Studies have repeatedly shown that early initiation of enteral feeds with the following has significant benefits on morbidity and mortality in very low birth-weight infants:
What is maternal breastmilk?
In very preterm infants, mother's own milk (MOM) feeding is associated with lower risks of necrotizing enterocolitis, retinopathy of prematurity, and sepsis.
You are called to the delivery of an term infant with the following prenatally-diagnosed congenital defect: The initial step in resuscitation is:
The initial step in resuscitation is:
Nasogastric/orogastric tube placement?
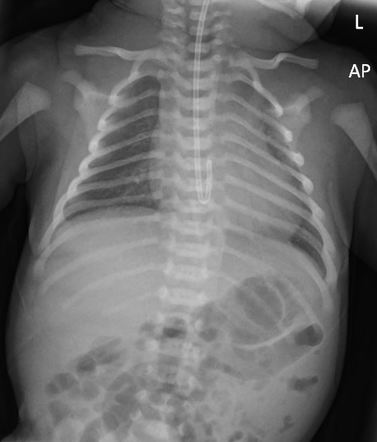
A 36 week infant born to a mother with GDM is admitted to SCN secondary to feeding intolerance and abdominal distention.
A contrast enema is done and shown above. The fruits of your labor are shown below.
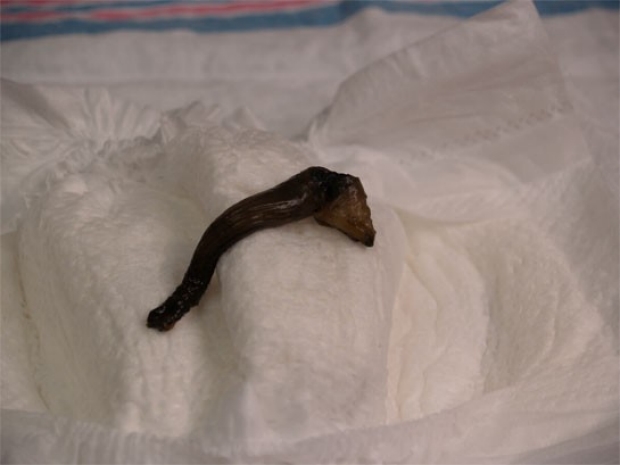 The following the is diagnosis:
The following the is diagnosis:
What is meconium plug syndrome?
Meconium plug syndrome is a condition that predominantly affects preterm-neonates of low birth weight. It presents with an inability to pass meconium within the first 24 to 48 hours of life, and it must be properly differentiated from similar conditions.
 You are caring for an ex 24-week infant, now 30 weeks CGA, who is on full enteral feeds. During your routine care time, you notice the abdomen appears full and slightly discolored, a change from your previous assessment. You obtain the above KUB. The following subsequent type of X-ray will (unfortunately) confirm your suspicions.
You are caring for an ex 24-week infant, now 30 weeks CGA, who is on full enteral feeds. During your routine care time, you notice the abdomen appears full and slightly discolored, a change from your previous assessment. You obtain the above KUB. The following subsequent type of X-ray will (unfortunately) confirm your suspicions.
What is a right lateral decubitus or a cross-table lateral.
Pneumoperitoneum, or free air in the abdominal cavity, is a surgical emergency. One the diagnosis is made, the infant should be made NPO, a Replogle should be placed to low intermittent suction, IV antibiotics should be initiated, and the infant should be transferred immediately to a surgical NICU for further management.A well-appearing ex 29 week infant, now 34 weeks CGA, presents with bloody stools.
She has been on full enteral feeds of exclusive maternal milk since DOL 10. The abdominal exam is benign. She is made NPO and serial KUB show an unremarkable and reassuring bowel gas pattern. Sepsis labs remain negative, although CBCs show a significant eosinophilia.
What is the next best step in management once enteral feeds are resumed?
Eliminate dairy in maternal diet and/or start hydrolyzed formula.
Milk protein allergy is a recognized problem in the first year of life; cow’s milk protein allergy is the most common such allergy. Diagnosis is suspected on history alone, with laboratory evaluations playing a supporting role. Confirmation requires elimination and reintroduction of the suspected allergen. Management includes diet modification for nursing mothers and hydrolyzed formulas for formula-fed infants.
A term infant born to a 43 year-old mother is brought to TCN for repeated episodes of emesis in NBN. Her prenatal records are not available. On exam, the abdomen is mildly distended with hypoactive bowel sounds. You also notice subtle widened epicanthal folds and upslanting palpebral fissures. Name two other studies that should be evaluated prior to this infant's discharge home.
What are thyroid function tests and an echocardiogram.
Trisomy 21 is the most common chromosomal anomaly in humans, affecting about 5,000 babies born each year.
Approximately 1 in 3 infants with duodenal atresia will also test positive for Trisomy 21.
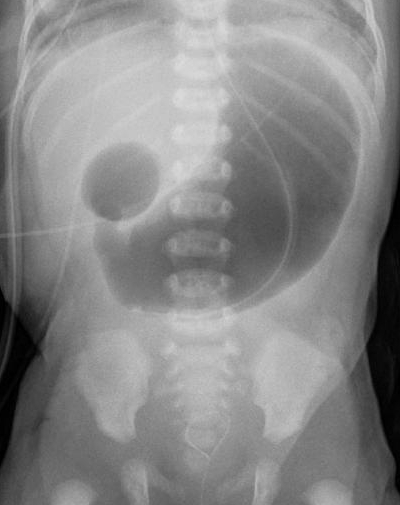
 A 34-week infant is admitted to the SCN on room air with a normal physical exam. Full enteral feeds are started on admission. By DOL 3, the infant has not stooled and the abdomen is increasingly distended. Glycerin suppositories are scheduled Q12 hours without stool. A contrast enema is done and shown above.
A 34-week infant is admitted to the SCN on room air with a normal physical exam. Full enteral feeds are started on admission. By DOL 3, the infant has not stooled and the abdomen is increasingly distended. Glycerin suppositories are scheduled Q12 hours without stool. A contrast enema is done and shown above.
The arrows are indicating the following:
What is the transition zone?
Hirschsprung's disease (also called congenital aganglionic megacolon) occurs when an infant's intestinal ganglion (nerve) cells don’t develop properly, delaying the progression of stool through the intestines.
Eighty percent of children with Hirschsprung's disease have symptoms in the first six weeks of life. However, children who only have a short segment of intestine that lacks normal nerve cells may not exhibit symptoms for several months or years. Their primary symptom is constipation.

What are portal venous gas and pneumatosis?
A well-appearing ex 28-week infant, now 31 weeks CGA suddenly develops bradycardia and desaturation episodes during two consecutive feeds. A KUB is obtained and is shown above. The following measures (should) fix the problem:
What is NG tube replacement?
The following x-ray is obtained on a 1-hour old term infant with excessive oral secretions, recurrent emesis, and tachypnea. In addition to the obvious anomaly, what secondary anomaly must be present?
In addition to the obvious anomaly, what secondary anomaly must be present?
What is a tracheo-esophageal fistula?
 An infant born with the defect above is also noted to have an enlarged tongue and persistent hypoglycemia. He is at increased risk for the following in childhood:
An infant born with the defect above is also noted to have an enlarged tongue and persistent hypoglycemia. He is at increased risk for the following in childhood:
What are childhood cancers?
Omphalocele is a rare congenital abdominal wall defect with a reported prevalence of 3.38 per 10,000 pregnancies.Omphalocele can be isolated but is more frequently associated with other congenital anomalies and syndromes such as Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and trisomies 13, 18, and 21. The survival rate is close to 80%, and it is directly related to the severity of the associated anomalies, as infants with isolated omphalocele have a higher survival rate (90%).
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) is the most common congenital overgrowth syndrome. Specifically, the condition is a human imprinting disorder caused by genetic and epigenetic changes affecting molecular regulation on chromosome 11p15.
The most notable BWS features are hemihypertrophy, macrosomia, macroglossia, and abdominal wall defects. Patients also have an increased risk of childhood cancers.
The following x-ray is obtained on a 3-week-old, ex 25-week infant that was previously stable on BCPAP. Currently, she is on HFOV with an amplitude of 45, Hz of 10, MAP of 20 and Fi02 of 80%. The mechanical etiology of her increased respiratory requirements is:
The mechanical etiology of her increased respiratory requirements is:
What is lung compression due to severe abdominal distention?
A term infant born after an uncomplicated pregnancy presents with true bilious emesis. A KUB shows a non-specific bowel gas pattern.
The following study should be ordered urgently:
What is an upper GI with small bowel follow through?

During embryonic development, the small bowel usually rotates in a counterclockwise direction around the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) axis between the fourth to eight weeks of gestation. During this period in embryonic development, the bowel protrudes through the yolk stalk (which will become the future umbilicus). During this process, the digestive tract elongates and undergoes counterclockwise 90 degrees rotation, followed by retraction of the bowel into the abdominal cavity where another 180-degrees counterclockwise rotation occurs.
A 33-week infant is delivered secondary to preterm labor. On the initial exam, the abdomen is noted to be mildly distended and a KUB is obtained. The infant's newborn screen results will likely be flagged for the following finding:
What is a cystic fibrosis gene mutation?
Meconium peritonitis is an aseptic chemical peritonitis resulting from intrauterine bowel perforation. The meconium spilled in the peritoneal cavity leads to an intense inflammatory reaction with fibrotic tissue formation and rapid calcification.Common causes include meconium ileus.
In cystic fibrosis, the mutated CFTR gene changes a protein that regulates the movement of salt in and out of cells. These changes cause thick and sticky mucus in the respiratory tract and thick and stagnant meconium in the GI tract.
 The defect shown above is located where:
The defect shown above is located where:
What is to the right of the umbilicus?
Gastroschisis is a paraumbilical, full-thickness abdominal wall defect associated with protrusion of the bowel through the defect. It is rarely associated with genetic conditions. A membrane does not cover the bowel exposed in utero and, as a result, may be matted, dilated, and covered with a fibrinous inflammatory rind. Infants have a high proportion of intrauterine growth restriction. Diagnosis is often made on the 20-week ultrasound with free-floating bowel loops in the uterine cavity. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein is elevated in pregnancies with gastroschisis. Compared with other abdominal wall defects diagnosed prenatally, such as omphalocele, only 10 percent of cases with gastroschisis are associated with malformations outside of the gastrointestinal tract.
The infant you are caring for, an ex 25-week baby that is now 33 weeks CGA, has a history of medical NEC at 29 weeks treated with bowel rest and IV antibiotics. She had been tolerating feeds until the last several days during which she developed abdominal distention and recurrent emesis. Given her history, the most likely cause of the feeding intolerance is:
What is an intestinal stricture?
A 2014 retrospective study of infants with NEC over 10 year period showed the incidence of post-NEC intestinal stricture is high but development of stricture is difficult to predict. Leucocytosis during NEC and length of bowel resected at surgery may be associated with development of post-NEC intestinal stricture. A substantial number of infants with post-NEC intestinal stricture fail to thrive, have co-morbidities and need prolonged hospitalization.