Louise is cutting out shapes in the art center while her friends are showing her the new markers. Louise finishes cutting out her shapes before so joins the others to use the new markers.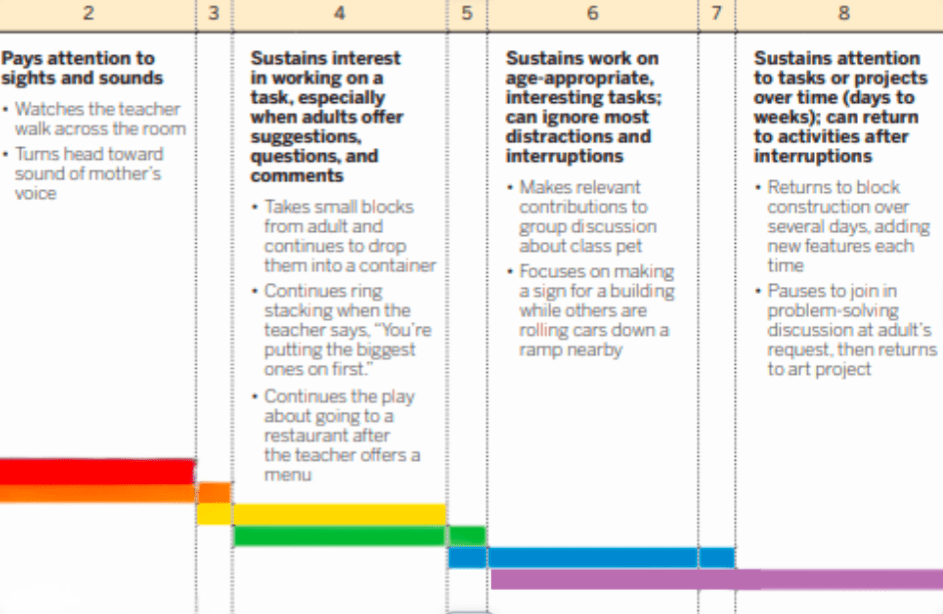
6: Sustains work on age appropriate, interesting tasks; can ignore most distractions or interruptions.
Louise is able to complete her cutting project before moving on to the markers.
What are four solutions in the solution kit?

Lisa counts out loud "One, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten." When counting 4 stickers she points to each object counting faster than she points "One, two, three, four, five, six!"
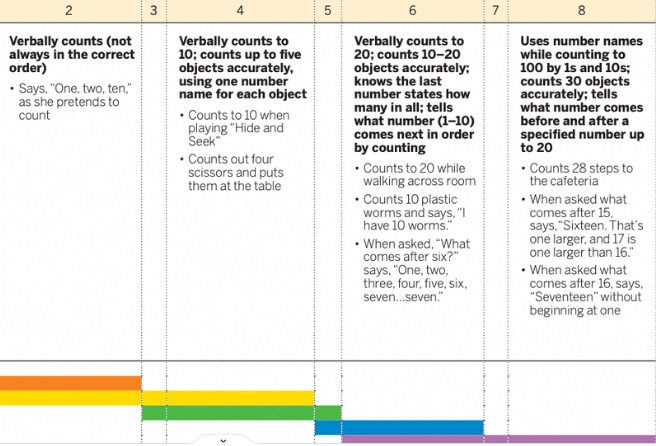
3. Lisa can count to ten as needed for level 4 but is not yet able to count 5 objects putting her in the in-between level.
What are the three B's?
Be Safe, Be Responsible, Be Respectful
I have a back and legs, but I don’t have hair. What am I?
A chair
Tina attempts to do a puzzle. After unsuccessfully moving a few pieces he put the incomplete puzzle on the shelf and walks away. 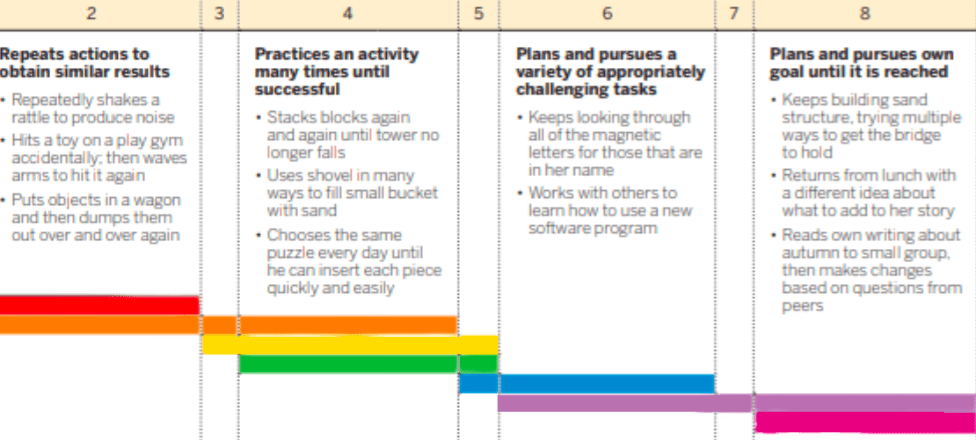
3: In this activity Tina is not yet trying an activity many times until successful.
Anton goes to dry his hands after washing but the paper towels are empty. Without prompting he goes to the sink on the other side of the room to get paper towels there.
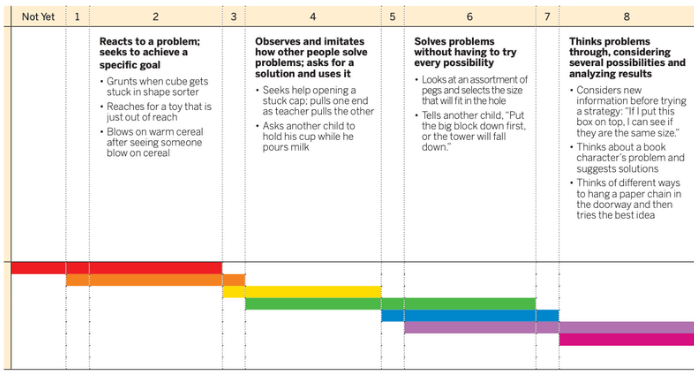
6 Solves problems without having to try every possibility.
Anton is able to get himself a paper towel even after his first attempt isn't successful.
Bart is looking at a coupon book. He points out and names the numerals he sees on the page 2,5,1,7,8,3,10,4. he says the numeral 21 is a two and a one. he then correctly counts 10 coupons on the page.
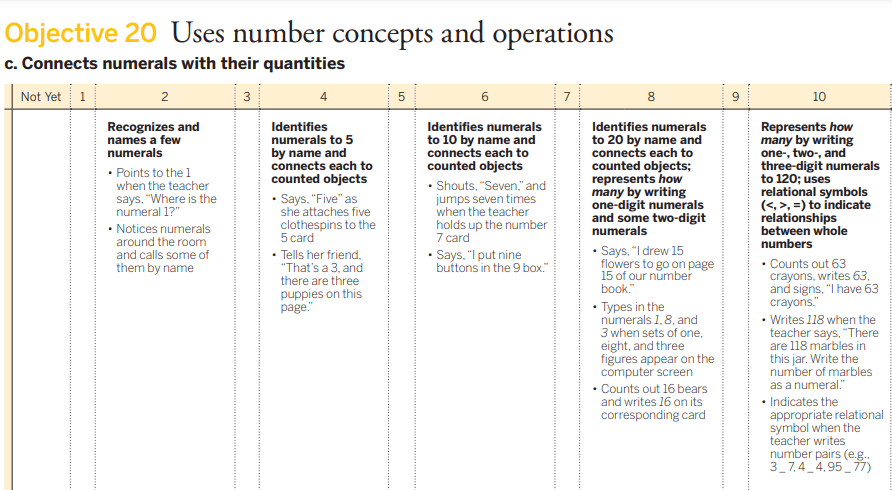
6. Identifies numerals to 10 by name and connects each to a counted object.
Bart can both recognize numerals and connect them to counted objects
What curriculum and assessment tool do we use?
Creative Curriculum and Teaching Strategies GOLD
There were 3 girls walking to school. They had 1 umbrella to share. How did they not get wet?
It wasn't raining
Although it has been almost a month since the class used watercolors, Gene asks if she should get a paint shirt on when she sees the teacher grabbing paint brushes.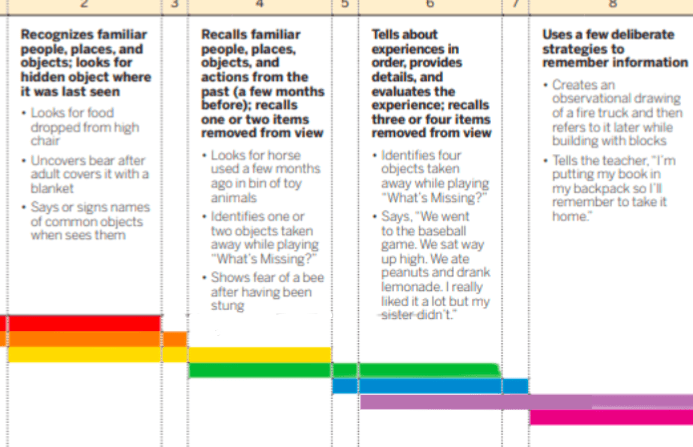
4: Recalls familiar people, places, objects, and actions for the past.
Gene is able to remember that he needs paint shirts when painting
What domains are the two different types of problem-solving we assess for?
Cognitive and Social-Emotional
True or False:
I can just skip over the math objects that don't apply to my age group without thinking about them.
False; Although most children will fall within the typically developing age range, it is important that we still look at those objectives, if only briefly, to ensure that they are actually in the "Not Yet" category during assessments and check points.
How often does Kaycee send out the Staff Newsletter during the school year?
Monthly
Despite my name, I am not a queen. When you hold me up to things, their length is seen. What am I?
A Ruler
Linda is drawing a picture in the art center. She has a pile of purple crayons, markers, and colored pencils and a pile of pink crayons, markers, and colored pencils because " I am making pink and purple flowers. She then states "I only want to use markers". Linda then made a pile of pink and purple markers, pink and purple crayons, and pink and purple pencils. 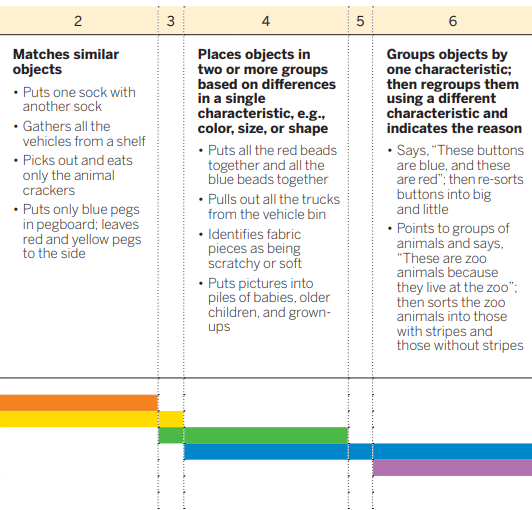
6. Groups objects by one characteristic; then regroups them using a different characteristic and indicates the reason.
Linda first groups the art supplies by color then regroups them by type to use just markers.
Kayla throws a block at a peer who knocked over her tower
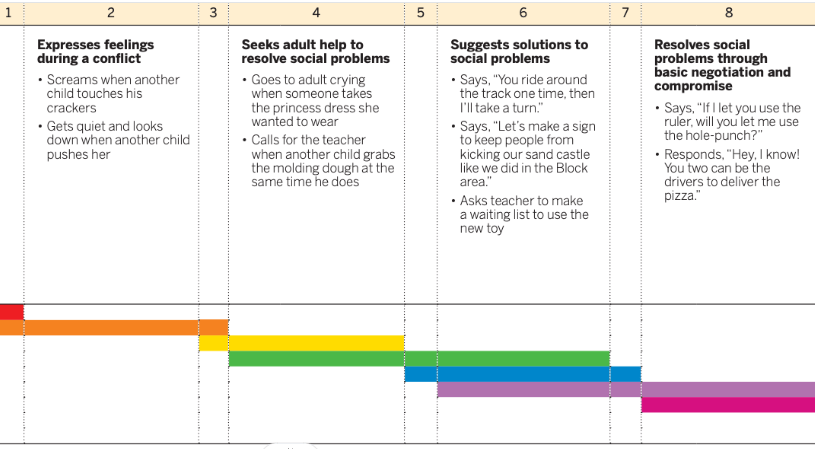
2. Expresses feelings during a conflict.
Kayla understands that there is a social problem and reacts to it by expressing feelings.
Maggie is making a block tower. She places a yellow block, then a red block, and continues yellow, red, yellow, red. "Look at my pattern," she tells the teacher.
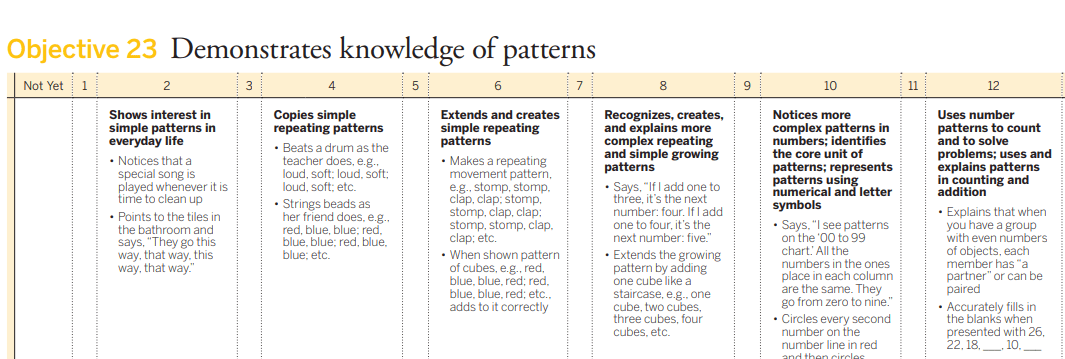
5. Extends and creates simple repeating patterns.
Maggies can successfully make an ABAB pattern on her own with the blocks
What SEL observation does each classroom do annually?
TPOT
It has keys, but no locks. It has space, but no room. You can enter, but can’t go inside. What is it?
A Keyboard
Bob watches his peers playing in the house center. He pushes buttons on the cash register after a peer does the same thing. After the door opens he closes it and leaves the center. 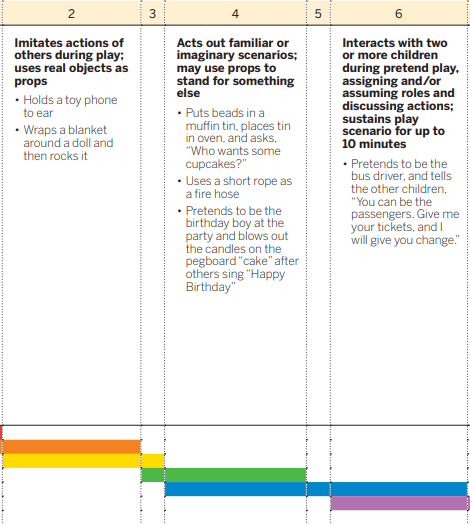
2. Imitates actions of others during play; uses real objects as props.
Bob uses the cash register following the example of his peers but is not yet acting out scenarios.
Are young children able to understand and express empathy naturally?
No, empathy starts to develop around age 4 and needs reinforced and encouraged.
Marge plays with a doll in the dollhouse. She says "up" when walking the doll up the stairs and "down" when walking the doll down the stairs.
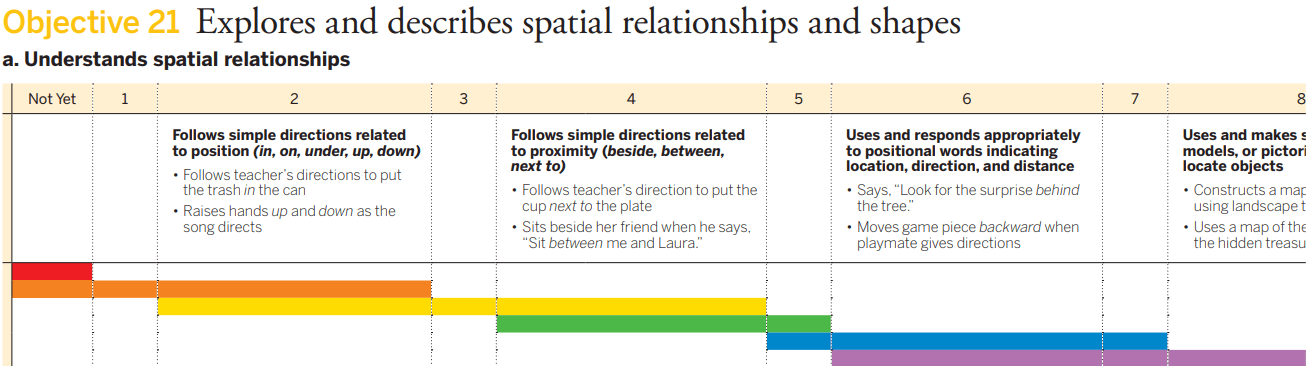
2. Follows simple directions related to position (in, on, under, up, down)
Marge can distinguish between the doll going up and down.
If you or your team are having a difficult time understanding, redirecting, or replacing a child's challenging behavior, what team can you or your director reach out to?
The Problem Support Team
What goes up and down stairs without moving?
A Carpet