and low-grade fever. He woke up in the middle of the night with a barky cough and inspiratory stridor at rest. What is the most likely cause of this child's symptoms? What is the recommended treatment?

Parainfluenza virus causing croup
Treatment:
Mild (no stridor at rest): humidified air +/- corticosteroids (decadron)
Moderate/severe (stridor at rest): corticosteroids (decadron) + nebulized epinephrine
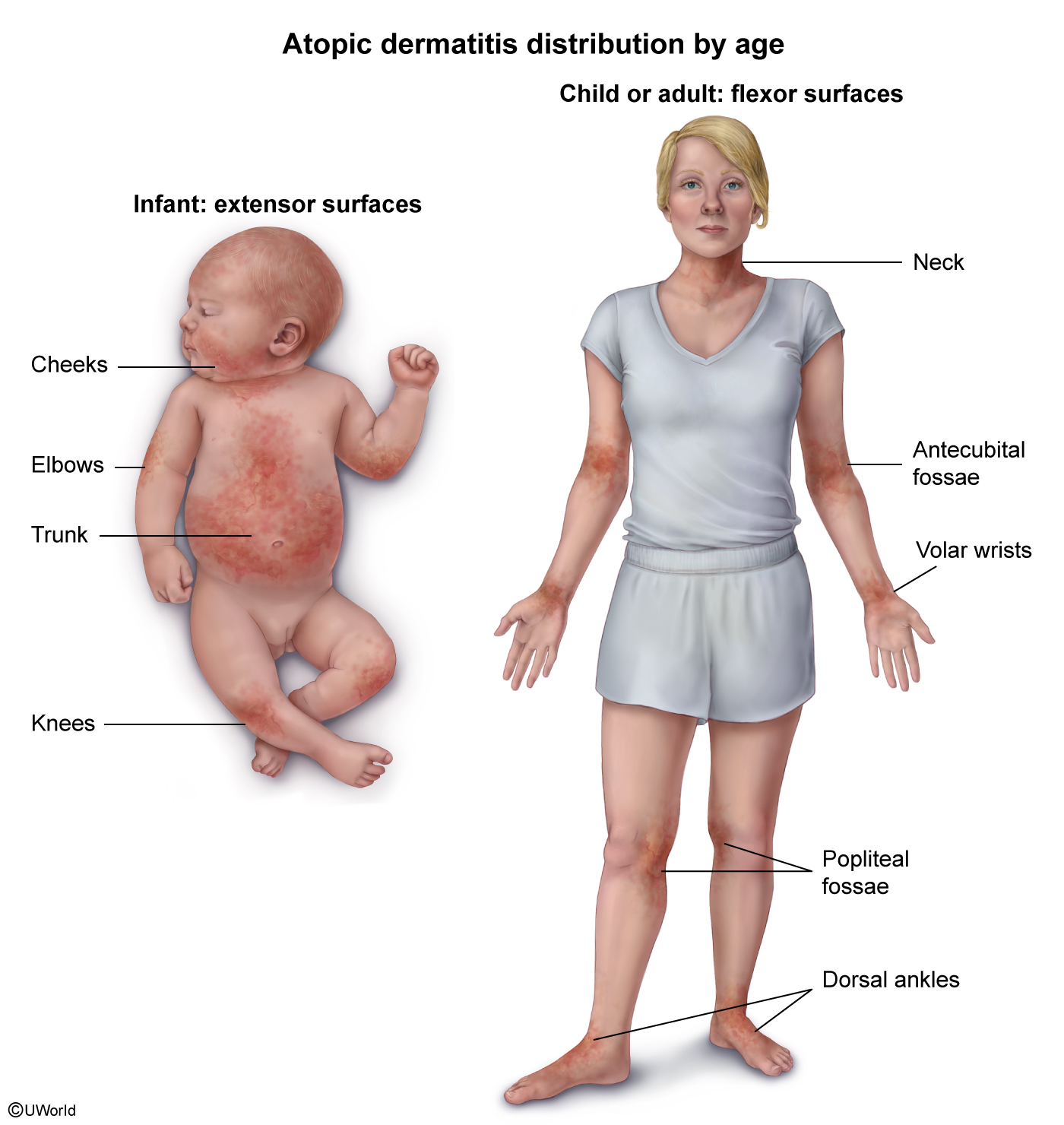
What is the most common location of eczematous plaques in infants?
3 years. Rule of 3's - 3 word sentences, 3/4 of speech understandable, rides 3 wheels (tricycle)

A neonate is found to have cataracts, continuous "machinery" murmur that radiates to the back, and sensorineural hearing loss. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital rubella
Risks of congenital defects are highest if contracted in the first trimester.
There is no treatment for congenital rubella.
Heart defects - PDA, PPS, VSD, ASD
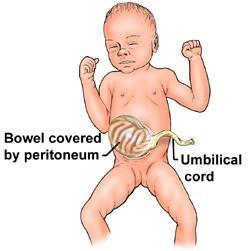
What abdominal wall defect is associated with genetic syndromes?
Omphalocele
1. 30% have a genetic disorder
2. most common are Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13, Trisomy 21, Turner syndrome, and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.
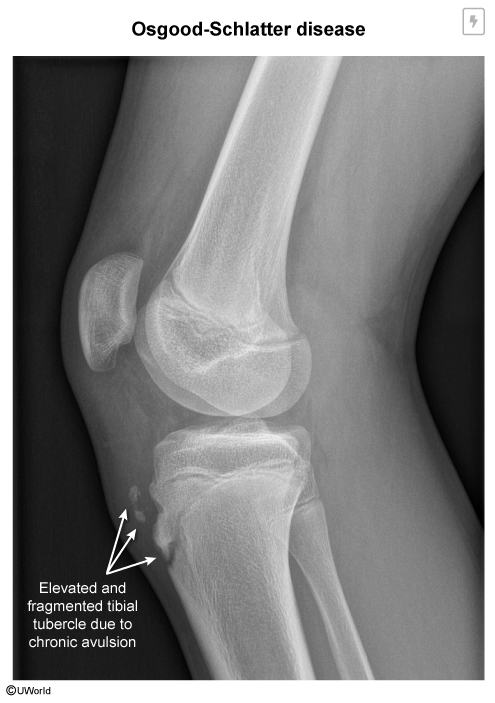
An adolescent volleyball player develops knee pain worse after she jumps and runs. She has noted swelling below her patella after practice. On exam she has full range of motion of the knee, tenderness and mild swelling of the tibial tuberosity. She denies fever, bone pain that gets worse at night, weight loss, or limp. The X-ray is shown below. What is the diagnosis? What is the recommended treatment?
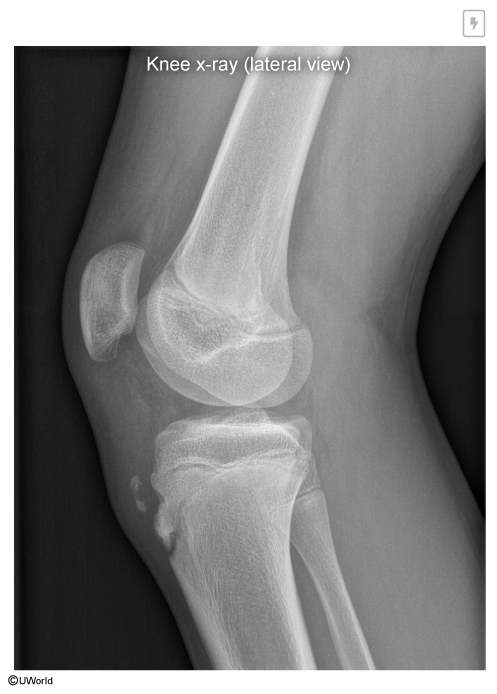
Diagnosis Osgood-Schlatter disease
OSD is an overuse injury most common in adolescents.
During periods of rapid growth, the quadriceps pull on the patellar tendon insertion site, causing traction apophysitis that can lead to elevation and avulsion of the tibial tubercle.
Treatment: RICE initially. May also benefit from NSAIDS, knee stabilization during activity, physical therapy
A 2-year-old developed a fever, sore throat, runny nose, and headache. After 3 days, she developed a rash on her cheeks (see below). What is the cause of her rash? What is the treatment?
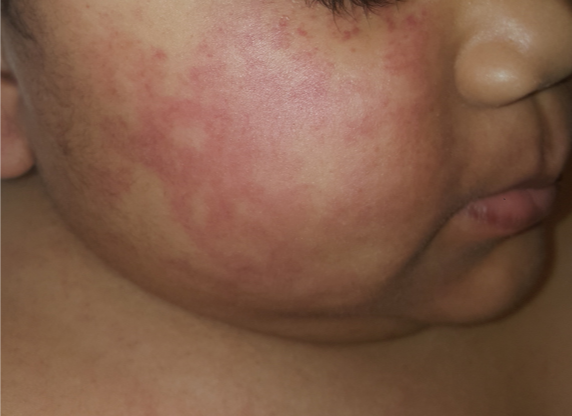
Erythema infectiosum (ie, parvovirus B19, fifth disease)
Treatment: supportive care
15 months

An infant started with an intermittent cough and runny nose a 2 weeks ago. The parents brought him to the ER because they were worried he was having trouble breathing. He had developed prolonged episodes of intense coughing followed by high-pitched sound during inspiration. What is the diagnosis? What is the treatment?
Dx: Bordetella pertussis (gram-negative coccobacilli)
Catarrhal (weeks 1-2): mild cough, rhinitis
Paroxysmal (weeks 2-8): severe coughing spells
± Inspiratory whoop, posttussive emesis, apnea/cyanosis (infants); posttussive syncope (older patients)
Convalescent (weeks 8+): symptoms resolve gradually
Diagnosis: Pertussis PCR
Treatment: macrolide (azithromycin) for patient and all close contacts regardless of vaccination status
Prevention: vaccination (DTaP/Tdap)
A previously healthy 18-month-old presents with a large amount of dark red blood in her diaper. Her parents deny she has had any recent fever, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Meckle diverticulum
Rule of 2s:
- Presentation by age 2
- <2 inches long
- Location within 2 feet of ileocecal valve
Diagnosis: Technetium-99m pertechnetate (Meckel) scan detects gastric mucosa
A 15 year-old male presents to clinic after developing dull hip pain and a change in his gait (limp). He is afebrile. BMI is 99%. On exam he has limited internal rotation and abduction of the hip.
What is the next best step for diagnosis? What is the diagnosis?
Plain-film radiography, typically AP pelvis and frog leg lateral views of both hips, is the gold standard for confirming an Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) diagnosis.
Treatment is immediate surgical fixation.
Possible complications if untreated are avascular necrosis and early osteoporosis.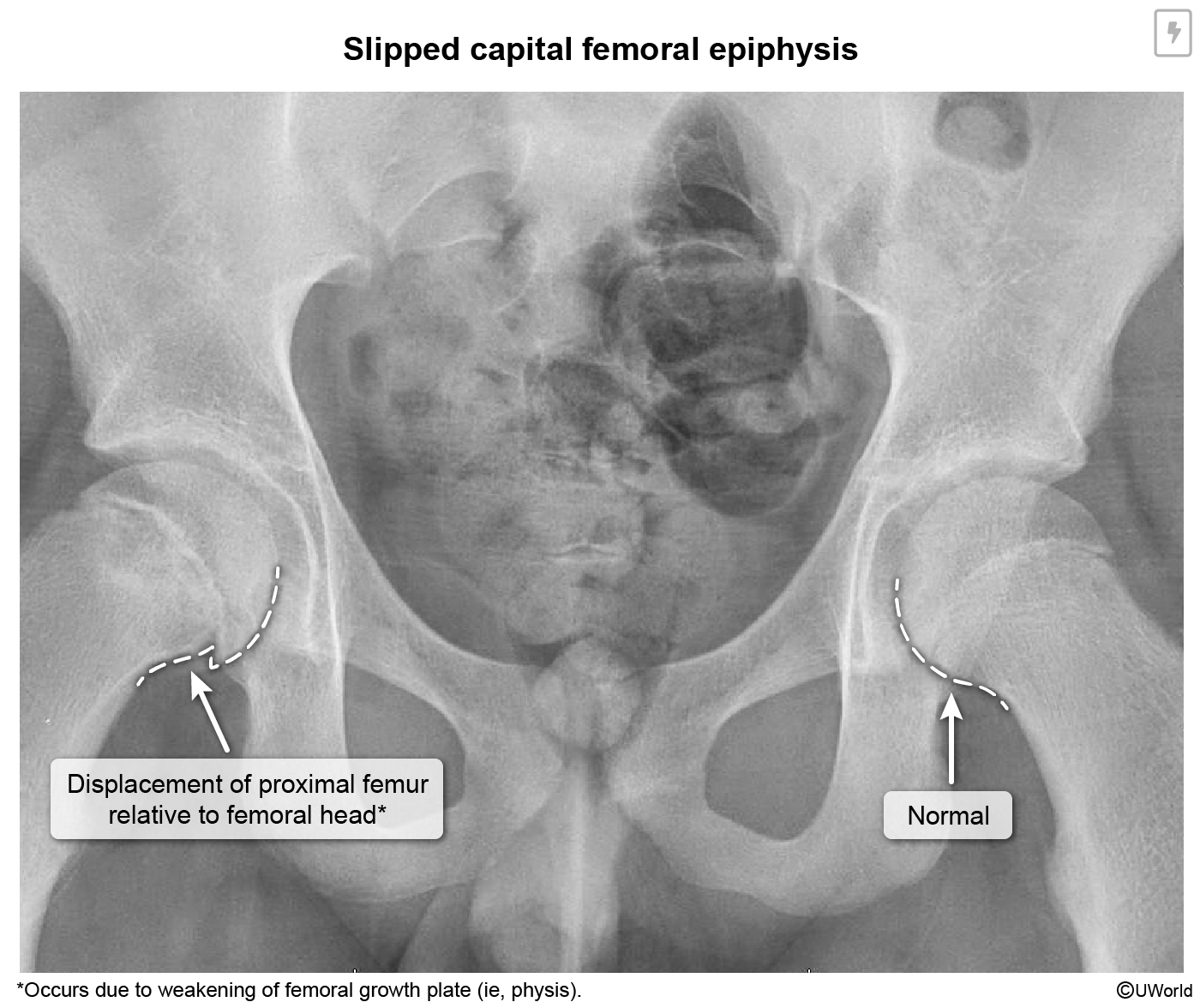
A 7-year-old develops fever, chills, malaise, and a rash on his face. What is the diagnosis?

Diagnosis: Erysipelas (typically has a rapid onset, fever early in the course of the disease, raised surface, and well-demarcated borders)
It affects the upper dermis and lymphatic vessels.
Typically affects the face.
Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A strep) is the most common cause.
Treatment: amoxicillin
Can write the letters in her name, gets herself dressed, counts to 10, loves playing with her friends, strangers understand everything she says. When asked to draw her family, she draws the picture below. 
5 years old
Name 5 organisms that cause infection in children with chronic granulomatous disease? Hint - SPACE mnemonic
Staphylococcus aureus
Pseudomonas
Aspergillus
Candida albicans
Enterobacteriaceae (Klebsiella, Serratia)
X-linked recessive mutation of NADPH oxidase causes inhibition of phagocytic intracellular killing.
A 16-month-old girl no longer meets verbal developmental milestones, has poor social interaction with new onset hand flapping, and head circumference decline on growth charting. What is the diagnosis? How do you diagnose?
Rett syndrome
1. Rare progressive neurological disorder (normal development until 6-18 months of age, when they have regression including loss of speech and loss of purposeful hand use).
2. Primarily affects females
3. High risk of developing seizures
4. Dx through DNA analysis for MECP2 mutation