What is the concept of a network?
A network is a system of interconnected devices that communicate and share resources. It enables data transmission and resource sharing, facilitating various applications and services. Networks can vary in size and technology, supporting local connections (LAN) or global connectivity (WAN).
What is PAN and what are its characteristics?
PAN (Personal Area Network) is a network used for communication among devices located close to a person. Its characteristics include:
- Small geographic area (typically within a few meters).
- Personal ownership and control by an individual.
- Uses technologies like Bluetooth or Zigbee for wireless connections.
- Supports communication between devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices.
What is a node?
A node in networking is a device like a computer or printer that connects to a network, each having a unique address for data communication and sharing resources.
What are characters, fields, records, files, and databases?
- Characters: Individual letters, numbers, or symbols that make up data.
- Fields: Units of data containing a single attribute of an entity, like a name or age.
- Records: Collections of related fields that represent a complete set of information about an entity.
- Files: Collections of records stored together, often in a structured format like a spreadsheet or text file.
- Databases: Organized collections of related data stored electronically, typically managed by database management systems (DBMS) for efficient retrieval, manipulation, and storage.
What is operational database?
An operational database is a database designed to support day-to-day operational processes and transactions within an organization. It typically:
- Stores current and real-time data related to the organization's operations.
- Facilitates efficient data entry, retrieval, and modification.
- Supports transactional operations with ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).
- Is optimized for high performance and availability to handle frequent and concurrent transactions.
What the definitions of router and switch/hub?
A router connects different networks and directs data packets between them using routing tables. A switch connects devices within a LAN and forwards data based on MAC addresses, enhancing network efficiency. A hub is a basic device that broadcasts data to all connected devices, making it less efficient than a switch.
What is LAN and what are its characteristics?
LAN (Local Area Network) is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office building, or campus.
Its characteristics include:
- Restricted geographic area, typically within a single building or campus.
- High data transfer rates with low latency.
- Often connected via Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
- Shared resources such as printers, file servers, and internet connections.
- Managed and controlled by a single organization or individual.
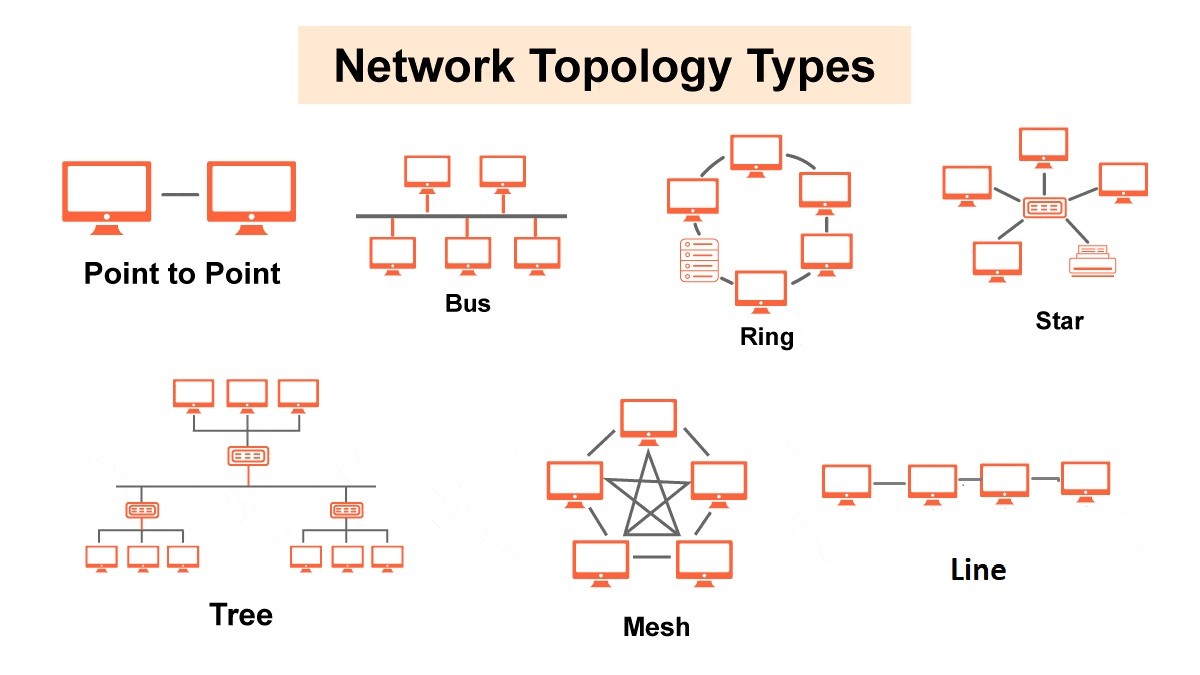
What is a star topology?
In a star topology, every device connects directly to a central hub or switch, forming a radial structure. This hub manages communication between devices, offering centralized control and easy fault detection, but requiring more cabling than other topologies.
What the limitations of file processing system?
- Data redundancy
- Data isolation
- Data inconsistency
- Data dependence
- Lack of security
What are the advantages of operational database?
- Real-time data access
- Transactional support (ACID properties)
- High performance
- Scalability
- Integration capabilities
- Security
What is bandwidth, NIC and network topology?
- Bandwidth: Bandwidth refers to the maximum data transfer rate of a network or internet connection, typically measured in bits per second (bps). It determines how much data can be transmitted in a given amount of time.
- NIC (Network Interface Card): A NIC is hardware that enables a device to connect to a network. It provides the physical interface between the device and the network medium, facilitating communication.
- Network Topology: Network topology refers to the layout or structure of a computer network, defining how devices are interconnected. Common topologies include bus, star, ring, and mesh configurations, each influencing how data is transmitted and network resilience.
What is MAN and what are its characteristics?
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) is a network that spans a larger geographic area than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, typically covering a city or large campus. Its characteristics include:
- Covers a larger geographical area than a LAN, such as a city or metropolitan area.
- Uses technologies like fiber optics, Ethernet, and wireless connections.
- Provides high-speed connectivity between various LANs and end-users.
- Managed by multiple organizations or service providers.
- Supports a wide range of services, including internet access, video conferencing, and large-scale data transmission.
What is ring topology?
In ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop where each device connects to exactly two others, facilitating data transmission in one direction and requiring all devices to relay signals.
What the applications of database?
- Data storage and management
- Data retrieval
- Data integrity
- Multi-user access
- Data security
- Data analysis
- Transaction management
What is a distributed database?
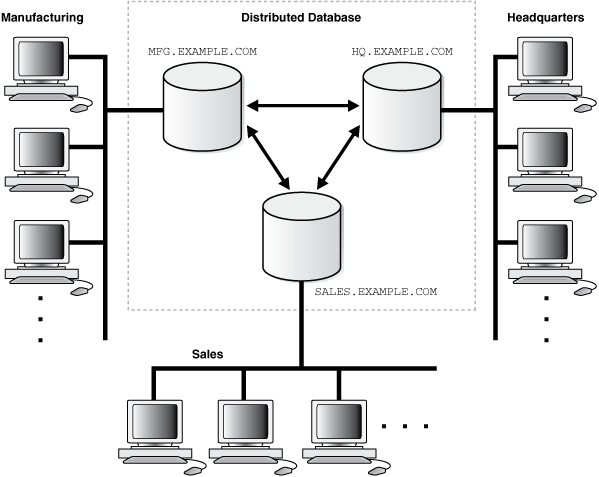
A distributed database is a collection of interconnected databases spread across different locations, managed as a unified system. It enables data storage, access, and management across geographically dispersed locations, enhancing performance, availability, and scalability.
What are business values of telecommunication network?
- Improved communication and collaboration
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- Facilitated remote work capabilities
- Cost savings through streamlined communications
- Access to global markets and customers
- Support for multimedia and data transmission
- Reliable and secure data transfer
What is WAN and what are its characteristics?
WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network that spans a large geographical area, typically a country, continent, or even globally, connecting multiple LANs and MANs. Its characteristics include:
- Covers a wide geographical area, often spanning across cities, countries, or continents.
- Uses various technologies such as leased lines, satellites, and optical fibers.
- Provides long-distance connectivity between geographically dispersed locations.
- Managed by multiple organizations and service providers.
- Supports a wide range of applications and services, including internet access, cloud computing, and centralized data storage.
What is tree topology?
Tree topology is a hierarchical network structure where multiple star topologies are interconnected through a central backbone or bus. It combines characteristics of both star and bus topologies, providing scalability and centralized control.
What are the types of database model?
- Hierarchical Model
- Network Model
- Relational Model
- Object-Oriented Model
- Entity-Relationship Model
What is external database?
An external database typically refers to a database that is accessed and used by an organization but is maintained and operated by an external entity or service provider.
What is the definition of server, client, network protocol and computer network?
Server: A server provides resources and services to clients over a network, such as hosting files, websites, or applications.
Client: A client requests and receives resources or services from servers, enabling users to access data, applications, or functionalities.
Network Protocol: Network protocols are rules governing data exchange between devices, ensuring standardized communication across networks for reliability and compatibility.
Computer Network: A computer network connects devices to share resources and enable communication, facilitating data transfer, collaboration, and access to distributed resources.
What are the characteristics of Coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, and fiber optic cable?

Coaxial Cable:
- Core: Central copper conductor surrounded by insulating material.
- Shielding: Metallic shield and outer insulating layer.
- Characteristics: Provides high bandwidth and is resistant to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Used in cable television (CATV) and broadband internet connections.
Twisted Pair Cable:
- Structure: Consists of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together.
- Types: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP).
- Characteristics: Cost-effective, flexible, and easy to install. UTP is commonly used in Ethernet networks, while STP offers better EMI protection.
Fiber Optic Cable:
- Core: Thin glass or plastic fibers that transmit data using light pulses.
- Structure: Core surrounded by cladding and protective layers.
- Characteristics: Offers high bandwidth and long-distance transmission capabilities. Immune to electromagnetic interference and secure against eavesdropping. Widely used in telecommunications, internet backbone networks, and high-speed data transmission.
What is bus, mesh, hybrid topology?
Bus Topology: Devices are connected to a single central cable (the bus), with terminators at each end to prevent signal reflection. It's simple and inexpensive but can suffer from a single point of failure.
Mesh Topology: Every device is connected directly to every other device, creating multiple redundant paths for data. It's highly reliable and fault-tolerant but requires a significant amount of cabling.
Hybrid Topology: Combines two or more different types of topologies (e.g., star and bus) to leverage their strengths. It's flexible and can be customized to suit specific organizational needs.
What is hierarchical DBMS, network model, relational model, object-oriented model, and entity relationship model?
Hierarchical DBMS: Organizes data in a tree-like structure with parent-child relationships, where each parent can have multiple children but each child has only one parent. It's efficient for representing one-to-many relationships but can be rigid in structure.
Network Model: Extends the hierarchical model by allowing each child to have multiple parents, creating a more flexible structure. It supports many-to-many relationships but can be complex to implement and manage.
Relational Model: Organizes data into tables (relations) where each row represents a record and each column represents an attribute. Relationships between tables are established using keys, providing a simple and efficient way to store and retrieve data.
Object-Oriented Model: Stores data as objects, combining data (attributes) and behavior (methods) into a single entity. It supports inheritance, encapsulation, and complex data types, suitable for applications with complex data structures and behavior.
Entity-Relationship Model: Describes data and relationships in terms of entities (objects) and their attributes, connected by relationships with cardinality and participation constraints. It's used for designing databases before implementation to ensure data integrity and clarity.
What are the advantages of operational, distributed, external, and hypermedia database?
Operational Database:
- Real-time data access
- Transactional support (ACID properties)
- High performance
- Scalability
- Integration capabilities
- Security
Distributed Database:
- Improved performance and availability
- Enhanced scalability
- Geographic data distribution for local access
- Fault tolerance and disaster recovery
- Reduced data duplication and improved data consistency
External Database:
- Access to external expertise and resources
- Cost savings on infrastructure and maintenance
- Scalability and flexibility
- Integration with external data sources
- Access to specialized databases and tools
Hypermedia Database:
- Integration of different media types (text, images, videos, etc.)
- Support for non-linear navigation and user interaction
- Rich multimedia content management
- Enhanced user experience and interactivity
- Flexibility in presenting and linking multimedia information