What is the largest organ in the human body?
Skin
Assessment of Total body surface area (TBSA) in burns changes between adults, small children, and infants.
T/F
True; changes for head and legs
What is the first phase of wound healing known as?
Exudative
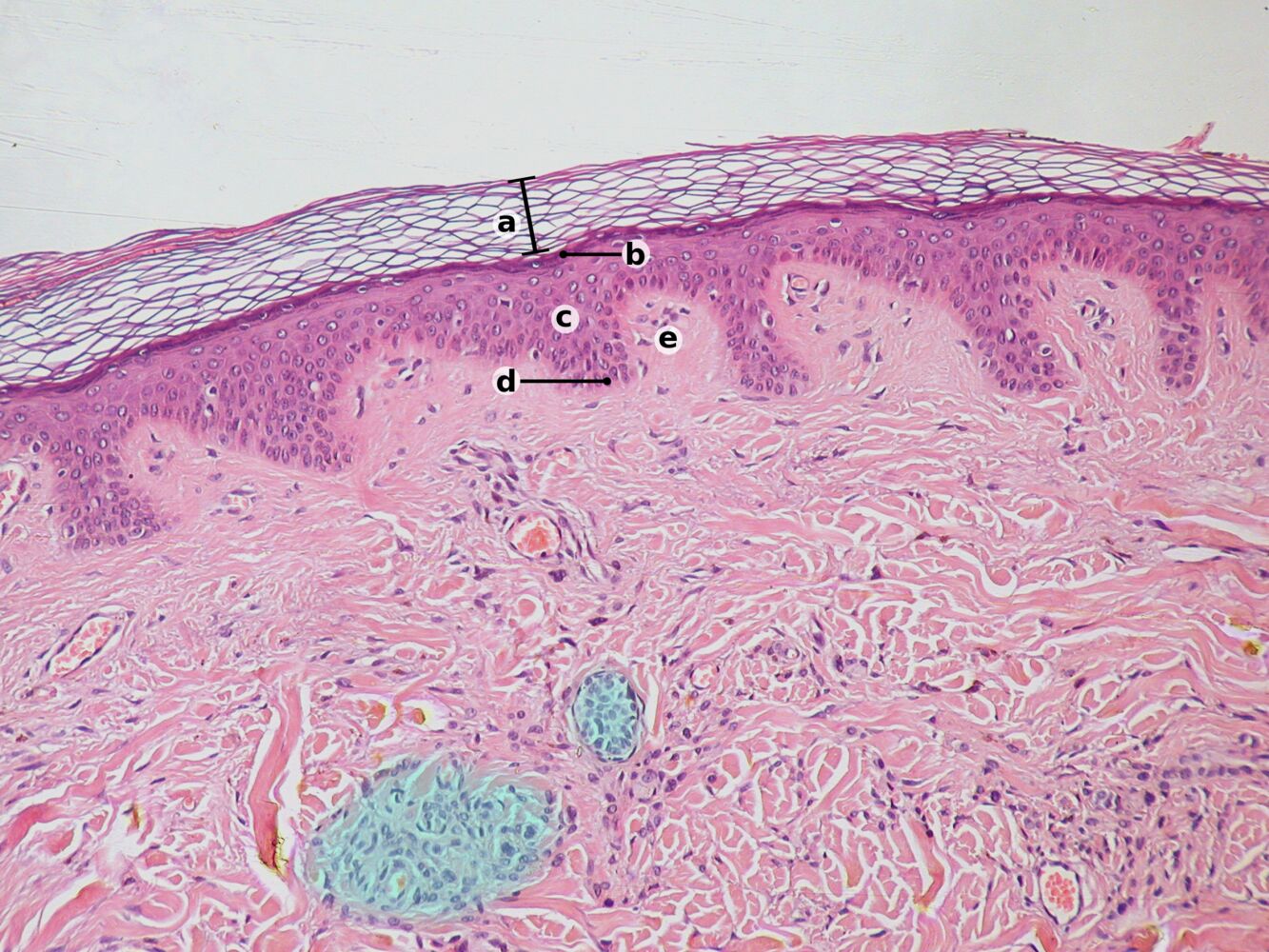
What layer of the skin is b?
Stratum granulosum
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
To produce sebum, which helps keep the skin and hair moisturized
Do regions experiencing a 3rd-degree burn perceive pain?
No (perception of deep pressure is intact)
Name a risk factor for delayed wound healing
Drugs (e.g., steroids, cytotoxics, etc), Infections/Ischemia, Diabetes, Nutritional deficiency (e.g., iron-deficiency anemia), Oxygen (hypoxia), Toxins (e.g., alcohol consumption, smoking), Hypothermia/hyperthermia, Excessive tension on the wound edges, Acidosis, Local anesthetics
The cells within the Stratum corneum consist of what type of cells?
dead (anuclear), keratin-filled cells
Which layer of the epidermis is responsible for cell division and regeneration?
The stratum basale (or stratum germinativum) is responsible for cell division and regeneration.
What is the difference between a 3rd and 4th-degree burn?
4th-degree burns affect deeper structures (muscles, fat, fascia, and bones). 3rd-degree burns stop at subcutaneous tissue.
4th-degree burns are completely dead tissue with zero means of repair; they require amputation. 3rd-degree burns do not heal by themselves.
What is a Keloid?
Skin lesions caused by high fibroblast proliferation and collagen production in excessive tissue response to typically small skin injuries.
Lesions grow beyond the original wound margins.
What layer of the skin contains melanocytes?
Stratum basale
What occurs in the stratum granulosum that is critical to the skin’s barrier function?
In the stratum granulosum, keratinocytes undergo keratinization, where they accumulate keratohyalin granules and lamellar bodies that release lipids, forming a waterproof barrier as the cells move upwards.
What is the percentage of the total body surface area affected if both legs and the anterior trunk are burned in an adult?
54% (18% for each leg and 18% for the anterior trunk).
What is a Contracture?
Excessive proliferation in myofibroblasts during proliferative and maturation phases leading to wound contraction

 What is e?
What is e?
Papillary dermis
Name all layers of the epidermis from superficial to deep. Which one is not always present (nonpathological)
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum (only present in thick skin, such as the palms and soles)
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
What is a major indication for escharotomy?
Vascular/respiratory compromise or compartment syndrome (a condition caused by tissue ischemia due to increased pressure within a fascial compartment obstructing venous outflow and collapse of arterioles)
Name a tissue mediator involved in wound healing and its purpose.
ex PDGF: Induces vascular remodeling and smooth muscle cell migration
FGF: Stimulates angiogenesis
TGF-β: Angiogenesis, fibrosis
VEGF: Stimulates angiogenesis
EGF: Stimulates cell growth via tyrosine kinases (eg, EGFR/ErbB1)
Metalloproteinases: Tissue remodeling
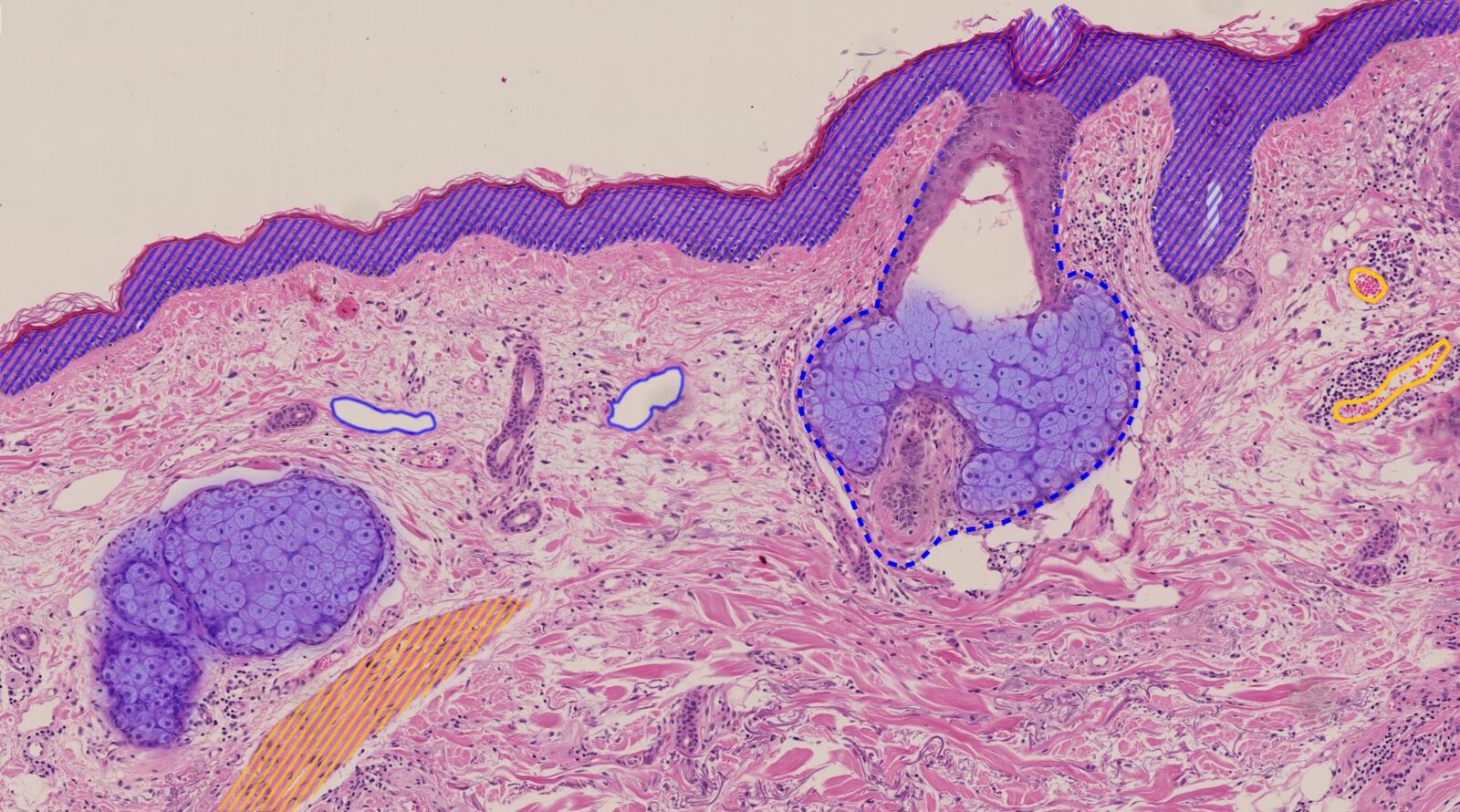
What is the thing with the blue overlay? (no stripes)
sebaceous glands